5 Ways to Ace Your Production Possibilities Frontier Worksheet

Understanding economics can be as exciting as exploring a new country, but it comes with its own unique challenges, especially when dealing with graphs and equations. One such fundamental concept in economics is the Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF), which students often encounter in their introductory economics courses. Let's dive deep into mastering your PPF worksheet, ensuring you not only understand the concept but also excel in its application.
1. Grasping the Basics of PPF
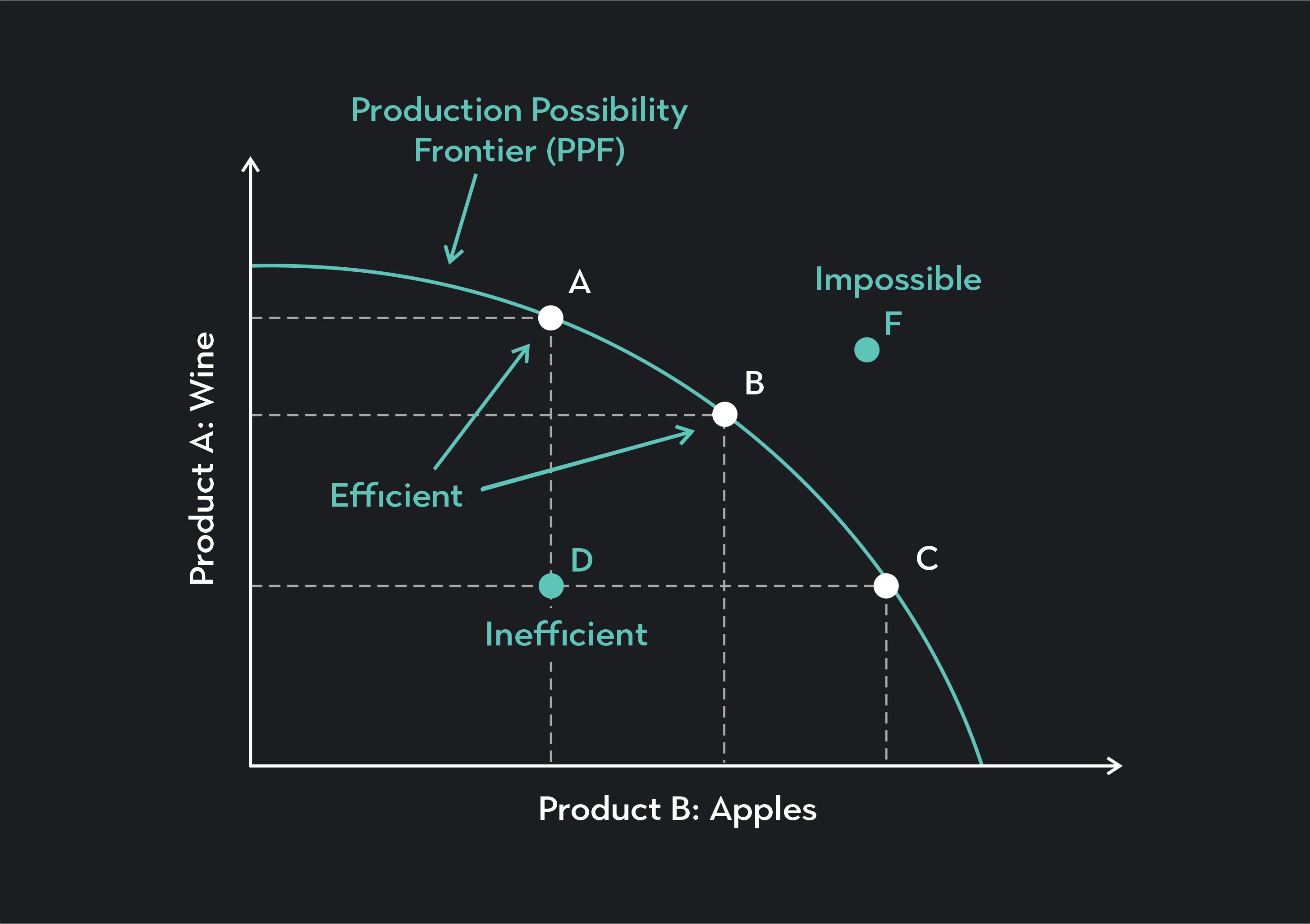
Before you can conquer the PPF worksheet, it’s crucial to understand what it represents:
- Definition: The PPF is a curve depicting the various combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its available resources and technology, assuming full employment and efficiency.
- Assumptions: Here are some key assumptions of the PPF:
- Resources are fixed and fully employed.
- Technology remains constant.
- Production takes place over a specific time frame.
- There are only two goods or services being considered.
🔹 Note: The PPF can show scarcity, choice, opportunity cost, and trade-offs in an economy. Keep these in mind when analyzing your worksheet problems.
2. Plotting Points on the PPF

Graphing is a key skill:
- Start with an axis. Usually, the horizontal axis represents one good (e.g., ‘Guns’), and the vertical axis represents another (e.g., ‘Butter’).
- Plot points using given data or scenarios. These points will help you construct the PPF curve.
- Ensure you understand the concept of attainable and unattainable combinations.
Here's a simple example of how you might plot points:
| Guns | Butter |
|---|---|
| 0 | 5 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 |

📌 Note: Points on the PPF curve represent efficiency. Points inside the curve are inefficient, while points outside are unattainable.
3. Calculating Opportunity Cost
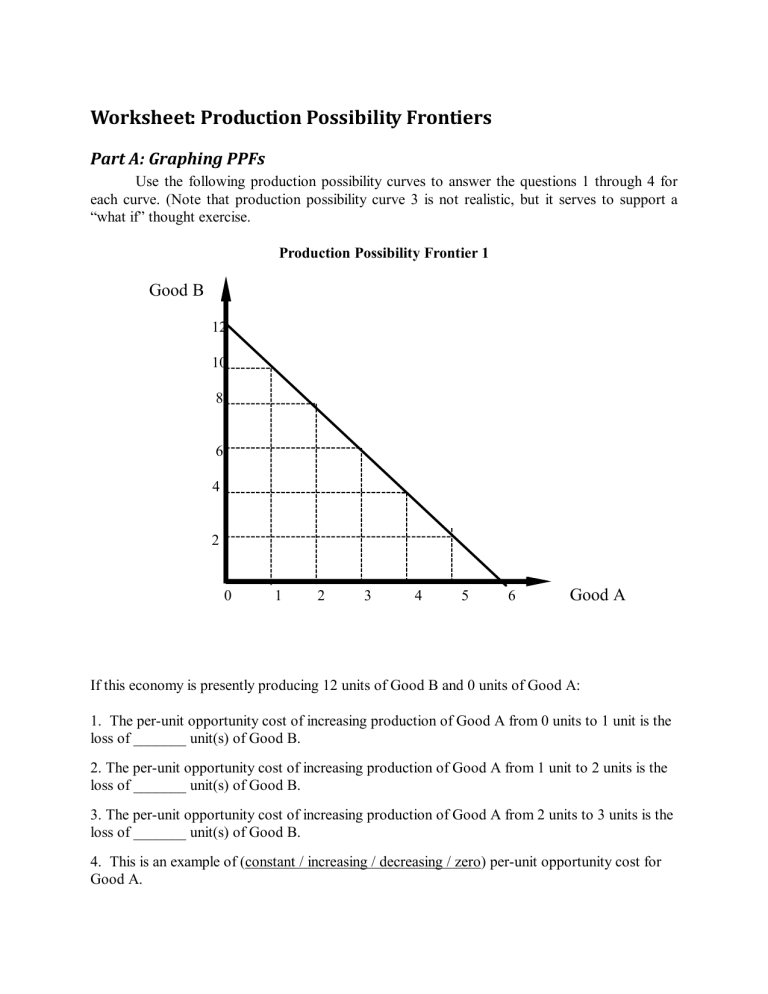
Calculating the opportunity cost along a PPF curve is central to understanding economic principles:
- Formula: Opportunity Cost = What is Given Up / What is Gained
- Example: If moving from producing 2 Guns to 3 Guns means reducing Butter from 3 to 1, then the opportunity cost of producing 1 more Gun is 2 units of Butter.
4. Analyzing Shifts in the PPF

Understanding what causes the PPF to shift is critical:
- Inward Shifts: A decrease in resources or technology.
- Outward Shifts: An increase in resources, technological advancements, or improvements in efficiency.
- Remember, a straight-line PPF indicates constant opportunity costs, while a bowed-out PPF reflects increasing opportunity costs.
5. Answering Complicated PPF Problems

To excel in your worksheet, follow these steps:
- Read the problem carefully to understand what’s being asked.
- Identify the key elements: resources, production possibilities, and economic trade-offs.
- Graph or sketch your PPF based on the scenario.
- Calculate opportunity costs if required.
- Discuss shifts in the PPF if the scenario describes changes in technology or resources.
📝 Note: Time management is key when working on PPF worksheets. Ensure you can move through problems efficiently.
Understanding and applying the concepts of PPF can open your eyes to the dynamics of economics, revealing how societies allocate scarce resources. Whether you're plotting points, calculating costs, or analyzing shifts, remember that the goal is to understand the trade-offs and efficiency of an economy. By mastering these steps, you'll not only ace your PPF worksheet but also gain a foundational understanding of economic principles that will serve you well in further studies or practical applications.
Why is it important to plot points accurately on a PPF?

+
Accurate plotting helps visualize the trade-offs and opportunity costs, allowing you to interpret economic scenarios correctly.
Can the shape of the PPF change?

+
Yes, the PPF can shift or change shape due to changes in resources or technology, indicating changes in production possibilities.
What does a point inside the PPF represent?

+
A point inside the PPF represents inefficient use of resources or unemployment within the economy.
How does technology affect the PPF?

+
Advancements in technology can expand an economy’s production capabilities, shifting the PPF outward, increasing efficiency and production possibilities.
What if there’s no trade-off between goods in a PPF?

+
If there’s no trade-off, the PPF would appear as a straight line, indicating constant opportunity costs across the production of the two goods.