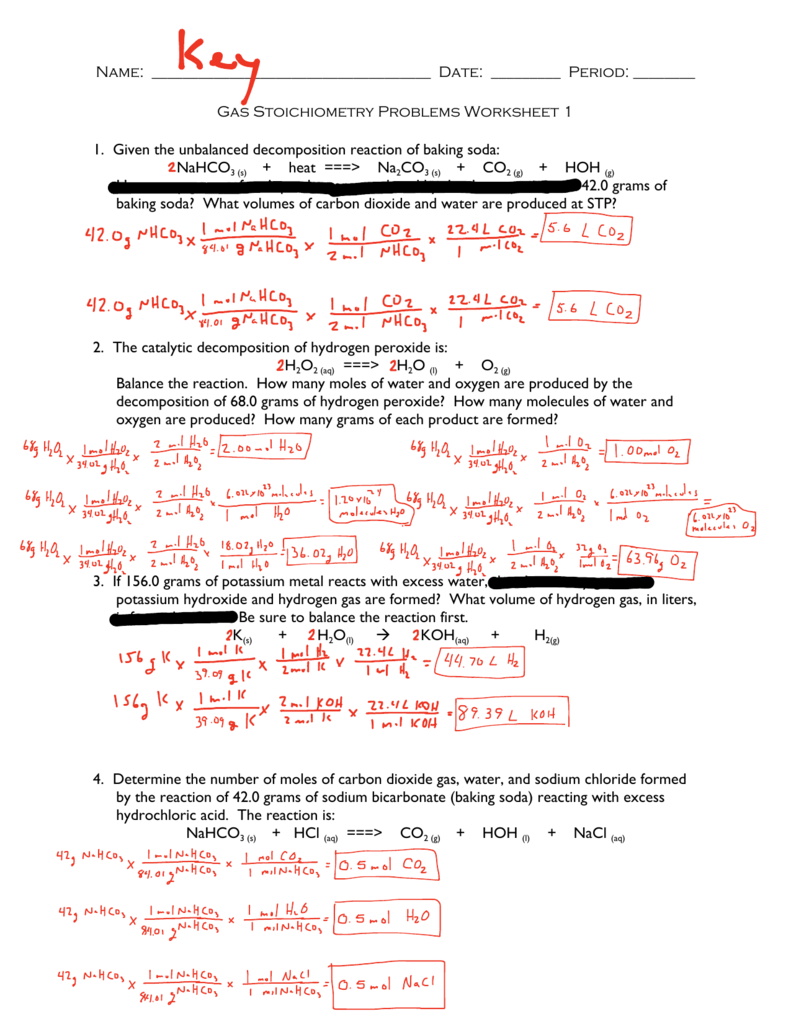Supply Curve Worksheet Answer Key: Simplified Economics Guide

The Supply Curve in economics provides a framework to understand how much of a product producers are willing to offer for sale at different price points. This fundamental concept helps predict changes in market behavior, informs businesses' production decisions, and plays a pivotal role in shaping economic policy. Let's dive into a detailed exploration of the supply curve through an accessible worksheet, demystifying economics for students and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding the Basics of the Supply Curve

A supply curve is a graphical representation that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied by producers. Here are the key points to understand:
- Positive Slope: The supply curve typically slopes upward from left to right, indicating that as the price increases, producers are willing to supply more of the good.
- Determinants of Supply: Factors that can shift the supply curve include technology, input prices, taxes, subsidies, expectations, and the number of suppliers.
- Equilibrium: The point where the supply curve meets the demand curve represents market equilibrium, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.

Worksheet: Understanding and Analyzing Supply Curves

Let's break down the supply curve through a worksheet designed to enhance your understanding:
Exercise 1: Identifying Movements Along the Supply Curve
Given the following data, identify how a change in price affects the quantity supplied:
| Price ($) | Quantity Supplied |
|---|---|
| 5 | 100 |
| 10 | 200 |
| 15 | 300 |

When the price moves from $5 to $10:
- The quantity supplied increases from 100 to 200 units.
When the price moves from $10 to $15:
- The quantity supplied increases from 200 to 300 units.
📝 Note: This illustrates the law of supply where an increase in price leads to an increase in quantity supplied, assuming other factors remain constant.
Exercise 2: Supply Curve Shifts

Analyze the following scenarios and determine if they cause a shift in the supply curve:
- Scenario A: A new technology increases efficiency in production.
- Scenario B: Prices of inputs rise due to inflation.
- Scenario C: A government imposes a tax on the product.
Results:
- Scenario A: This would shift the supply curve to the right, indicating an increase in supply at each price level.
- Scenario B: The supply curve shifts left, showing a decrease in supply because production costs have gone up.
- Scenario C: The supply curve shifts to the left as the tax increases the cost of production, leading to lower supply at each price level.
Incorporating SEO for Better Reach

Understanding and optimizing content for search engines can significantly enhance visibility:
- Use keywords like "supply curve economics," "supply curve shift," and "law of supply" naturally within the text.
- Structure content with headings, subheadings, and lists to make it easy for both readers and search engines to navigate.
- Ensure that the information is accurate and authoritative, fostering trust and encouraging further reading and backlinks.
Exercise 3: Application of Supply Curve Principles

Consider a hypothetical case where:
- A new factory opens, increasing market supply.
- Climate change affects crop yields, reducing the supply of agricultural products.
Answer:
- The new factory would shift the supply curve to the right, lowering prices and increasing market quantity supplied.
- The reduction in crop yield due to climate change would shift the supply curve leftwards, leading to higher prices and reduced quantity supplied.
🌍 Note: These examples illustrate how real-world events can impact the supply curve, affecting both consumers and producers.
Summing Up Key Insights

Through this worksheet, we've explored how the supply curve helps economists and market analysts understand production behavior, market dynamics, and policy impacts. We learned about the law of supply, how changes in various factors shift the supply curve, and how these shifts can have profound effects on prices and quantities in the market. By applying these concepts, businesses can make informed decisions, governments can craft effective economic policies, and consumers can better understand market fluctuations.
What does it mean when the supply curve shifts?

+
A shift in the supply curve means that the relationship between price and quantity supplied has changed. A rightward shift (increase in supply) indicates that producers are willing to supply more at each price level due to favorable changes in determinants of supply. Conversely, a leftward shift (decrease in supply) shows that producers supply less at each price due to unfavorable changes.
Why is the supply curve upward sloping?

+
The supply curve slopes upward because as the price of a good rises, producers are incentivized to increase production. This is due to the law of supply, where higher prices encourage more output to maximize profit.
How can government policy affect the supply curve?
+
Government policies like taxes, subsidies, regulations, or incentives can directly impact production costs or the willingness of producers to enter the market. For example, a subsidy reduces production costs, shifting the supply curve to the right, while a new tax increases costs, shifting it left.