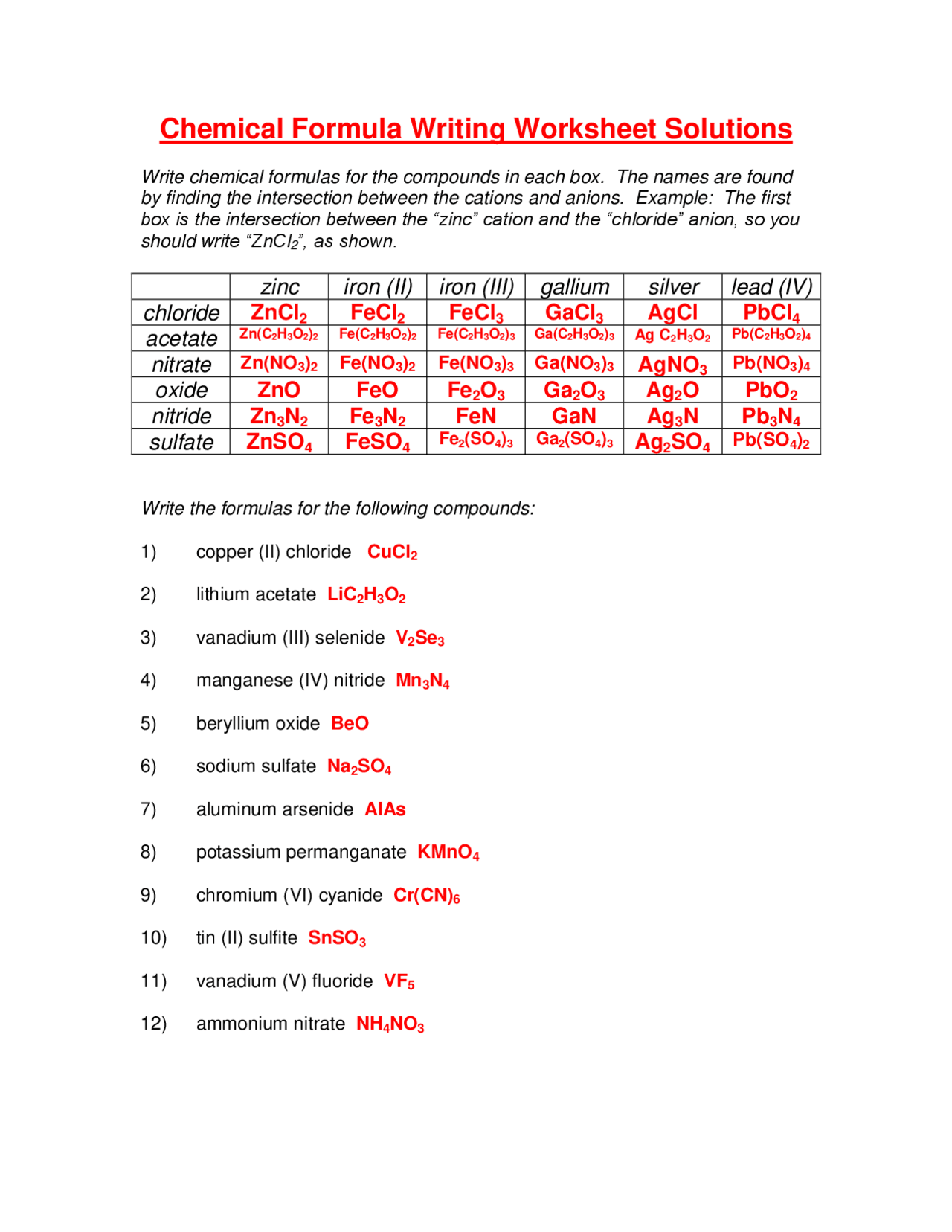
Stoichiometry Made Simple: 5-Step Worksheet Guide

Understanding Stoichiometry

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on stoichiometry, a fundamental part of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships in chemical reactions. Whether you’re a high school student or someone delving into chemistry for various reasons, understanding stoichiometry can seem daunting, but fear not! With this step-by-step worksheet guide, you’ll find that stoichiometry can indeed be made simple.

Step 1: Write and Balance the Equation

Every stoichiometric calculation starts with a balanced chemical equation. Here are the steps you should follow:
- Identify the reactants and products in your chemical reaction.
- Write down the skeleton equation using chemical formulas.
- Balance the equation by adjusting the coefficients to ensure the law of conservation of mass holds true. Remember, you cannot change the subscripts, only the coefficients.
Example:

Consider the reaction between methane (CH4) and oxygen (O2) to form carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- Reactants: CH4 and O2
- Products: CO2 and H2O
- Unbalanced equation: CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
- Balanced equation: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
🔍 Note: Balancing chemical equations is critical. An unbalanced equation can lead to incorrect stoichiometric calculations.
Step 2: Identify the Mole Ratio

From the balanced equation, you can determine the mole ratio of reactants and products:
- Use the coefficients to find the number of moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
- This ratio will be used in subsequent steps for calculating amounts.
Continuing with the example:

- Mole Ratio of CH4 : O2 : CO2 : H2O is 1:2:1:2
Step 3: Use Molar Mass to Convert to Grams
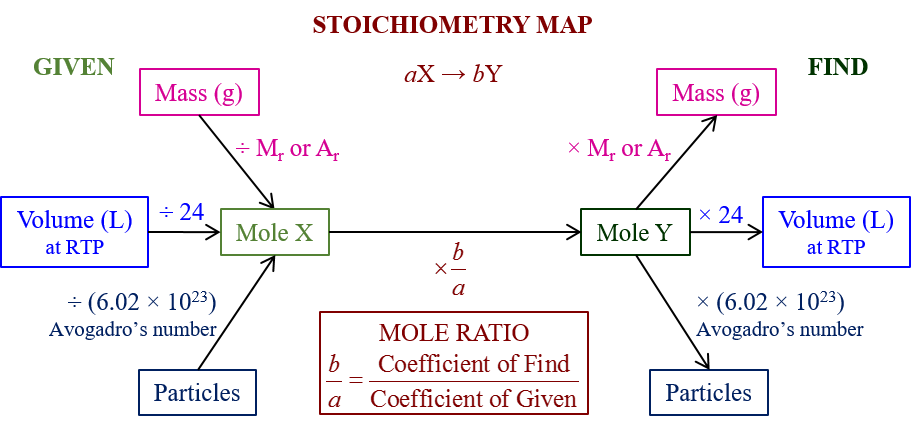
To connect the theoretical calculations to practical measurements, you’ll need to convert moles into grams or vice versa using molar mass:
- Determine the molar mass for each compound using the periodic table.
- Convert the moles to grams or grams to moles using this molar mass.
| Compound | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|
| CH4 | 16.043 |
| O2 | 32.00 |
| CO2 | 44.01 |
| H2O | 18.015 |

Step 4: Apply the Mole Concept to Stoichiometric Problems

This is where stoichiometry truly comes into play. Here’s how to use the mole ratio to solve problems:
- Given the amount of one reactant or product, use the mole ratio from Step 2 to find the amount of others involved.
- Remember, you’ll need to work with moles rather than grams or volumes directly.
Example Problem:
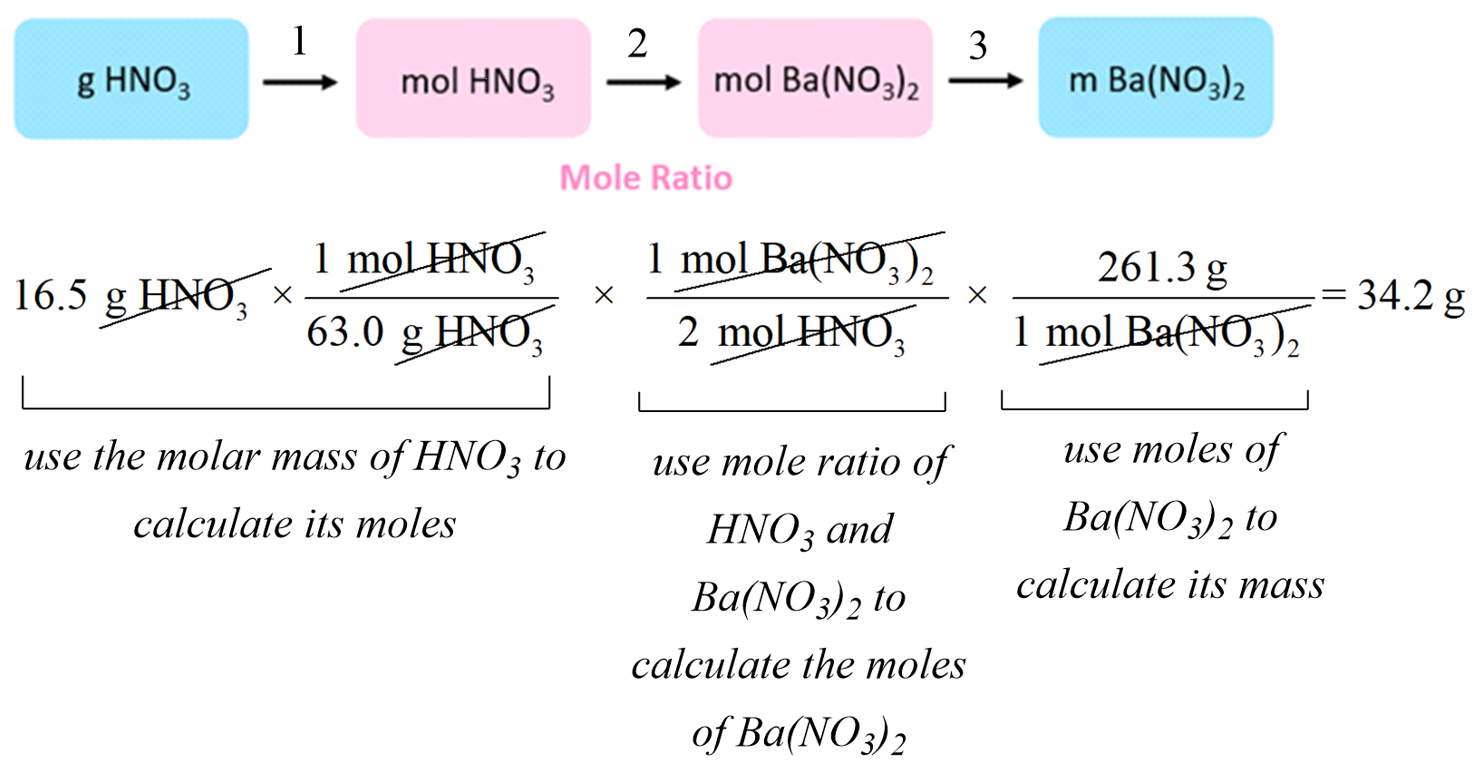
How many moles of CO2 would be produced if 4 moles of O2 react?
- Using the mole ratio: 2 moles of O2 yield 1 mole of CO2
- For 4 moles of O2 : (4 mol O2 x 1 mol CO2 / 2 mol O2) = 2 moles of CO2
⚗️ Note: Stoichiometry calculations assume the reaction goes to completion, which might not always happen in real conditions.
Step 5: Solve for Mass or Volume

Often, you’ll need to solve for actual quantities, not just moles:
- Convert the moles back into grams or liters if the problem requires.
- Use the stoichiometric ratio and molar mass for conversions.
Example:

Find the mass of CO2 produced from the same 4 moles of O2.
- From Step 4, 2 moles of CO2 are produced.
- Using the molar mass of CO2: 2 mol x 44.01 g/mol = 88.02 grams of CO2.
The Simplified Stoichiometry Worksheet
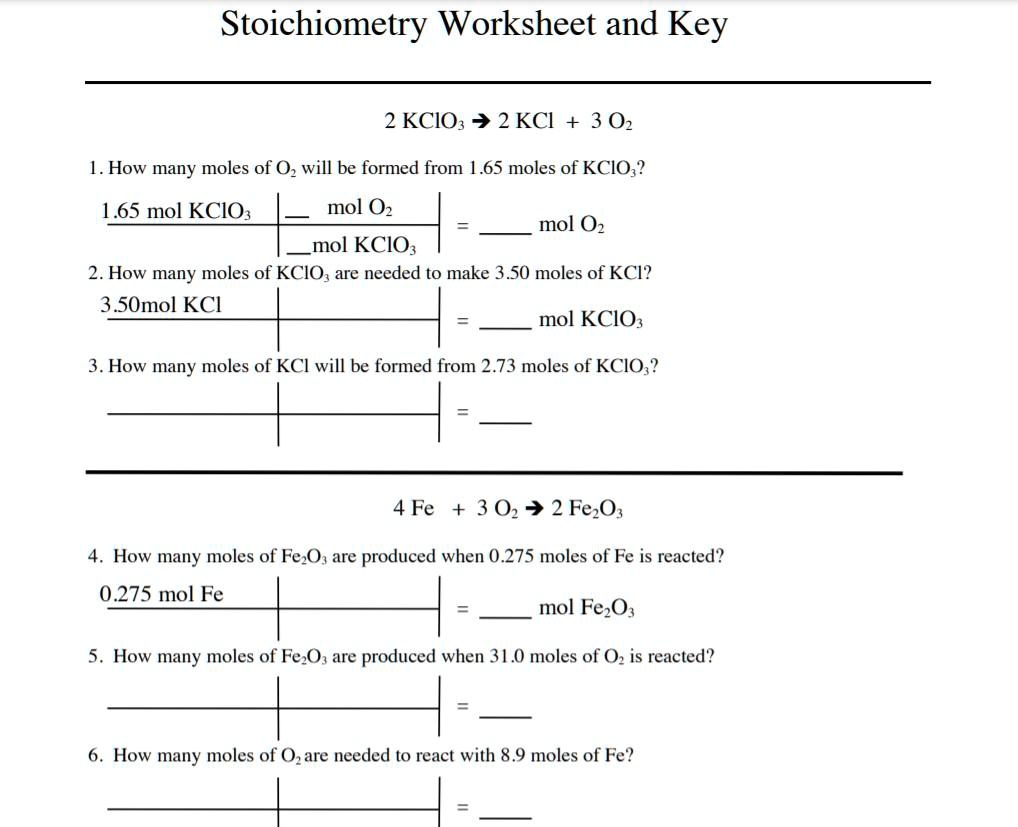
To make your learning experience smoother, here’s a simple worksheet that summarizes the steps:
- Write and balance the chemical equation.
- Identify the mole ratios from the balanced equation.
- Calculate the molar mass of each compound involved.
- Use the mole ratio to solve stoichiometric problems.
- Convert moles to mass or volume as required by the problem.
In mastering the art of stoichiometry, you've now got a structured approach that simplifies complex calculations into manageable steps. This guide is not only about finding answers but understanding why and how these calculations work, making chemistry accessible and less intimidating.
Why is balancing chemical equations so important in stoichiometry?

+
Balancing equations ensures that the law of conservation of mass is respected, where the number of atoms of each element in the reactants equals the number in the products. This is critical for stoichiometry because the coefficients provide the mole ratios needed for calculations.
Can I change the subscripts while balancing the equation?

+
No, you must not change the subscripts. The subscripts indicate the actual composition of the compound, and changing them alters the chemical identity. Only coefficients, which show the amount of each compound, can be modified during balancing.
How do I know if my calculations are correct?

+
To verify your calculations, make sure you have balanced the equation correctly, used the proper molar mass values, and applied the correct mole ratio. Also, cross-check your results with unit conversions to ensure that dimensions align as expected.