Bill Nye's Rock & Soil Answers: 5 Key Takeaways

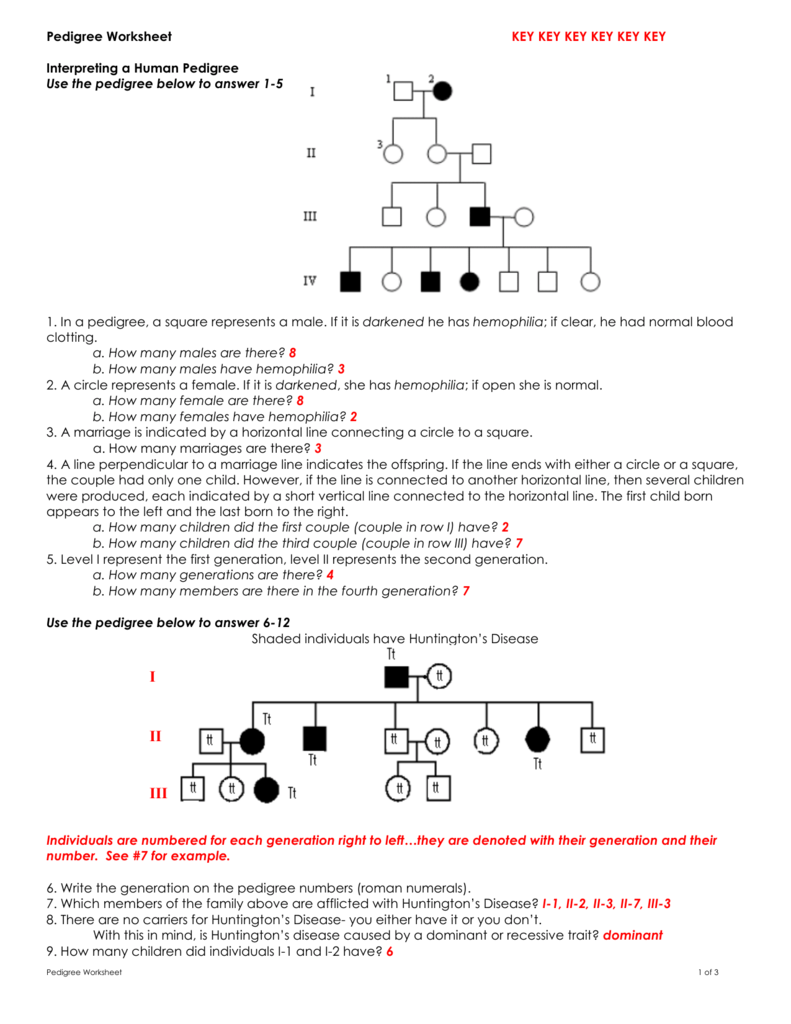
Understanding the Foundations of Our Planet: Rock and Soil Composition

The Earth beneath our feet is a complex tapestry woven from the most fundamental of materials: rock and soil. To truly appreciate the intricate dance of life on our planet, one must delve into the composition and characteristics of these elements. Here, we explore five key takeaways from Bill Nye, “The Science Guy,” as he enlightens us about the mysteries of rock and soil.
Rock Formation: The Geology Behind It

Rocks are not just inanimate objects; they are a chronicle of Earth’s history. Here are the steps through which rocks are formed:
- Igneous Rocks: These form from the cooling and solidification of molten rock or magma. Volcanic activity plays a crucial role here.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Created from layers of sediments that are compacted over time due to pressure, often holding evidence of ancient life in the form of fossils.
- Metamorphic Rocks: The heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface transform pre-existing rocks into new forms with different physical and chemical properties.
🌍 Note: Rocks are not just solid objects; they carry the history of our planet, telling stories of its fiery past and the life that once roamed its surface.
The Soil’s Role in Our Ecosystem

Soil is more than just dirt; it’s a living, breathing foundation for life:
- Fertility: Soil contains vital nutrients needed for plant growth, supporting ecosystems from forests to farmland.
- Water Retention: It holds water, essential for plants and sustaining life above the soil.
- Decomposition: Soil fosters microorganisms that decompose organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
The Mineralogical Diversity of Rocks and Soil

Both rocks and soil are composed of a variety of minerals, each contributing to their unique characteristics:
- Silicates: These are the most abundant minerals in the Earth’s crust, forming the backbone of most rocks.
- Carbonates: Found in limestone and other sedimentary rocks, aiding in carbon dioxide storage.
- Oxides and Sulfides: These influence soil pH and are critical for plant nutrition.
Rock and Soil’s Impact on Civilization

Throughout history, rock and soil have been instrumental in shaping human civilization:
- Construction Materials: From ancient monuments to modern skyscrapers, we owe much to these natural resources.
- Agricultural Land: The richness of soil determines the success of farming, influencing where civilizations can thrive.
- Geological Resources: Fossil fuels and other minerals embedded in rock layers have powered the industrial era.
The Dynamic Earth: Rock Cycle and Soil Formation

The continuous cycle of rock transformation and soil creation shapes our planet:
- Weathering and Erosion: Breaking down rocks into sediments that contribute to soil formation.
- Deposition: The laying down of sediment particles to build layers that could become sedimentary rocks or enrich soil.
- Metamorphism: High pressures and temperatures can convert these sediments back into rock.
- Recycling: Through plate tectonics, rocks return to magma, restarting the cycle.
In understanding the composition, origins, and interactions of rock and soil, we gain insights into the very building blocks of our world. We appreciate how these seemingly static elements are part of a grand, ever-evolving system, shaping our environment, influencing our societies, and sustaining life. By respecting and learning from these fundamentals, we can better manage our resources and preserve the delicate balance of our planet.
What is the rock cycle?

+
The rock cycle is a geological process by which rocks are transformed from one form to another through various geological activities like weathering, erosion, deposition, and tectonic activity. It consists of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic processes, each recycling rock material in a continuous loop.
How does soil fertility affect agriculture?

+
Soil fertility directly impacts agricultural productivity. Fertile soil contains necessary nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are crucial for plant growth. Without these nutrients, crop yields would be poor, and plants would be more susceptible to diseases and pests.
Why are minerals important in rock and soil?

+
Minerals form the basic structure of rocks and are essential in determining the soil’s texture, fertility, and water-holding capacity. They also provide the raw materials for industrial, agricultural, and domestic uses, significantly influencing economic and environmental sustainability.