5 Tips for Understanding the Skin Coloring Worksheet

The practice of skin coloring in art and anatomy classes can be an excellent method to learn about the complex structure and diversity of human skin. Understanding a Skin Coloring Worksheet involves both artistic finesse and a keen appreciation of anatomy. Here are five tips to help you excel in this fascinating exercise:
1. Understand Skin Anatomy
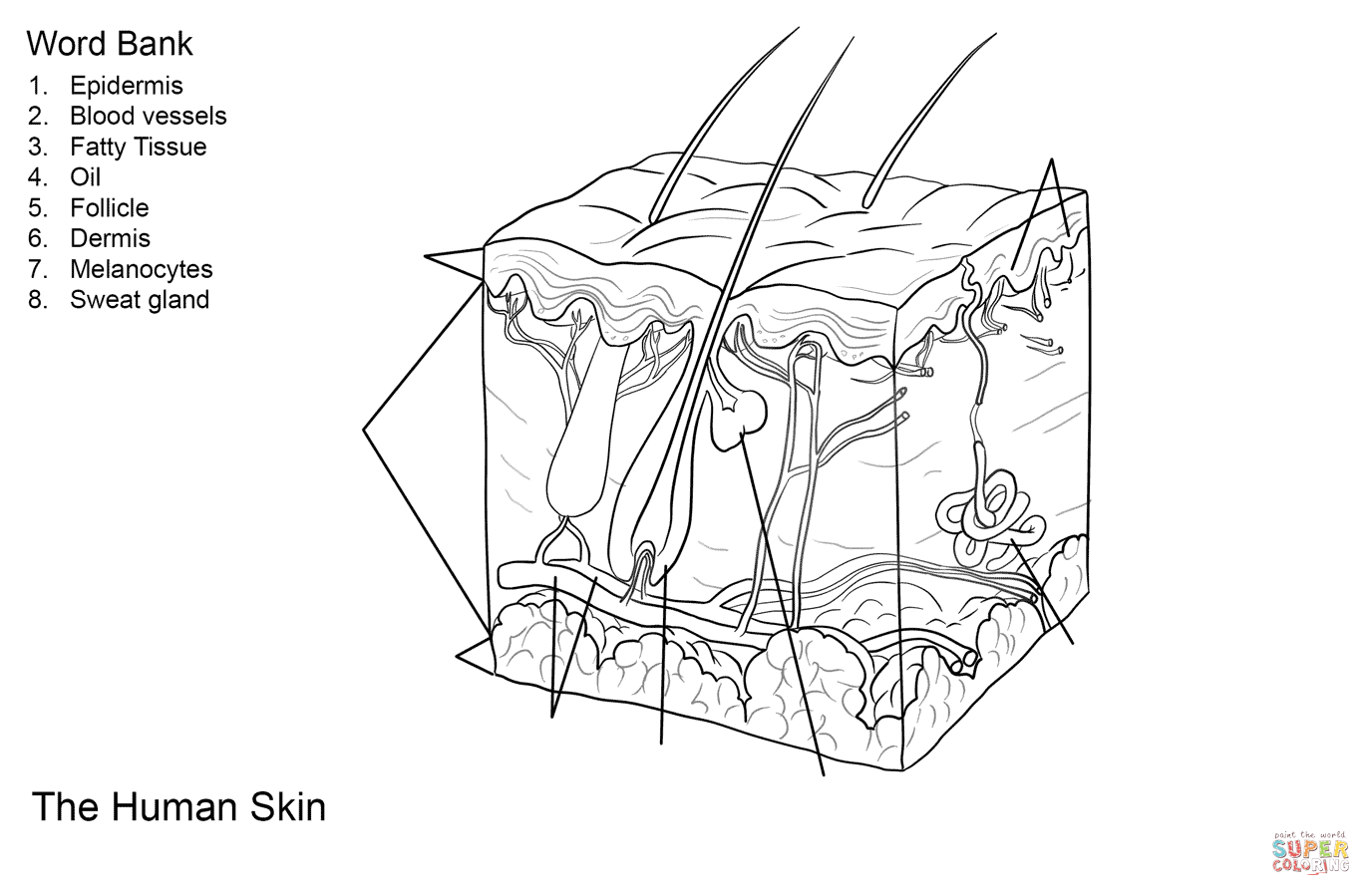
The first step in mastering skin coloring is grasping the basic anatomy of skin. Skin has three main layers:
- Epidermis: This top layer varies in thickness across the body. It contains melanin, which gives skin its color, and has a glossy appearance due to its composition.
- Dermis: Beneath the epidermis, this layer contains blood vessels, nerves, and structures like hair follicles. It affects skin color indirectly through the visibility of blood beneath the surface.
- Hypodermis: While not often colored in basic worksheets, knowing its composition helps understand how skin interacts with underlying muscle and fat.

2. Learn the Color Theory for Skin

Skin coloring isn’t just about painting it in brown or pink shades. Here’s how to approach color:
- Base Color: Choose your base color according to the skin tone you’re depicting. This can range from very light to deep dark.
- Undertones: Use warm (yellow, peach) or cool (blue, purple) undertones to add realism. Undertones are subtle and vary with individual skin color.
- Blending: Blending skin colors requires understanding light, shadow, and translucency. Use different brush techniques to simulate this.
3. Practice Layering Techniques
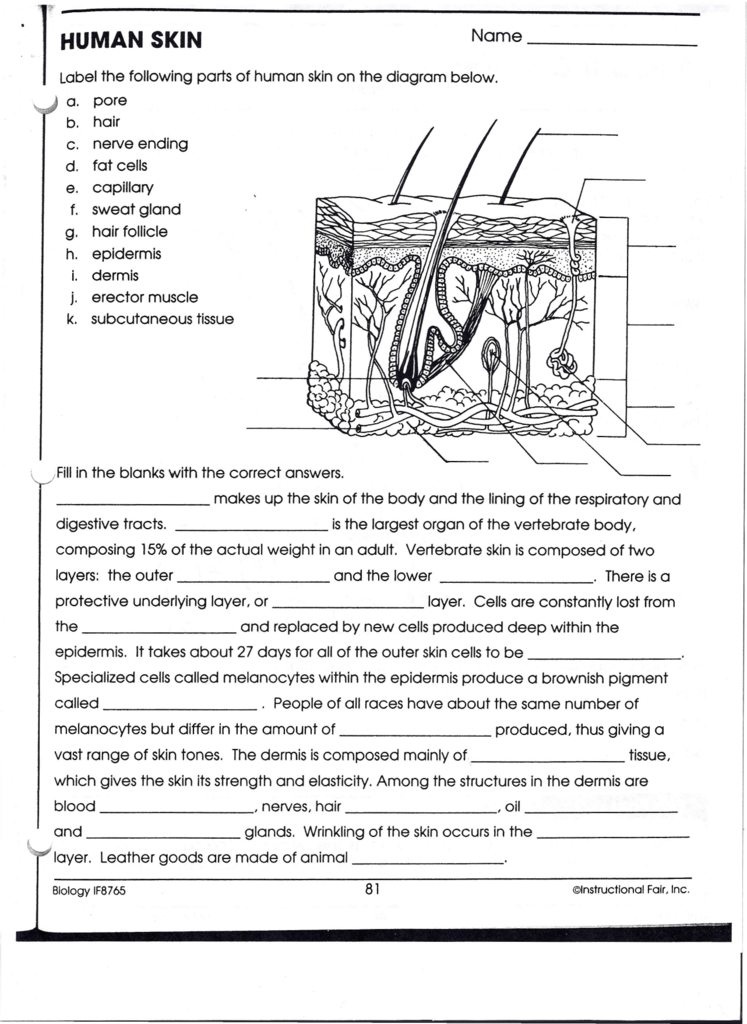
Layering is key in skin coloring:
- Translucency: Skin is somewhat translucent, so underlayers of color must be visible through the top layer, creating depth.
- Detailing: Add freckles, moles, and other skin imperfections to make the coloring more realistic.
💡 Note: For digital coloring, use layers to build up the skin color gradually for more control.
4. Use Reference Material

Even if you’re not copying, references help understand how light interacts with different skin types:
- Photographs: Use high-quality images to study skin under various lighting conditions.
- Live Models: If possible, observe how real skin looks in person. Notice how colors change with age, sunlight, and health.

5. Experiment with Mediums and Tools

Each medium from pencils to paint reacts differently:
- Pencils: Colored pencils can give you great control over detail and texture.
- Paints: Watercolor, acrylic, and oil paints can blend smoothly to create realistic skin textures.
- Digital Tools: Tablets and software offer limitless possibilities for layering and effects.
| Medium | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pencil |
|
|
| Paint |
|
|
| Digital |
|
|

By mastering these techniques, not only will you improve your skin coloring skills, but you'll also develop a deeper understanding of the human form. This knowledge enriches both your art and your appreciation of the complexity of skin. Remember, it's a skill that requires practice, patience, and an open mind for experimentation.
Why is understanding skin anatomy important for coloring?

+
Understanding skin anatomy helps in accurately depicting the nuances of skin coloration, texture, and how light affects different skin layers, making the artwork more lifelike.
How can blending be achieved in skin coloring?

+
Blending can be achieved through various techniques like using soft brushes, layers in digital art, or blending tools like tortillons for pencils and blending mediums in paint to create smooth transitions in skin color.
Can I practice skin coloring without formal training?

+
Yes, with dedication and by studying references, anyone can practice and improve skin coloring. It’s beneficial to learn basic anatomy and color theory, but self-taught methods are also effective.



