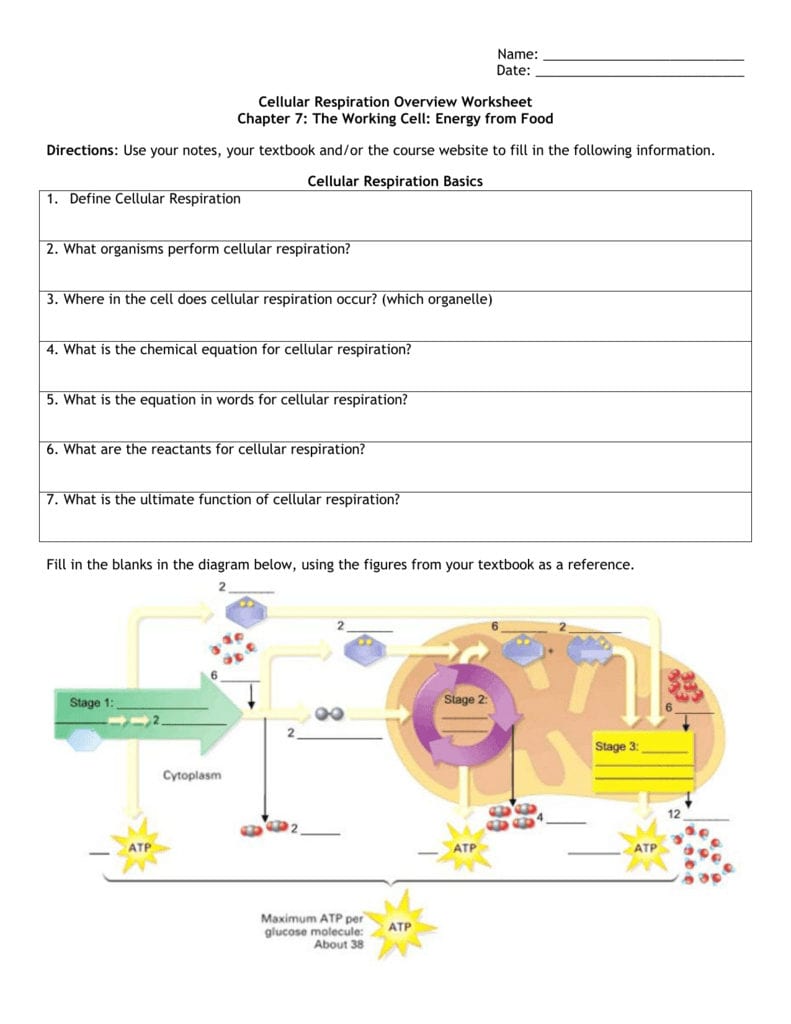
5 Essential Answers for Ionic Bonds Worksheet

📝 Note: Understanding the nuances of ionic bonds is fundamental in the realm of chemistry, enabling students to grasp how atoms interact to form compounds essential for various applications.
What is an Ionic Bond?

An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond formed through the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom or molecule to another. This results in the formation of ions with opposite charges which are attracted to each other, leading to the formation of an ionic compound. Here are the key aspects of ionic bonds:
- Electron Transfer: Electrons move from one atom (usually a metal) to another (usually a non-metal) to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically an octet or noble gas configuration.
- Formation of Ions: The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged cation, while the one that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged anion.
- Strong Electrostatic Attraction: The attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms a strong ionic bond.
- Crystal Lattice Structure: Ionic compounds often exist in a lattice structure, where each ion is surrounded by oppositely charged ions, maximizing attraction and minimizing repulsion.
How Are Ionic Bonds Different From Covalent Bonds?

Ionic and covalent bonds represent the two primary ways atoms bond to form compounds. Here are the differences:
Nature of Bonding:
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, creating ions.
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, forming molecules.
Type of Compounds:
- Ionic compounds generally form between metals and non-metals.
- Covalent compounds usually form between non-metals.
Physical Properties:
- Ionic compounds tend to have high melting and boiling points due to the strong ionic forces. They are typically solids at room temperature, are brittle, and often dissolve in water.
- Covalent compounds, on the other hand, might be gases, liquids, or low-melting-point solids as they don’t have as strong intermolecular forces as ionic compounds.
Electrical Conductivity:
- Ionic compounds can conduct electricity when molten or in solution because the ions are free to move and carry charge.
- Covalent compounds generally do not conduct electricity because electrons are not free to move within the compound.
🔍 Note: While ionic bonding is traditionally thought of as electron transfer, in reality, there's often a degree of covalent character in many ionic compounds due to partial electron sharing.
Why Are Ionic Bonds Important in Everyday Life?

Ionic compounds play numerous vital roles in our daily lives:
Household Products:
- Table salt (NaCl) is an everyday example of an ionic compound used for flavoring and preserving food.
Health and Medicine:
- Medications like lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) for bipolar disorder rely on the ionic bond structure for their functionality.
Nutrition:
- Many essential minerals such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium exist in ionic form in our bodies, aiding in various biochemical processes.
Environmental Applications:
- Ionic compounds are used in pollution control, water treatment, and fertilizers.
Industrial Uses:
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is used in soaps, paper, textiles, and dyes.
How to Predict Ionic Charges Using the Periodic Table?

The periodic table can guide the prediction of ionic charges:
- Group 1 (Alkali Metals) like sodium (Na) lose one electron to achieve a +1 charge.
- Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals) like magnesium (Mg) lose two electrons to achieve a +2 charge.
- Group 13 (Boron Group) elements lose three electrons to get to a +3 charge, though not all follow this rule exactly.
- Group 14 (Carbon Group) doesn’t form ions readily, but when they do, they can be +4 or -4.
- Group 15 (Nitrogen Group) elements gain three electrons to form -3 ions.
- Group 16 (Chalcogens) gain two electrons to form -2 ions, except oxygen which commonly forms -1 in peroxides.
- Group 17 (Halogens) gain one electron to achieve a -1 charge.
- Group 18 (Noble Gases) do not typically form ions as they are inert, having a stable octet configuration.
What Are the Steps to Balance Ionic Equations?

Balancing ionic equations involves several steps to ensure charge neutrality:
Identify the Reactants and Products: Write down all the species involved, noting their charges.
Determine the Reacting Ratio: Understand how many ions are needed to form a neutral compound.
Use Multipliers: Multiply the cations and anions by the lowest whole numbers that will balance the charges:
- Example: Balancing NaCl formation:
- Na+ + Cl- → NaCl
- Here, we have a ratio of 1:1 as each Na+ requires one Cl- to balance the charge.
- Example: Balancing NaCl formation:
Check for Multiple Ions: In more complex reactions, some ions might not change their state (spectator ions). You balance the equation focusing on the ions that do participate.
Verify Charge Balance: Ensure that the sum of positive and negative charges is equal on both sides.
Incorporate States of Matter: If required, include the state of matter (s), (l), (g), (aq).
⚠️ Note: While balancing ionic equations, make sure to include the phases of the substances involved to clarify their solubility or reactivity conditions.
Summing up, understanding ionic bonds, their distinctions from covalent bonds, their significance in our daily lives, how to predict charges, and balancing equations provides a robust foundation for chemical knowledge. From the food we eat to the chemicals we use in industry, ionic bonds play an integral role in our lives, making it essential for students and professionals in chemistry to master these concepts.
Can an ionic compound be a gas?

+
Under normal conditions, ionic compounds are usually solids due to their strong ionic bonds. However, when heated to their melting points, some ionic compounds can turn into a gas or vapor, like lithium fluoride (LiF).
Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity in water?

+
When an ionic compound dissolves in water, the ions separate and become free to move, carrying an electric charge, which allows the solution to conduct electricity.
How do you predict if an ionic bond will form between two elements?

+
Ionic bonds are likely to form if there is a significant difference in electronegativity between the elements involved, typically between metals and non-metals. The metal atom loses electrons to become a cation, while the non-metal gains electrons to become an anion.