5 Essential Tips for Stoichiometry Mastery

Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that involves calculating quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. It is an essential tool for chemists and students to understand the chemical reactions' proportions, quantities, and yields. Mastery of stoichiometry can transform your approach to solving problems in chemistry, making it a foundational skill for any budding scientist. Here are five key tips to achieve proficiency in this crucial area of study:
Understand the Concept of Moles
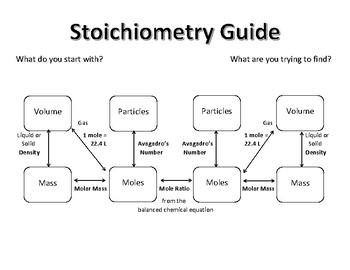
The concept of moles is the bedrock of stoichiometry. A mole is a unit that links the microscopic world of atoms to the macroscopic world we observe. Here’s how you can solidify your understanding:
- Avogadro’s Number: Know that one mole contains 6.022 x 1023 entities. This constant is crucial for converting between grams and moles.
- Molar Mass: Calculate the molar mass of substances from the periodic table. It helps in converting mass to moles and vice versa.

🌡 Note: When dealing with moles, always remember that the units you use must be consistent with the reaction equation you are analyzing.
Master Balanced Equations

Balancing equations is fundamental in stoichiometry. An unbalanced equation misleads calculations, so:
- Use the inspection method or the algebraic method for balancing complex reactions.
- Understand that each atom in the reaction must be accounted for; coefficients represent moles, not individual atoms or molecules.
- Check your work by ensuring the number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation is equal.
| Substance | Balanced Equation | Total Mass (Before Reaction) | Total Mass (After Reaction) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O | 8.04 g | 18.02 g |

💡 Note: The Law of Conservation of Mass ensures that the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products in a balanced chemical equation.
Apply Molar Ratios Effectively

Once you have a balanced equation, you can use the molar ratios to relate reactants and products. Here’s how:
- From the balanced equation, deduce the mole-to-mole relationships, which are not just useful for calculations but also for understanding the reaction’s efficiency.
- Calculate limiting reactants and excess reactants by using these ratios.
🔬 Note: In stoichiometry, the limiting reactant dictates the extent of the reaction; all other reagents will be in excess.
Practice Conversions and Dimensional Analysis

Dimensional analysis is a tool that simplifies stoichiometric calculations. Follow these steps:
- Start with what you know, convert it to moles using molar mass or Avogadro’s number.
- Use the mole-to-mole ratio from the balanced equation to get moles of the desired substance.
- Convert back to the required units (grams, liters, etc.) using appropriate conversion factors.
📐 Note: Dimensional analysis reduces errors in calculations by ensuring units cancel out appropriately.
Visualize and Interpret

Finally, visualization aids in mastering stoichiometry:
- Use molecular diagrams or models to represent particles in reactants and products.
- Understand how the physical properties of substances change during a reaction.
- Analyze the theoretical yield and compare it with the actual yield to understand reaction efficiencies and practical limitations.

To sum up, mastering stoichiometry is about embracing the concepts of moles, balancing equations, applying molar ratios, practicing dimensional analysis, and visualizing chemical processes. Each of these tips not only helps in solving problems but also in building a deeper understanding of chemical reactions, which is crucial for anyone studying or working in the field of chemistry.
What are limiting reactants in stoichiometry?

+
Limiting reactants are the reagents in a chemical reaction that get completely consumed, thereby limiting the amount of product formed. The reaction stops once the limiting reactant is exhausted.
Why is dimensional analysis important in stoichiometry?

+
Dimensional analysis ensures that calculations are carried out with consistency in units, reducing errors and helping to solve multi-step problems by canceling out unnecessary units.
How can visualization aid in understanding stoichiometry?

+
Visualization helps students conceptualize the molecular interactions, stoichiometric ratios, and the transformation from reactants to products, providing a tangible link to abstract concepts.