Simple Division With Remainders Worksheet for Kids

Introduction

Division, one of the four basic operations in mathematics, is not only about the quotient but also about understanding remainders. Teaching children how to handle division with remainders can lay a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts in the future. Today, we’re going to explore how to create an engaging and educational worksheet on division with remainders for kids.
Why Teach Division with Remainders?

Division with remainders introduces children to:
- The concept of divisibility and the idea that not all numbers divide evenly.
- The importance of fractions and decimals as remainders.
- Real-world applications where not all items are split evenly, like distributing candies among friends.
Creating the Worksheet

Setting the Theme
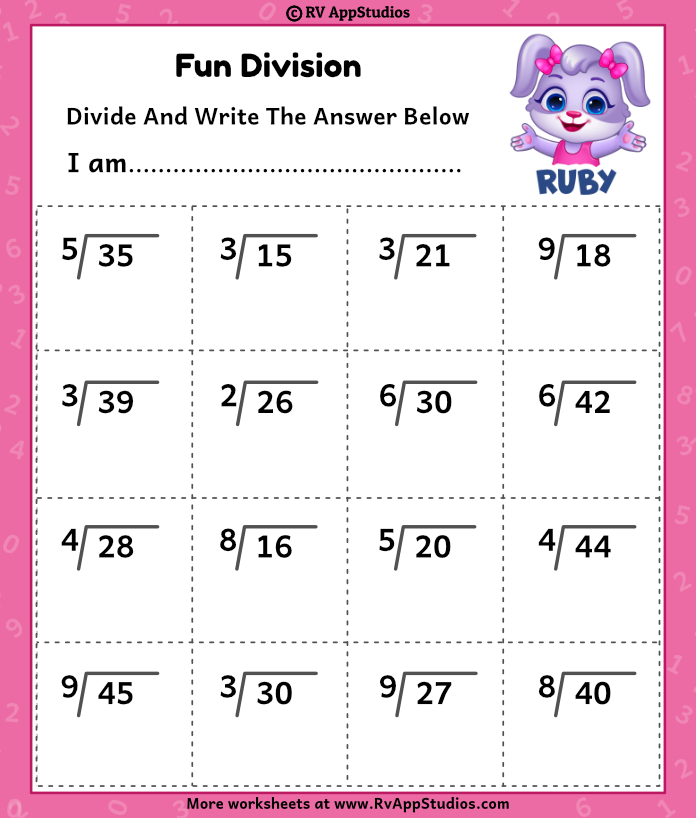
Start by choosing a theme that will resonate with the children. For example, using scenarios involving their favorite animals, characters, or hobbies can make learning division more appealing.
Designing the Problems

Here are some tips for creating division problems with remainders:
- Begin with Simple Problems: Start with easy numbers to ensure comprehension.
- Vary Complexity: Gradually increase the difficulty by introducing larger numbers and multi-step problems.
- Use Visual Aids: Incorporate pictures or diagrams that help visualize the division process.
Example Problems

| Problem | Visualization |
|---|---|
| Divide 14 candies among 3 friends. How many candies do each friend get? | Image of 14 candies divided into three piles, with one pile having one more candy than the others. |
| There are 20 cookies. If you split them between 6 people, how many will each get, and how many will be left? | A visual representation of cookies being shared, showing 3 cookies per person and 2 remainders. |

🎓 Note: Visual aids can significantly enhance a child's understanding of division and remainders.
Interactivity and Engagement

Engage children with:
- Puzzles and Games: Incorporate division puzzles or board games that involve calculating remainders.
- Storytelling: Create a narrative where characters face division scenarios in their adventures.
- Physical Activities: Use real items (like blocks or toys) to enact division problems.
Reinforcement Activities

After introducing the worksheet, reinforce the concept with:
- Word Problems: Encourage children to write their own division problems based on real-life situations.
- Math Journals: Have them explain in their own words what a remainder means to them.
- Group Activities: Have them work in teams to solve division problems and explain their solutions.
Understanding that not all division problems result in an exact answer can be an enlightening moment for kids, leading to a deeper appreciation of mathematics and its practical applications. Through well-designed worksheets, puzzles, and engaging activities, we can demystify remainders and make learning a joyous adventure.
Why is it important for kids to understand division with remainders?

+
Understanding remainders helps children grasp the concept of divisibility, introduces them to fractions and decimals, and prepares them for real-life situations where even division is not always possible.
How can I make division fun for kids?

+
By incorporating storytelling, puzzles, games, and visual aids, you can make division more engaging and fun for children, turning the learning process into an enjoyable adventure.
What are some real-life examples of division with remainders?

+
Dividing candies among friends, distributing cookies at a party, or sharing toys among siblings can all involve division with remainders.
How can I assess a child’s understanding of division with remainders?

+
Ask them to explain what a remainder means, create their own division problems, or solve puzzles that require them to calculate remainders.
Are there any common misconceptions about remainders that children might have?

+
Children might mistakenly think that remainders should be added back into the quotient or that remainders are always a bad thing in division, not understanding the different contexts where remainders can have significance.