Counting Subatomic Particles: Interactive Worksheet Guide

Understanding the structure of atoms is fundamental to many branches of science, including chemistry, physics, and material science. At the heart of this understanding is the knowledge of subatomic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. This article provides an interactive guide to counting these particles through a worksheet-based approach, designed to deepen your grasp on this crucial topic.
Introduction to Subatomic Particles

An atom is composed of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons - Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
- Neutrons - Neutral particles also located in the nucleus, adding to the mass of the atom.
- Electrons - Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus.
The number of protons determines the element's identity, while the combination of protons and neutrons influences the atom's mass and stability. Here’s how you can start counting:
Understanding Atomic Number and Mass Number

To count subatomic particles accurately, understanding two fundamental concepts is essential:
- Atomic Number - This is the number of protons in an atom and defines the element's identity on the periodic table.
- Mass Number - This is the sum of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
Here's a simplified example using an interactive worksheet:
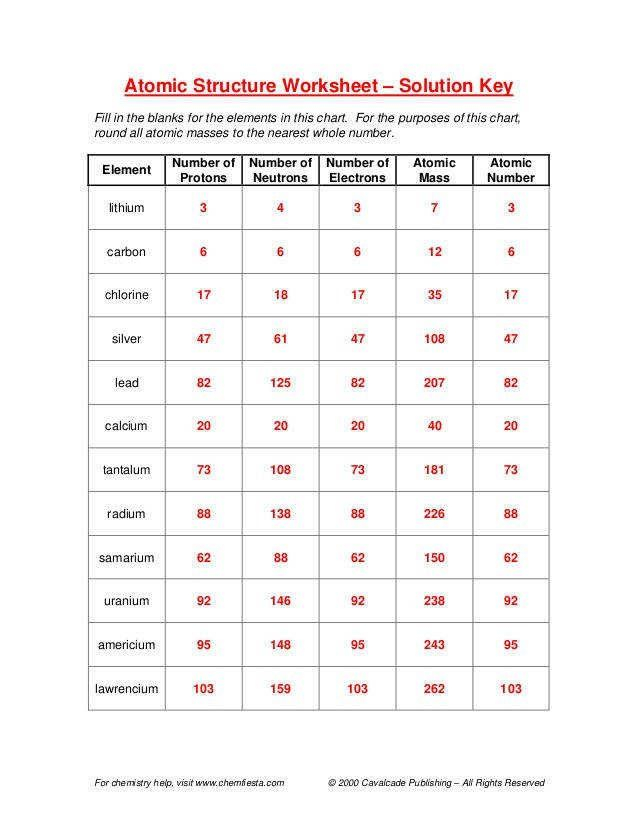
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Mass Number | # Protons | # Neutrons | # Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 |

🔍 Note: Neutrons can be calculated as Mass Number - Atomic Number.
Calculating Protons and Neutrons

Counting protons and neutrons involves:
- Identify the atomic number to know the number of protons.
- Determine the mass number for the specific isotope.
- Calculate neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
Worksheet Activity

Let's engage with an interactive worksheet to practice counting:
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Mass Number | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
|---|
Instructions:
- Fill in the atomic number and mass number based on the given element.
- Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons (assuming the atom is neutral).
Advanced Concept: Isotopes

Isotopes are versions of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Here's how isotopes affect our counting:
- Two isotopes of the same element will have the same number of protons but different mass numbers.
- By comparing isotopes, you can infer the different neutron counts.
Why Counting Matters

The significance of accurately counting subatomic particles extends beyond academic exercises:
- Chemical Reactions: The balance of electrons in an atom affects its reactivity and how it forms bonds.
- Nuclear Physics: Neutron counts influence nuclear stability and the potential for radioactive decay.
- Material Science: Isotopes can change material properties, which is crucial in research and industry.
In our interactive journey through subatomic particles, we've covered how to count protons, neutrons, and electrons, understand isotopes, and appreciate why this knowledge is vital. Whether for education, scientific research, or industrial applications, a firm grasp on counting subatomic particles provides a foundation for further exploration in the atomic world. This guide, through its interactive approach, aims to make these concepts accessible and practical.
How do I find the number of electrons in an ion?

+
For an ion, you adjust the electron count based on its charge. Add electrons for a negative ion or subtract for a positive ion, starting from the atomic number.
What happens if the number of protons changes in an atom?

+
If the number of protons changes, you essentially have a different element, as the atomic number defines the element’s identity.
Can we have atoms with zero electrons?
+
Atoms with zero electrons exist, but they are highly reactive and usually unstable, known as positive ions or cations.
Related Terms:
- Counting subatomic particles worksheet pdf
- Counting subatomic particles worksheet answers
- Protons Neutrons Electrons Worksheet pdf
- Subatomic particles answer key
- Atomic number Worksheet pdf