Protein Synthesis & Amino Acid Worksheet Key Unveiled

Unlocking the mystery of protein synthesis and amino acids can be a formidable task for students. These biological processes are crucial for life, yet their intricacies can seem complex. However, by understanding the fundamentals of these biochemical pathways and using tools like a protein synthesis worksheet with amino acid keys, we can make the learning process much more approachable and engaging.
Understanding the Basics of Protein Synthesis
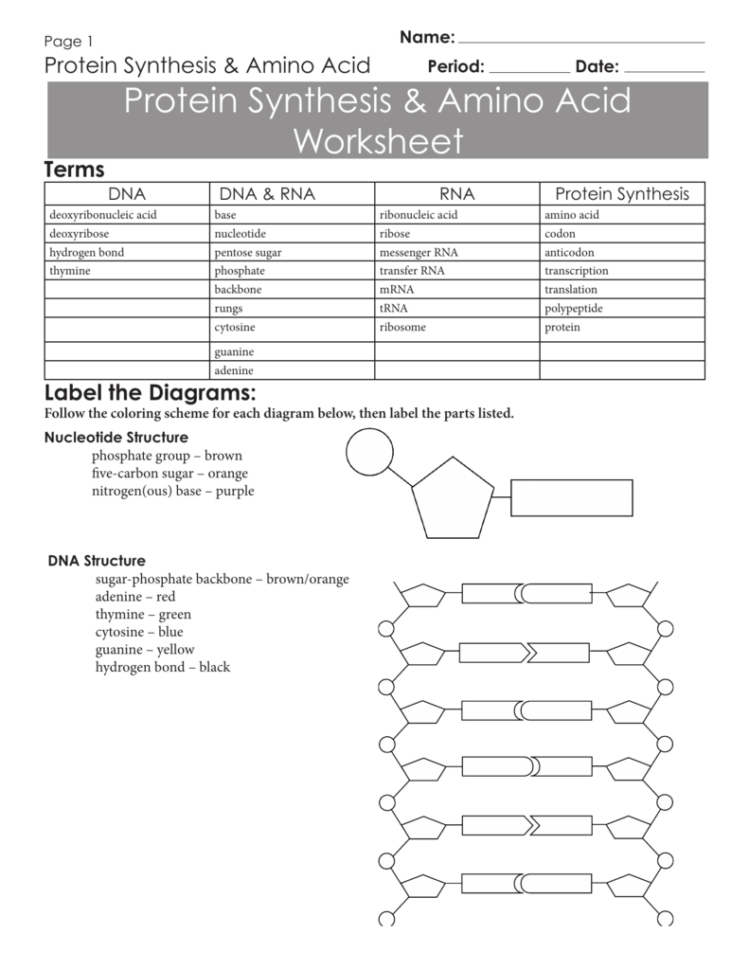
Protein synthesis is a process where cells build proteins. This process involves two main stages: transcription and translation. Here's a breakdown:
- Transcription: DNA is read and an RNA molecule is created. This RNA molecule, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes.
- Translation: mRNA at the ribosomes is read, and the ribosome assembles a polypeptide chain according to the mRNA's codons, which are sequences of three nucleotides. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid, which is then linked together to form proteins.

The Role of Amino Acids

Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 common amino acids, and they are combined in various sequences to make different proteins. Here's what you need to know:
- Structure: Each amino acid has an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a unique R group or side chain, which defines the properties of the amino acid.
- Importance: Their sequence in proteins determines protein folding, function, and interaction with other molecules.
- Codons: Each amino acid is coded by at least one codon, and some amino acids have multiple codons. This genetic code is universal, with few exceptions.
Protein Synthesis Worksheet & Key

Amino acids and their codons can be confusing, but a well-designed worksheet helps:
| Amino Acid | Codons |
|---|---|
| Alanine | GCA, GCC, GCG, GCU |
| Arginine | AGA, AGG, CGA, CGC, CGG, CGU |
| Asparagine | AAC, AAU |
| Aspartic Acid | GAC, GAU |
| Cysteine | UGC, UGU |

🔎 Note: The table represents the standard codons found in most organisms. Some exceptions exist, such as in mitochondria or in rare organisms where codon usage can differ.
Utilizing Worksheets for Better Understanding

Worksheets on protein synthesis should engage students with these strategies:
- Matching Games: Match codons to amino acids or vice versa.
- Fill-in-the-Blank: Students can practice predicting amino acids from mRNA sequences.
- Transcription and Translation Exercises: Students can transcribe a DNA sequence into mRNA, then translate this into a protein sequence.
Using a key like the one shown above is instrumental for:
- Checking accuracy when doing translation exercises.
- Understanding the redundancy in the genetic code.
- Appreciating how changes in the DNA sequence (mutations) can lead to protein variation or malfunction.
🔍 Note: This kind of worksheet is particularly useful for visualizing the genetic code and understanding how cells interpret DNA information.
Common Misconceptions

Here are some common misconceptions and clarifications:
- Genetic Code is Universal: While mostly true, there are exceptions, such as the mitochondrial genetic code.
- One Amino Acid per Codon: While many codons specify a single amino acid, some amino acids can be coded by multiple codons.
- Linear Protein Synthesis: Proteins often require post-translational modifications for proper functionality.
Understanding these points clarifies the dynamic nature of protein synthesis.
In summary, delving into the world of protein synthesis and amino acids is both fascinating and essential. By using a protein synthesis worksheet with an amino acid key, students can grasp the complex interplay between genetics and biochemistry. From transcription to translation, the journey from DNA to protein involves a meticulously orchestrated process that ensures our bodies function correctly. Every amino acid placement, every codon used, plays a critical role in our biological narrative. Education tools like these worksheets not only facilitate learning but also illustrate the wonder and beauty of life's molecular machinery.
What are the differences between transcription and translation?

+
Transcription is the process where DNA is copied into RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus. Translation is the subsequent process where mRNA is used to create proteins in the ribosomes.
Why are there multiple codons for some amino acids?

+
Multiple codons for one amino acid result from the genetic code’s redundancy, providing a fail-safe mechanism against mutations by having multiple ways to code for the same amino acid.
Can changes in the genetic code cause diseases?

+
Yes, mutations that change the sequence of amino acids can result in the production of non-functional or harmful proteins, leading to various genetic diseases.
How do amino acids affect protein function?

+
The sequence and properties of amino acids in a protein determine its shape, functionality, and interactions with other molecules, thus playing a critical role in its biological activity.
What tools can students use to learn about protein synthesis?

+
Students can use protein synthesis worksheets, online simulations, textbooks, and interactive learning apps to understand and practice the processes involved in protein synthesis.