Ancient Greece Worksheet Answer Key: Unlock History!

Ancient Greece is a period of history that offers us an incredible glimpse into the lives, achievements, and cultural contributions of a civilization that has profoundly influenced the modern world. From the development of democracy to the inception of Western philosophy, art, literature, and science, ancient Greece has left an indelible mark on history. For students and enthusiasts alike, diving into this rich history can be as exciting as solving a puzzle. Here, we present an Answer Key to a comprehensive worksheet on Ancient Greece, providing insights and detailed explanations to enhance your understanding of this fascinating era.
The Geography of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece's geography played a crucial role in shaping its civilization:
- Peninsulas and Islands: Greece is characterized by its rugged, mountainous landscape and numerous islands. This natural segmentation led to the development of city-states (poleis) like Athens, Sparta, Corinth, and Thebes, each with its own government and culture.
- Mountains: The Pindus mountain range separated the Greek peninsula, making land travel difficult, which in turn fostered naval prowess and trade via the sea.
- Climate: Greece's Mediterranean climate, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, influenced agricultural practices, and the timing of various festivals and activities.
🌍 Note: The geography of Greece was not just a backdrop but actively shaped its history, politics, and culture.
The Rise of City-States

The political fragmentation of Ancient Greece resulted in the rise of city-states, each with unique characteristics:
- Athens: Known for its democratic government, where citizens could vote on laws and issues. It was also the cultural hub with philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle.
- Sparta: Focused on military prowess and simplicity. Life in Sparta revolved around preparing for war, with its unique social system where all male citizens were soldiers.
- Corinth: Famous for its pottery, shipbuilding, and as a center of trade due to its strategic location.
| City-State | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Athens | Democracy, arts, philosophy |
| Sparta | Militaristic, communal living |
| Corinth | Trade, commerce, wealth |

Contributions to Culture and Knowledge

Ancient Greeks made lasting contributions to various fields:
- Philosophy: Pioneers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle laid down the foundations of Western philosophical thought, questioning ethics, politics, and metaphysics.
- Theatre and Literature: Sophocles, Euripides, and Aeschylus crafted tragedies, while comedies by Aristophanes satirized contemporary issues. Poetry, through figures like Homer and Hesiod, became an immortal literary treasure.
- Art: Greek sculptors sought perfection, capturing the human form in their iconic statues and architectural friezes.
- Science and Mathematics: The likes of Pythagoras and Archimedes made groundbreaking contributions to mathematics and physics.
Democracy: Its Birth in Athens
The concept of democracy was born in Athens around 508 BC. Key features included:
- Direct Democracy: All citizens had the right to attend the Ekklesia, the assembly where laws were debated and voted upon.
- Ostracism: A method to protect the democratic system by allowing citizens to vote to exile potentially dangerous individuals for 10 years.
- Legal equality: All citizens were equal before the law, although women, slaves, and foreigners were excluded.
🗳️ Note: While democratic, Athens' version excluded a large portion of its population from political participation, illustrating the complexities of ancient democracy.
Military and Naval Power

Ancient Greece's history is also a tale of military prowess:
- Hoplite Warfare: The Greeks developed the phalanx formation with heavily armored infantrymen known as hoplites.
- Naval Warfare: The trireme was a key warship, equipped with a ram to sink enemy vessels.
- Battles: Events like the Battle of Marathon, Thermopylae, and Salamis are testament to Greek military strategy and heroism.
In wrapping up this extensive guide to Ancient Greece, we've journeyed through its geographical influences, the rise of influential city-states, monumental cultural contributions, and the genesis of democracy. The keys provided here are meant to deepen your comprehension of this dynamic period, where every stone, battle, and idea has shaped the world we know today.
What made Athens’ democracy unique?

+
Athens’ democracy was unique because it was direct; citizens had the right to participate directly in legislative decisions, unlike modern representative democracies. However, participation was limited to free, adult male citizens.
How did the geography of Greece influence its history?
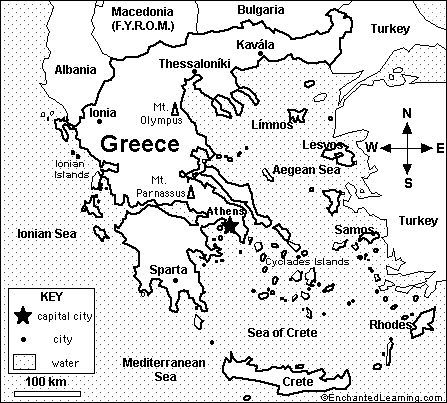
+
The rugged terrain, including mountains and numerous islands, led to the development of independent city-states, fostering diversity and competition, which in turn influenced trade, warfare, and cultural development.
Were all contributions from Ancient Greece positive?

+
While Ancient Greece gave us invaluable cultural and intellectual contributions, it also had negative aspects, such as slavery, gender inequality, and exclusionary citizenship laws.


