Force Units Explained
Introduction to Force Units

Force is a measure of the push or pull that causes an object to change its state of motion. It is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and understanding the units of force is crucial for calculating and analyzing various physical phenomena. In this article, we will delve into the world of force units, exploring the different types, their applications, and the conversions between them.
Types of Force Units

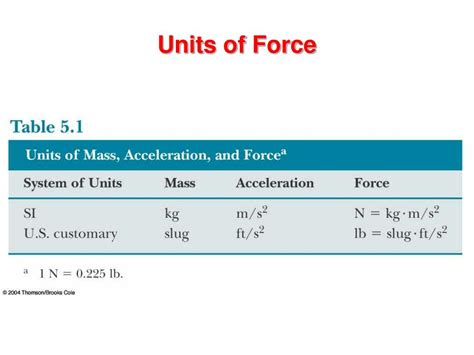
There are several types of force units, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common force units include: * Newton (N): The Newton is the standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1-kilogram object by 1 meter per second squared. * Pound-force (lbf): The pound-force is a unit of force commonly used in the United States and other countries that have not adopted the SI system. It is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1-pound object by 1 foot per second squared. * Kilopond (kp): The kilopond is a unit of force that is equal to the weight of a 1-kilogram object under standard gravity conditions. * Dyne (dyn): The dyne is a unit of force that is equal to the force required to accelerate a 1-gram object by 1 centimeter per second squared.
Applications of Force Units

Force units have a wide range of applications in various fields, including: * Physics and Engineering: Force units are used to calculate and analyze the motion of objects, the stress and strain on materials, and the energy transferred between systems. * Construction and Architecture: Force units are used to calculate the loads and stresses on buildings, bridges, and other structures. * Mechanical Engineering: Force units are used to design and optimize mechanical systems, such as engines, gears, and linkages. * Biomechanics: Force units are used to study the movement and forces exerted by living organisms, such as the human body.
Conversions Between Force Units
Converting between different force units is essential for ensuring accuracy and consistency in calculations. The following table shows the conversions between some common force units:
| Force Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| 1 Newton (N) | 0.2248 pound-force (lbf) |
| 1 Pound-force (lbf) | 4.4482 Newton (N) |
| 1 Kilopond (kp) | 9.8067 Newton (N) |
| 1 Dyne (dyn) | 0.00001 Newton (N) |

💡 Note: When converting between force units, it is essential to consider the context and the specific application to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Best Practices for Working with Force Units

When working with force units, it is essential to follow best practices to ensure accuracy and consistency. Some tips include: * Always specify the unit of force when reporting measurements or calculations. * Use the correct conversion factors when converting between different force units. * Consider the context and application when selecting a force unit. * Use bold or italic text to highlight important information, such as the unit of force.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

When working with force units, there are several common mistakes to avoid, including: * Inconsistent units: Using inconsistent units can lead to errors and inaccuracies in calculations. * Incorrect conversions: Using incorrect conversion factors can lead to errors and inaccuracies in calculations. * Lack of specificity: Failing to specify the unit of force can lead to confusion and errors.
In summary, force units are a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and understanding the different types, applications, and conversions between them is crucial for accurate calculations and analysis. By following best practices and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure accuracy and consistency in your work with force units.
What is the standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI)?

+
The standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) is the Newton (N).
How do I convert between different force units?

+
To convert between different force units, use the conversion factors provided in the table above.
What are some common applications of force units?
+
Force units have a wide range of applications, including physics and engineering, construction and architecture, mechanical engineering, and biomechanics.