5 Bill Nye Genetics Worksheet Answers You Need

Are you a student or a teacher struggling with Bill Nye's genetics worksheet? Not to worry! Understanding genetics can be challenging, but with the right explanations and resources, you'll find it much more approachable. Here, we'll dive into five specific answers to help enhance your comprehension of genetics as explored in Bill Nye's educational materials. Let's get started!
Understanding Genetic Basics

Genetics is the study of heredity and how traits are passed from parents to offspring. It's a fascinating and complex field that affects all living organisms. Before we delve into specific worksheet answers, let's review some fundamentals:
- DNA: The molecule that carries genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms.
- Genes: Segments of DNA that determine specific traits.
- Alleles: Different versions of a gene that lead to variations in inherited characteristics.

Answer 1: What is DNA?

DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blueprint for life. It's a long molecule that contains unique genetic code or instructions necessary for an organism's development and functioning:
- DNA has a double helix structure, resembling a twisted ladder.
- It consists of four nucleotide bases: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G).
- These bases pair specifically (A with T, C with G) to form the rungs of the DNA ladder.
🔬 Note: DNA replication is crucial during cell division, ensuring each new cell gets an identical copy of genetic material.
Answer 2: How do Traits Pass to Offspring?

Traits pass from parents to offspring through the inheritance of genes:
- Each parent contributes one allele for each gene to their offspring.
- The combination of these alleles determines the trait. For example, if both parents contribute alleles for brown eyes, the child might have brown eyes.
- The inheritance patterns are governed by Mendelian genetics, where traits can be dominant or recessive.

🧬 Note: This simple model of inheritance often gets complex due to factors like incomplete dominance, codominance, and polygenic traits.
Answer 3: Explaining Genetic Mutations

Genetic mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can result in varied effects:
- They can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial.
- Mutations can occur due to errors in DNA replication, exposure to mutagens like UV radiation, or due to the insertion or deletion of nucleotides.
- While most mutations are neutral or harmful, occasionally, they can lead to evolution or adaptation.
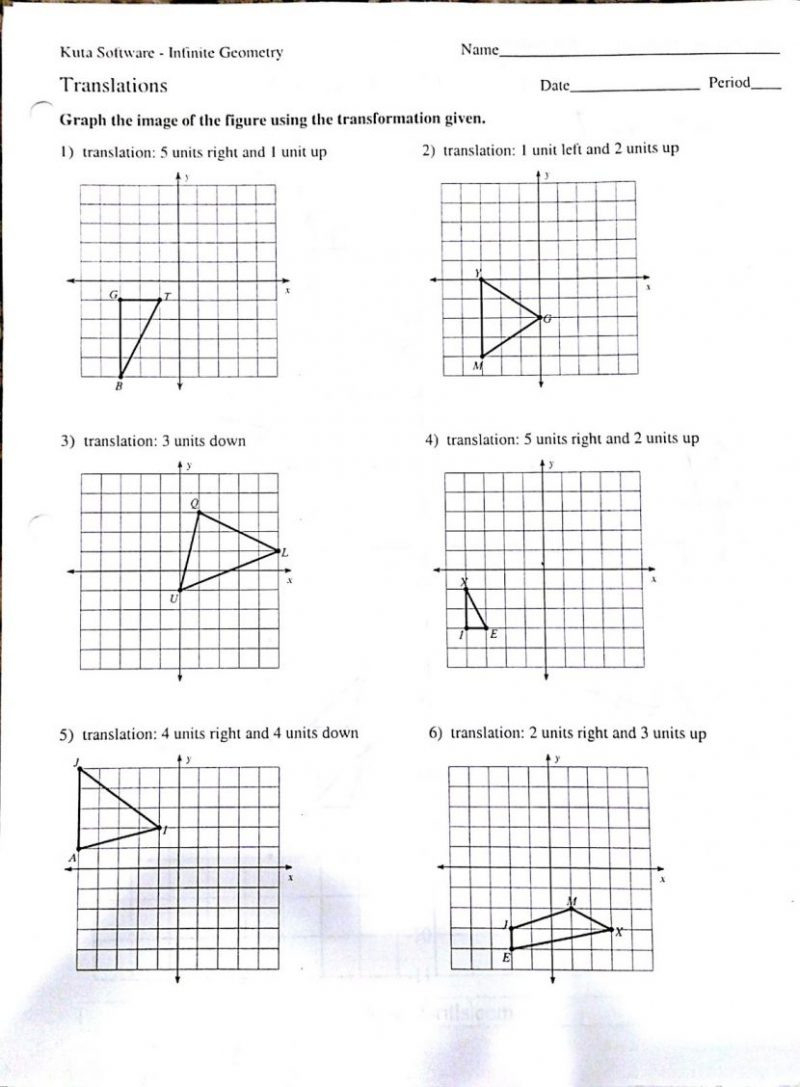
Answer 4: The Punnett Square

The Punnett Square is a diagrammatic tool used to predict the genotypes of offspring from known parental genotypes:
| Parent 1 | Parent 2 | Offspring |
|---|---|---|
| Rr | Rr | RR, Rr, Rr, rr |

This example shows the cross between two heterozygous parents (Rr), where R stands for a dominant allele and r for recessive, illustrating possible genetic outcomes.
Answer 5: Genetic Engineering and Its Impact

Genetic engineering refers to the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology:
- It includes techniques like gene splicing, where genes from one species are transferred to another.
- The applications range from creating disease-resistant crops to producing medicines or even gene therapies for humans.
- There are ethical considerations and debates about altering the genetic makeup of organisms.

🌿 Note: Genetic modification in agriculture can lead to crops with enhanced nutritional value or resistance to pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
To wrap up our deep dive into Bill Nye's genetics worksheet, we've explored the foundational aspects of genetics, the role of DNA, how traits are inherited, the significance of mutations, the utility of the Punnett Square, and the exciting field of genetic engineering. Understanding these concepts not only aids in solving genetics worksheets but also in appreciating the complexity and wonder of life itself. Whether you're teaching or learning, this knowledge equips you with the tools to make sense of the genetic world around us.
What is the difference between phenotype and genotype?

+
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, which determines its traits. Phenotype, on the other hand, is the physical or biochemical expression of those genes, including visible traits like eye color or height.
Can mutations always be inherited?
+
No, not all mutations are inheritable. Somatic mutations occur in body cells and aren’t passed to offspring, while germline mutations affect reproductive cells and can be inherited.
Why is genetic engineering controversial?

+
Genetic engineering raises ethical questions about modifying life forms, potential ecological impacts, long-term health effects, and the possibility of unintended genetic changes or outcomes.