Thermochemistry Worksheet Answer Key: Boost Your Chemistry Skills
Understanding Thermochemistry: A Comprehensive Guide

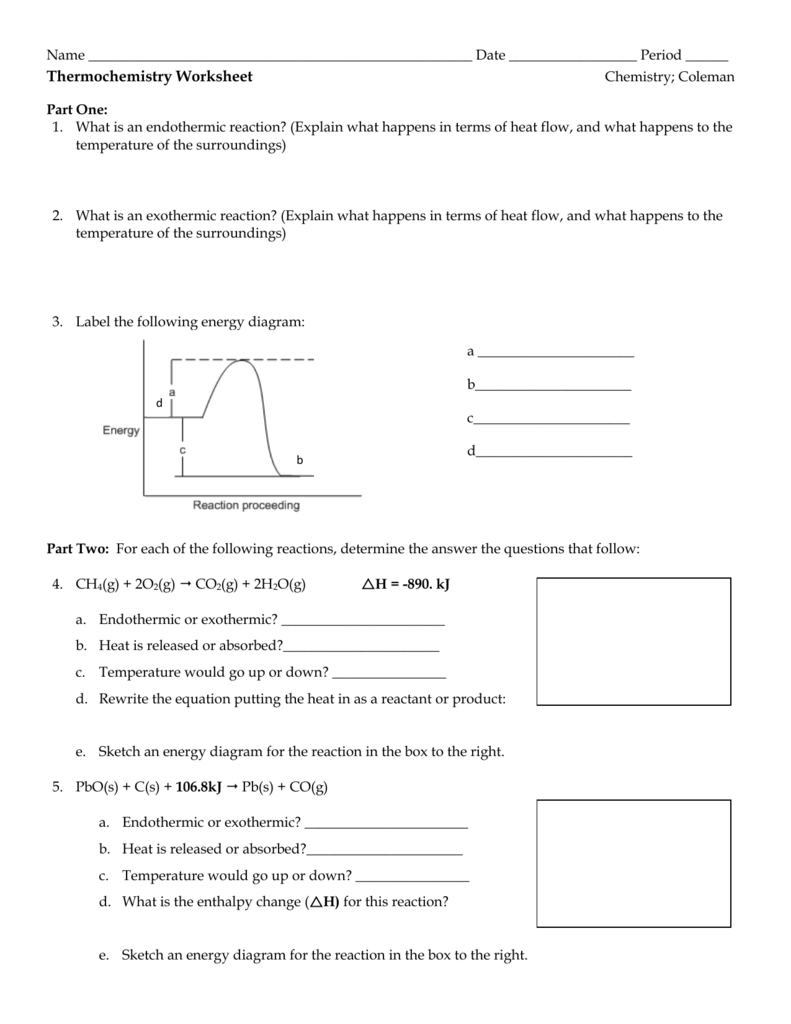
If you're delving into the world of chemistry, you'll quickly encounter thermochemistry, the branch that deals with the heat involved in chemical reactions. Understanding thermochemistry is crucial for grasping how reactions occur, their efficiency, and their impact on our environment. This comprehensive guide will walk you through essential concepts, provide you with a thermochemistry worksheet answer key, and enhance your understanding of this fascinating science.
What is Thermochemistry?

Thermochemistry explores the changes in energy, particularly heat, that accompany chemical reactions. Here's how it breaks down:
- Endothermic Reactions: These reactions absorb heat from their surroundings. The surroundings become cooler, and energy is considered to be stored within the system.
- Exothermic Reactions: These reactions release heat to their surroundings, causing the environment to warm up. Here, the system loses energy in the form of heat.
- Energy Profiles: Diagrams that show the energy of reactants, products, and the activation energy required for a reaction to occur.
Knowing the basics, let's explore how heat transfer influences reaction behavior and how we quantify these changes.
Key Concepts in Thermochemistry

Heat Capacity and Specific Heat

Heat capacity is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of an object by one degree Celsius. For chemistry, we often deal with specific heat, the heat capacity per unit mass, which varies for different substances. Here's why it matters:
- It helps in calculating the amount of heat absorbed or released in reactions.
- It determines how quickly substances change temperature.
Calorimetry

Calorimetry involves measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes, often using a device called a calorimeter. There are two main types:
- Constant Pressure Calorimetry: Used to measure enthalpy changes at constant pressure.
- Constant Volume Calorimetry: Measures internal energy changes at constant volume.
The data from calorimetry experiments can provide insight into:
- The amount of heat absorbed or released by reactions.
- The efficiency of chemical reactions, which is key in industrial processes.
Enthalpy of Reaction (ΔH)

The enthalpy change of a reaction (ΔH) is the difference in enthalpy between the products and the reactants. Here are some key points:
- ΔH < 0: The reaction is exothermic.
- ΔH > 0: The reaction is endothermic.
- Hess’s Law: Allows us to calculate enthalpy changes for complex reactions by summing simpler reactions.
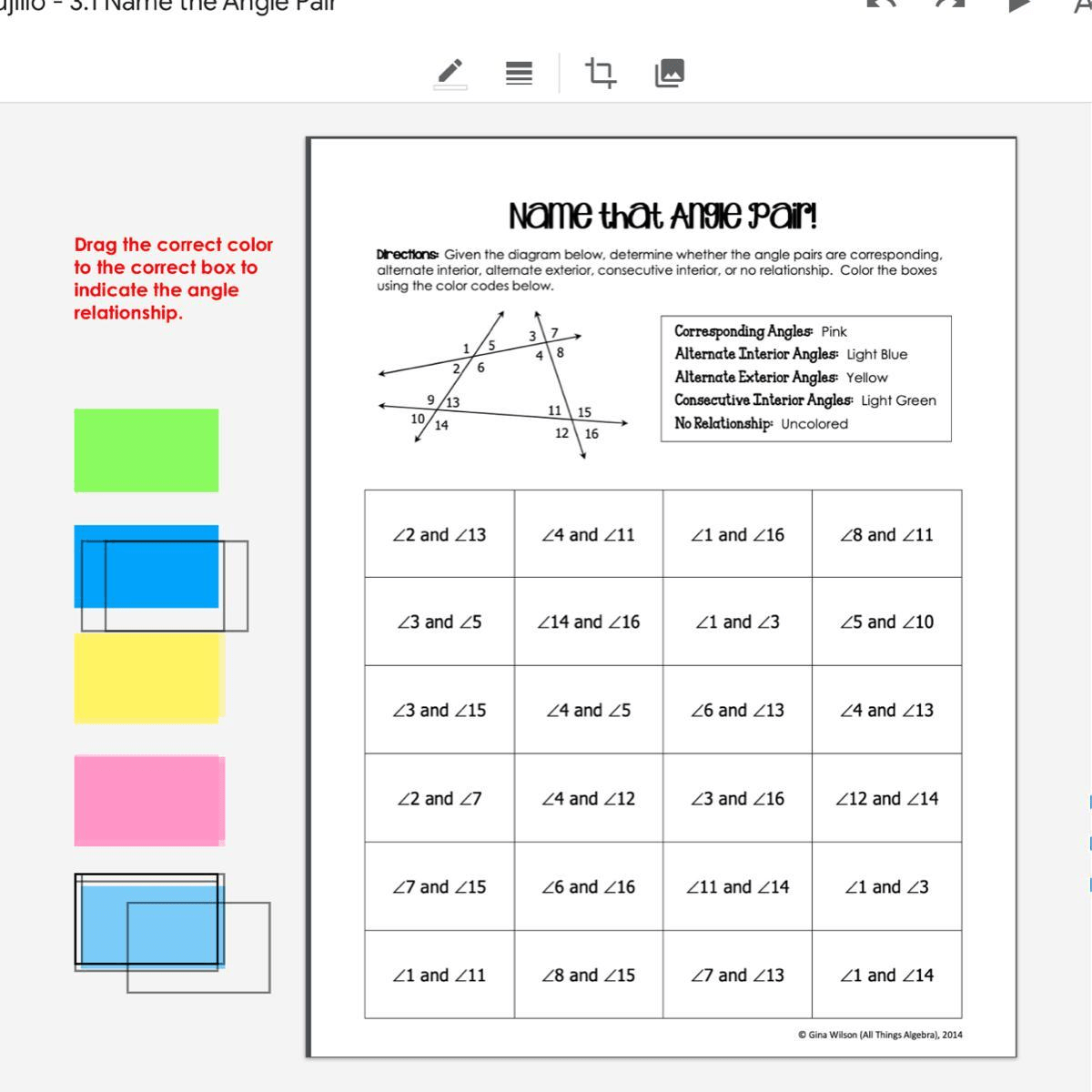
Thermochemistry Worksheet Answer Key

To solidify your understanding of these concepts, let's walk through a thermochemistry worksheet answer key. Here, you'll find problems covering enthalpy calculations, heat transfer, and energy changes:
| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| Calculate ΔH for the combustion of methane. | ΔH = -890 kJ/mol |
| Determine the specific heat of copper if 100 J raises the temperature of 15 g copper by 60°C. | Specific heat = 0.385 J/g°C |
| If 2.00 g of magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid and releases 837 kJ of heat, find ΔH for the reaction. | ΔH = -837 kJ/g * 24.31 g/mol = -1586 kJ/mol |

Tips for Mastering Thermochemistry

Here are some actionable tips to help you master thermochemistry:
- Practice: Use the worksheet provided, and try variations of the problems to reinforce your understanding.
- Understand Units: Make sure you're comfortable with the units used in thermochemistry (kJ/mol, J/g°C, etc.).
- Visualize: Use energy profile diagrams to visualize reaction pathways.
- Experiment: If possible, perform or observe simple calorimetry experiments in a lab setting to experience the concepts firsthand.
🔧 Note: Always double-check your unit conversions in thermochemical calculations to ensure accuracy.
Summing Up Your Learning Journey

Thermochemistry is a fascinating area of study that reveals how energy transfer governs chemical reactions. Through understanding concepts like heat capacity, enthalpy changes, and the principles of calorimetry, you'll have a solid foundation to appreciate how reactions work and why they are important in various fields like material science, environmental science, and chemical engineering. Engaging with problems, as exemplified in the worksheet answer key, sharpens your skills, ensuring you're not just learning but also applying what you've learned in practical scenarios. Keep practicing, visualize the reactions, and use real-world examples to solidify your knowledge. This approach not only enhances your understanding but also prepares you for further complex studies in chemistry.
What is the difference between heat capacity and specific heat?

+
Heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object by one degree Celsius. Specific heat, on the other hand, is the heat capacity per unit mass. It indicates how much heat a particular material can absorb per unit of mass per degree temperature change.
Can an endothermic reaction occur spontaneously?

+
Yes, an endothermic reaction can occur spontaneously if the system’s increase in entropy outweighs the decrease in enthalpy, making the overall Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) negative. This is based on the principle of thermodynamics where ΔG = ΔH - TΔS.
How do I calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction?

+
You can calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH) by subtracting the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants from that of the products. This can also be done through experimental methods like calorimetry, where heat exchange is measured directly.