5 Tips for Solving Genetics Pedigree Worksheets
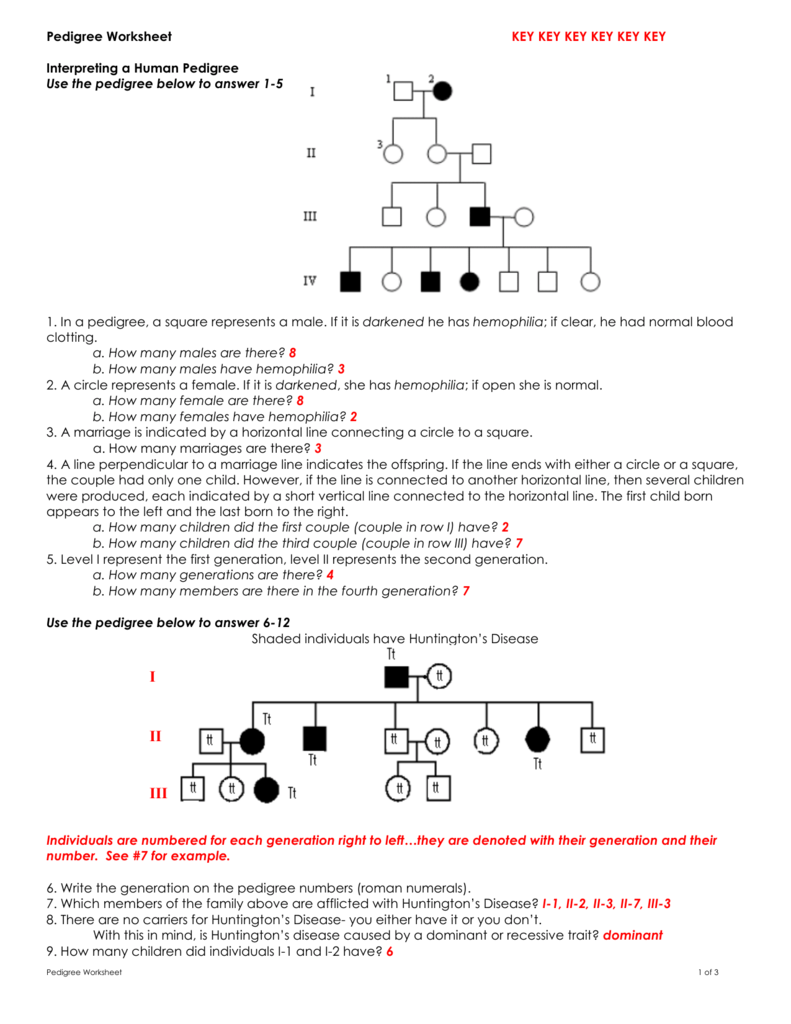
Have you ever come across a genetics pedigree worksheet and felt overwhelmed by the intricate patterns of inheritance? Pedigree analysis, a fundamental tool in genetics, provides invaluable insights into how traits are passed down through generations. This guide will provide you with five essential tips to help you master solving genetics pedigree worksheets, making what might seem like a daunting task into a manageable and even enjoyable process.
Understand the Basic Symbols and Patterns

The key to interpreting any pedigree lies in understanding the symbols used. Here are some common symbols you’ll encounter:
- Males are usually represented by squares and females by circles.
- Carriers (individuals who carry a gene for a trait but do not express it) are denoted with a dot or half-filled shape.
- Shading indicates an affected individual, while no shading means the person is unaffected or unknown.

🔍 Note: Not all pedigrees will use the same symbols, so always check the key or legend provided with the worksheet.
Identify the Mode of Inheritance

Before you delve into the intricacies of the pedigree, identify the mode of inheritance:
- Autosomal Dominant: The trait appears in every generation, often in affected individuals having affected parents.
- Autosomal Recessive: The trait might skip generations, showing up in offspring of unaffected parents who are carriers.
- X-linked: Often more males are affected, and traits can skip generations but typically follow the maternal line.
- Mitochondrial: Only females pass the trait, affecting both genders equally.
| Mode of Inheritance | Common Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Autosomal Dominant | Appears in every generation, affected parents have affected children |
| Autosomal Recessive | Trait can skip generations, carriers can have affected children |
| X-linked Recessive | More males affected, trait skips generations, carrier females |
| Mitochondrial | Passed through mother to all offspring |

Determine the Genotypes and Use Punnett Squares

Once you’ve identified the inheritance pattern, assign genotypes to the individuals:
- Use letters to represent alleles. A for dominant allele, a for recessive allele, or XA and Xa for X-linked traits.
- Employ Punnett squares to predict the offspring genotypes:
- Set up a square with one parent’s alleles on one axis and the other’s on the second axis.
- Fill in the square to see the possible combinations.
🔬 Note: Punnett squares are a simplified model. In reality, meiosis and recombination can lead to unexpected results.
Analyze Generation Patterns and Seek Additional Information

Pedigree analysis often requires examining how traits are distributed across generations:
- Look for unusual patterns that might indicate a new mutation, incomplete penetrance, or variable expressivity.
- Consider the following:
- The prevalence of the trait in the population.
- Any consanguinity (related marriages) which might increase the likelihood of recessive traits.
- The age of onset, as this can affect diagnosis and detection.
Check Your Work with Test Crosses
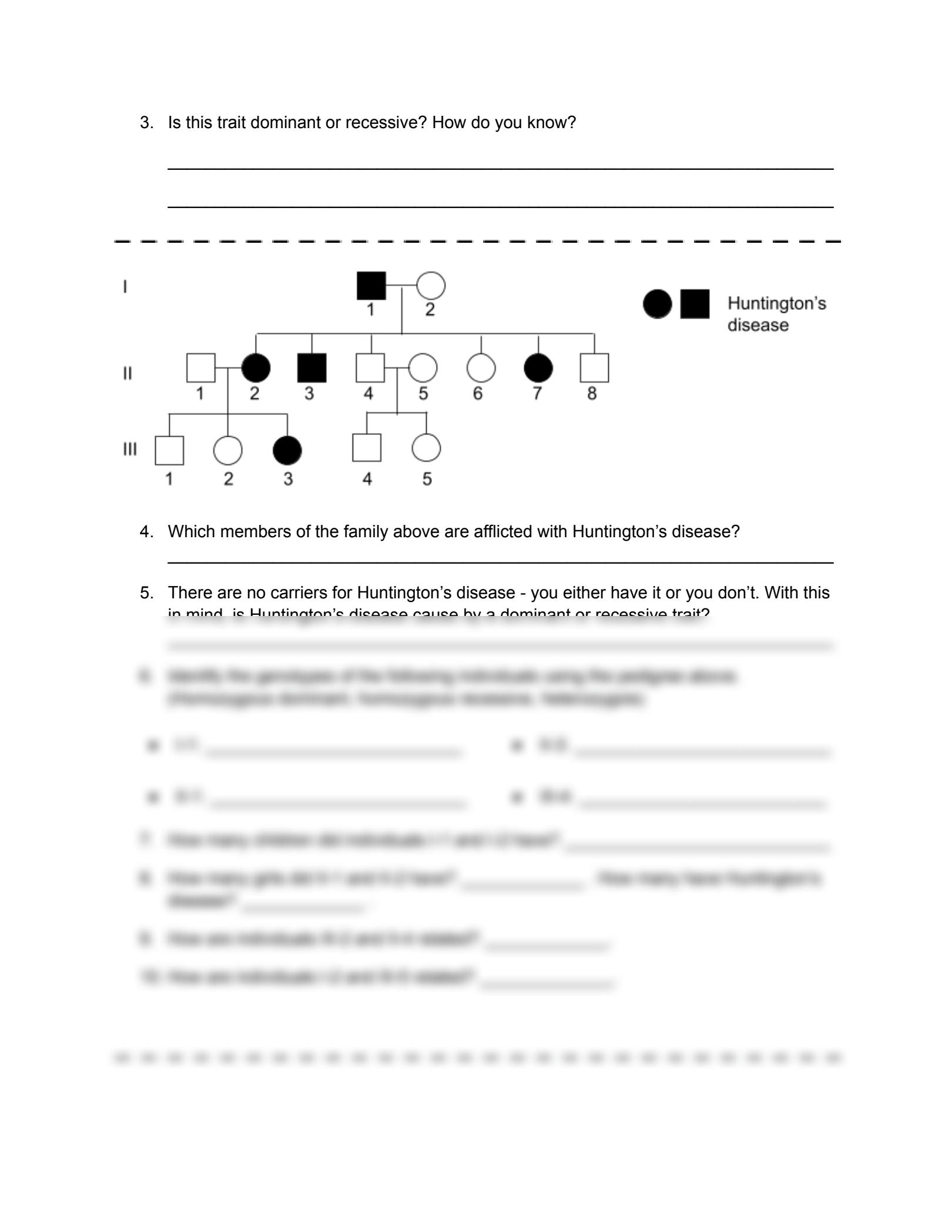
To verify your analysis, consider hypothetical crosses or “test crosses”:
- Predict what children or siblings would look like if a certain individual were to mate with someone of a known genotype.
- Use these test crosses to confirm your understanding of the inheritance pattern and genotypes.
Finalizing the pedigree involves cross-referencing your results with known genetic principles:
- Ensure your interpretation fits with established genetics laws, like Mendel’s laws.
- Revisit any assumptions or complex scenarios to refine your analysis.
By following these five tips, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how to solve genetics pedigree worksheets. This skill not only enhances your grasp of genetics but also opens up fascinating avenues for understanding human health, disease patterns, and even evolution.
What is a pedigree in genetics?

+
A pedigree is a diagram that shows the inheritance pattern of a particular trait, usually a disease or physical characteristic, through a family over generations.
How do I determine if a trait is dominant or recessive from a pedigree?

+
Check if the trait appears in every generation (suggestive of dominant inheritance) or skips generations (suggestive of recessive inheritance). Also, observe if unaffected parents have affected offspring, which indicates recessive inheritance.
Why is it important to understand pedigrees?

+
Understanding pedigrees helps in predicting the likelihood of inheriting genetic conditions, aiding in genetic counseling, family planning, and medical diagnosis.