5 Essential Tips for Fannie Mae Income Calculation
In the intricate process of mortgage underwriting, understanding and accurately calculating income according to Fannie Mae guidelines is crucial for both borrowers and lenders. Whether you're a first-time home buyer or a seasoned real estate investor, having a solid grasp of these rules can streamline your loan application process and potentially secure better mortgage terms. Here, we delve into five essential tips that will help you master the nuances of Fannie Mae income calculation.
Understanding the Basics of Fannie Mae Income

Fannie Mae, one of the leading secondary mortgage market companies in the U.S., has set forth guidelines to determine a borrower's ability to repay a mortgage. These guidelines focus on:
- Stable and Predictable Income: Fannie Mae looks for income that is likely to continue, considering the nature of the borrower's employment, historical income patterns, and future likelihood.
- Verification: All income must be verified through documents like pay stubs, W-2 forms, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Calculating Gross Income: Before deductions and taxes, gross income forms the basis for loan qualification.

Tip 1: Properly Documenting Income Sources

When you apply for a mortgage:
- Collect all relevant documentation like W-2s, recent pay stubs, and federal tax returns for the last two years.
- Ensure your documentation covers all income sources including:
- Primary employment
- Part-time work
- Bonus or commission
- Investment income
- Self-employment
- Be prepared for additional verification or documentation requests from the lender.
🌟 Note: Maintaining organized and comprehensive records can significantly speed up the approval process.
Tip 2: Handling Fluctuating Income
If your income varies due to seasonal work or variable income sources:
- Stabilization through Averaging: Lenders might calculate an average of your income over the last two years, which can help stabilize the qualifying income if your earnings have been volatile.
- Documenting Temporary Fluctuations: If there's a temporary decrease in income, provide documentation to explain these fluctuations, such as a letter from your employer or a business financial statement.
- Consider the 12-Month Income Method: In some cases, Fannie Mae allows lenders to use income from the most recent 12 months if it's higher than the two-year average.
Tip 3: Self-Employment and Business Income

Self-employed individuals or small business owners face additional scrutiny:
- Provide Business Financials: Include profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and a breakdown of business expenses versus personal draws.
- Tax Returns: Always provide the last two years of personal and business tax returns, including schedules for self-employment tax (Schedule C).
- Business Stability: Lenders will assess the stability of your business. Ensure you can demonstrate consistent income over time.
| Document | Details |
|---|---|
| Profit and Loss Statement | Covering the most recent 12 months |
| Balance Sheet | Showing assets, liabilities, and owner's equity |
| Tax Returns | Last two years including Schedule C for self-employment |

Tip 4: Addressing Gaps in Employment

Having periods of unemployment or career changes can affect your loan eligibility:
- Document the Reason: Provide letters or documents explaining any employment gaps or career transitions.
- Show Reemployment: Proof of new employment or return to work can help mitigate concerns about income stability.
- Qualify with Part-Time or Temporary Income: If you've been working part-time or temporarily, show that this income can be expected to continue.
Tip 5: Special Income Considerations

There are specific guidelines for income from:
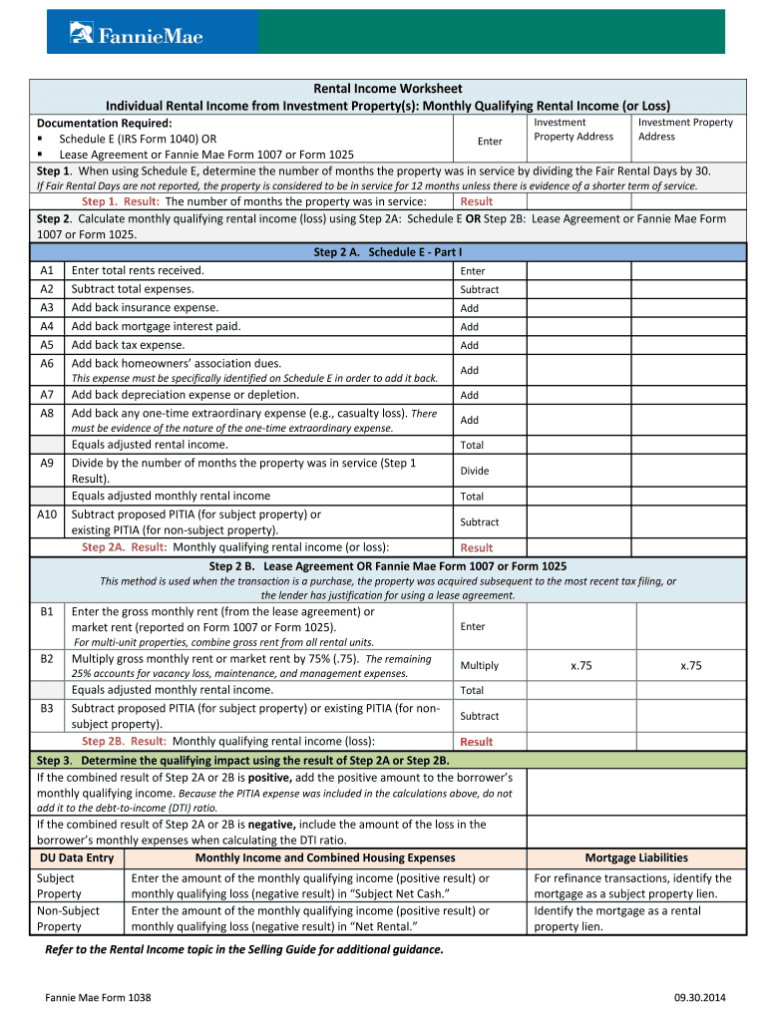
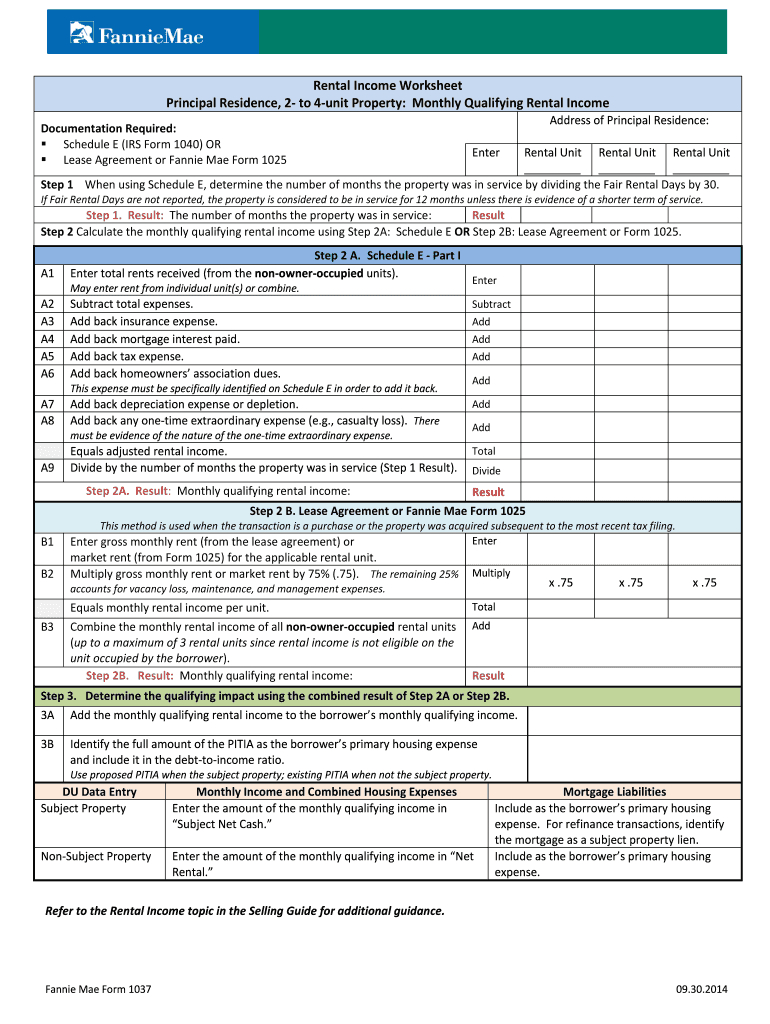
- Rental Properties: Use lease agreements, property management statements, and Schedule E from your tax returns to verify rental income.
- Alimony or Child Support: Provide divorce decree or legal documents showing payments and ensure consistent payment history.
- Retirement or Social Security: Offer award letters, benefit statements, or documentation from the Social Security Administration.
📜 Note: For retirement income, prove that you've received these benefits for the past two years.
By following these tips, you'll be better equipped to navigate the complexities of Fannie Mae's income calculation requirements. Accurate documentation and understanding of these guidelines can make a significant difference in your mortgage application's approval chances and terms. With the mortgage industry continually evolving, staying informed about the latest updates from Fannie Mae can further enhance your preparedness.
Summing up, the key to successfully managing Fannie Mae's income calculation lies in thorough documentation, understanding the nuances of different income streams, and proactively addressing any potential red flags in your income history. By adhering to these principles, you'll not only facilitate a smoother mortgage application process but also set a solid foundation for future real estate investments.
What documentation do I need for Fannie Mae income verification?

+
You need to provide recent pay stubs, W-2 forms for the past two years, tax returns, and additional documents for self-employment or investment income. Detailed records enhance your application’s credibility.
How does Fannie Mae handle fluctuating income?

+
Fannie Mae uses a two-year average method to stabilize income or considers the most recent 12 months if higher. Temporary income dips require documentation explaining the fluctuation.
Can part-time income be used for Fannie Mae mortgage qualification?

+
Yes, as long as you can demonstrate that this part-time income is likely to continue. You’ll need to provide proof of current employment and past earnings.



