HR Diagram Worksheet Answers for Stellar Learning

Are you embarking on a journey through the vast expanse of stars with an HR Diagram Worksheet? Then you've come to the right place. Understanding the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, often referred to simply as the HR Diagram, is foundational for anyone interested in astronomy or stellar evolution. Here, we provide comprehensive answers and explanations to enhance your learning experience.
What is an HR Diagram?

The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between their absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temperatures. It’s a pivotal tool in astronomy for the following reasons:
- Stellar Classification: It classifies stars by their spectral types (O, B, A, F, G, K, M).
- Evolutionary Tracks: It shows how stars evolve over their lifetimes.
- Galactic Insights: It provides insights into the makeup of different populations of stars within our galaxy and others.
Key Concepts on an HR Diagram

Let’s delve into the critical components of the HR Diagram:
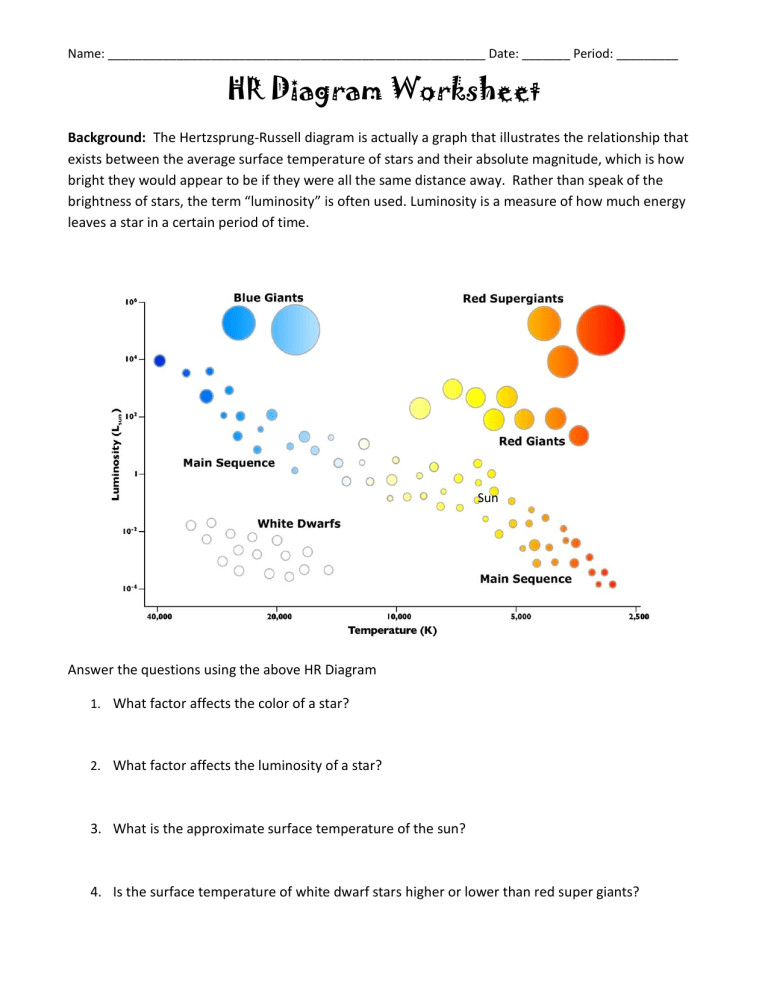
- Luminosity vs. Temperature: The Y-axis shows the brightness or luminosity of stars, while the X-axis plots the stars’ temperature (often as spectral types).
- Main Sequence: A diagonal band where most stars reside, indicating their current stage of hydrogen fusion.
- Red Giants and Supergiants: Large, evolved stars above the main sequence with lower surface temperatures but significantly higher luminosities.
- White Dwarfs: Small, hot, and dim stars located at the bottom left of the diagram.
- Variable Stars: Stars that vary in luminosity can move across the HR Diagram over time.
| Spectral Type | Color | Temperature (K) |
|---|---|---|
| O | Blue | >30,000 |
| B | Blue-White | 10,000 - 30,000 |
| A | White | 7,500 - 10,000 |
| F | Yellow-White | 6,000 - 7,500 |
| G | Yellow | 5,200 - 6,000 |
| K | Orange | 3,700 - 5,200 |
| M | Red | 2,400 - 3,700 |
Analyzing HR Diagrams

Analyzing an HR Diagram requires:
- Understanding the distribution of stars across different regions.
- Recognizing patterns in star evolution based on their position.
- Identifying stellar types by spectral classes.
🪐 Note: Not all stars fit neatly into the typical categories, and there are anomalies like Wolf-Rayet stars, neutron stars, or brown dwarfs.
HR Diagram in Star Cluster Analysis

Studying star clusters with an HR Diagram helps in:
- Age dating of the cluster.
- Determining metallicity (the proportion of elements heavier than helium) through the stars’ spectra.
- Understanding mass-luminosity relations by plotting a cluster’s stars on the diagram.
Here’s a summary of the critical takeaways:
- The HR Diagram is essential for understanding stellar properties, evolution, and the makeup of galaxies.
- Different regions of the diagram represent various stages of a star’s life cycle.
- Analyzing clusters provides valuable information about their evolution and composition.
Why are some stars not on the main sequence?

+
Stars not on the main sequence are either evolving or in stages outside of their typical hydrogen-burning phase. These include red giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs which represent different stages of stellar life cycles.
How can the HR Diagram help predict the life expectancy of stars?

+
By locating a star on the HR Diagram, you can deduce its age based on where it falls in the evolutionary tracks. Stars on the main sequence burn hydrogen, and their position gives an indication of how long they’ve been there and how long they might continue.
What is the significance of the color variation in stars?

+
Color indicates temperature; bluer stars are hotter, and redder stars are cooler. This variation in color on the HR Diagram helps classify stars and understand their evolutionary states.



