1812 Napoleonic Europe Map Worksheet Solutions Revealed

Dive into the rich historical tapestry of Europe during the Napoleonic Era with our comprehensive worksheet solutions!
Introduction to Napoleonic Europe

Welcome to an enthralling journey through Napoleonic Europe. This era, marked by the expansive influence of Napoleon Bonaparte, provides historians and enthusiasts with a complex map of shifting alliances, battles, and territorial changes. Our focus today will be on decoding the intricate details of this period through a meticulously prepared 1812 Napoleonic Europe Map Worksheet.

Understanding the Map's Components

To delve into the solutions of the map worksheet, let's first understand its components:
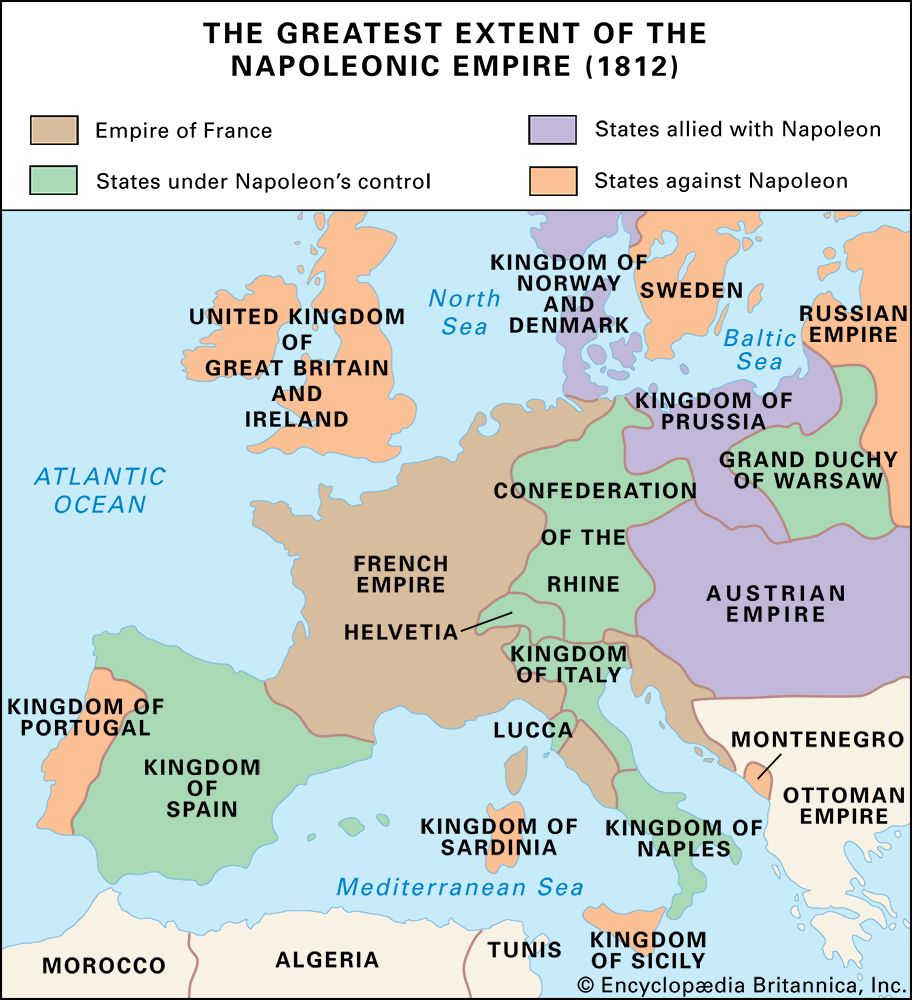
- Boundaries and Territories: Each kingdom, duchy, or republic is uniquely identified through various colors and shading to represent the control under Napoleon and other ruling factions.
- Military Campaigns: Arrows and symbols illustrate Napoleon's conquests, his retreat, and the coalitions formed against him.
- Historical Context: Timelines and annotated notes provide context to the major events shaping this era.
Solutions to Worksheet Questions
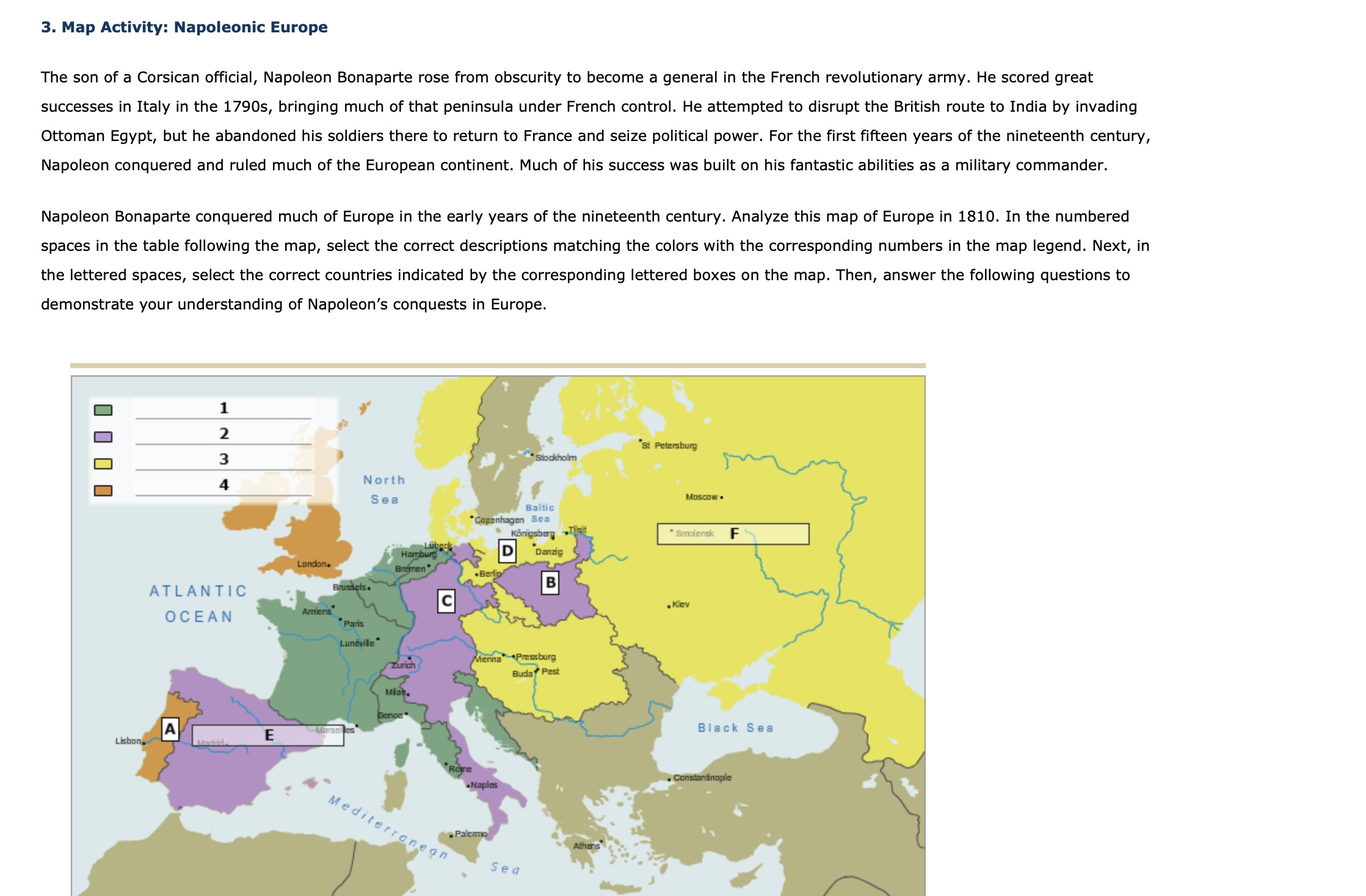
Which Major Powers Controlled Territories in 1812?

Here is an overview:
| Power | Territory |
|---|---|
| France | Spain, Belgium, The Netherlands, parts of Germany |
| Austria | Parts of Italy, Austria, Bohemia |
| Russia | Vast regions of Eastern Europe |
| Prussia | Some parts of Germany |
| United Kingdom | Maritime supremacy, allied control in Spain |

Napoleon's 1812 Invasion of Russia

- Objective: To force Russia back into the Continental System, crippling British trade.
- Route: Napoleon's path led him from the Duchy of Warsaw, through Poland, and toward Moscow.
- Aftermath: The catastrophic retreat from Moscow, with the French army facing severe losses due to Russian tactics and harsh winter conditions.
🔍 Note: This campaign marked the beginning of Napoleon's downfall, influencing subsequent power dynamics in Europe.
Identify Coalitions Against Napoleon

There were several coalitions formed to counter Napoleon's ambitions:
- The Third Coalition: Formed in 1805 by the United Kingdom, Russia, Austria, Sweden, and others.
- The Fourth Coalition: In 1806, including Prussia, Russia, Saxony, and others.
- The Fifth Coalition: Austria, United Kingdom, Portugal, and Spain in 1809.
- The Sixth Coalition: This coalition, formed in 1812, eventually led to Napoleon's abdication in 1814.
Territorial Changes and Their Significance

- The Confederation of the Rhine: Created in 1806, it bound German states to Napoleon's France, weakening the Holy Roman Empire.
- The Grand Duchy of Warsaw: Established after the Third Coalition's defeat, it served as a buffer against Russian expansion.
- Spain's Peninsular War: The uprising in Spain led to prolonged conflicts, drawing French forces away from other fronts.
Evaluating Historical Impact

By examining this map worksheet, we can see how:
- Napoleon's military ambition reshaped European politics, influencing the formation of modern nations.
- The erosion of the old regimes led to a rise in nationalism and political change.
- The constant warfare led to significant economic and human costs, setting the stage for future conflicts.
To sum up, the exploration of the 1812 Napoleonic Europe Map Worksheet reveals not just historical boundaries and battles but the intricate web of diplomatic relations, alliances, and resistance movements that defined this tumultuous period. Each question answered delves into a rich narrative of European history, where power dynamics, territorial shifts, and the legacy of Napoleon Bonaparte's reign continue to resonate in our understanding of European geopolitics today.
Why was the invasion of Russia in 1812 significant?

+
The invasion of Russia marked the beginning of the end for Napoleon. His failure to subdue Russia and the subsequent retreat with heavy losses weakened his military power and influenced his allies to turn against him.
What was the aim of the Continental System?
+
The Continental System was an embargo imposed by Napoleon against British trade to weaken its economy. Its aim was to isolate Great Britain economically, but its inconsistent enforcement led to dissatisfaction among European states.
How did the Peninsular War influence Napoleon’s strategy?

+
The Peninsular War drained French resources due to guerrilla warfare and British support for Spanish and Portuguese resistance. This protracted conflict forced Napoleon to spread his forces thin, weakening his ability to consolidate power in central and Eastern Europe.