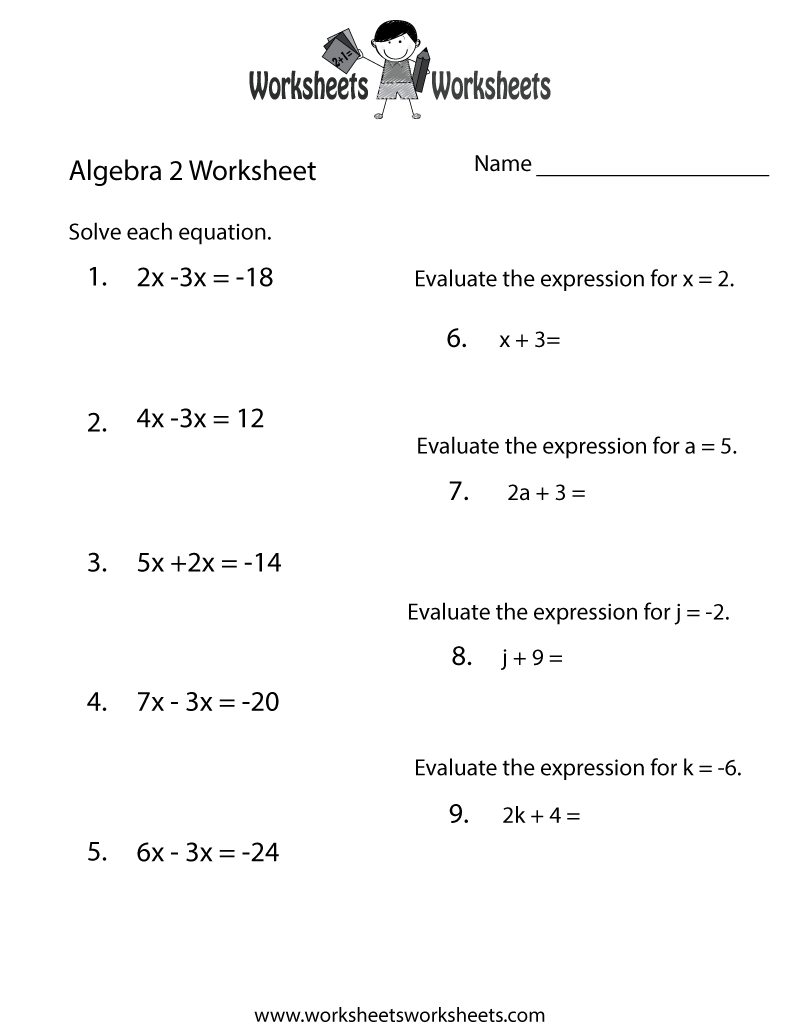
Stoichiometry Worksheet: Master Calculations with Ease

Learning stoichiometry might feel overwhelming initially, but with the right tools and practice, you can quickly get the hang of it. Whether you're a high school student gearing up for a chemistry exam or a college undergraduate delving into the complexities of chemical reactions, mastering stoichiometry is essential for success in chemistry. Let's dive into a step-by-step guide on how you can tackle stoichiometry problems effectively using a worksheet, and help you turn those complex chemical equations into manageable calculations.
The Basics of Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions. It's based on the law of conservation of mass, where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products. Here’s a brief overview:
- Balanced Chemical Equations: The foundation of stoichiometric calculations.
- Molar Ratios: Derived from coefficients in balanced equations, these ratios help in quantifying reactants and products.
- Molar Mass: Essential for converting between moles and grams of substances.
The Importance of Stoichiometry Worksheets

Stoichiometry worksheets are vital learning tools that:
- Promote Understanding: They force students to apply concepts learned in class to real problems.
- Enhance Problem-Solving Skills: Regular practice with these problems sharpens one's ability to analyze and solve complex calculations.
- Provide Practice: Repetition through worksheets helps in understanding the principles of stoichiometry better.
How to Use a Stoichiometry Worksheet

Step 1: Balancing the Chemical Equation

Before you start calculations, ensure the chemical equation is balanced. For example:
Original Equation: CH_4 + O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 + H_2O
Balanced Equation: CH_4 + 2O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 + 2H_2O
Step 2: Determine the Moles

Using the balanced equation, determine the moles of each reactant or product. If you have grams:
- Convert grams to moles using molar mass.
- Use molar ratios from the balanced equation to find moles of other substances.
Step 3: Apply the Molar Ratios

Use the stoichiometric coefficients to find the moles of the desired substance. Here’s how:
- If you have 5 moles of (CH_4), how many moles of (CO_2) will be produced? (5 \text{ moles } CH_4 \times \frac{1 \text{ mole } CO_2}{1 \text{ mole } CH_4} = 5 \text{ moles } CO_2)
Step 4: Convert Back to Grams

Once you have the moles, convert back to grams if needed:
- Moles (CO_2 = 5 \text{ moles } \times \text{ Molar Mass of } CO_2 = 5 \text{ moles } \times 44.01 \text{ g/mol} = 220.05 \text{ g } CO_2)
Step 5: Review and Check Your Work

Go through each step, ensuring your units cancel out correctly and your calculations are accurate:
🔎 Note: Always round off your answers to an appropriate number of significant figures to match your given data.
Common Stoichiometry Problems and Their Solutions

Let's look at some common types of problems you might encounter:
Mass to Mass Stoichiometry

Converting from the mass of one reactant to the mass of another reactant or product:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the mass of (CO_2) produced from 45 g of (C_3H_8). |
|

Limiting Reactant and Excess Reactant
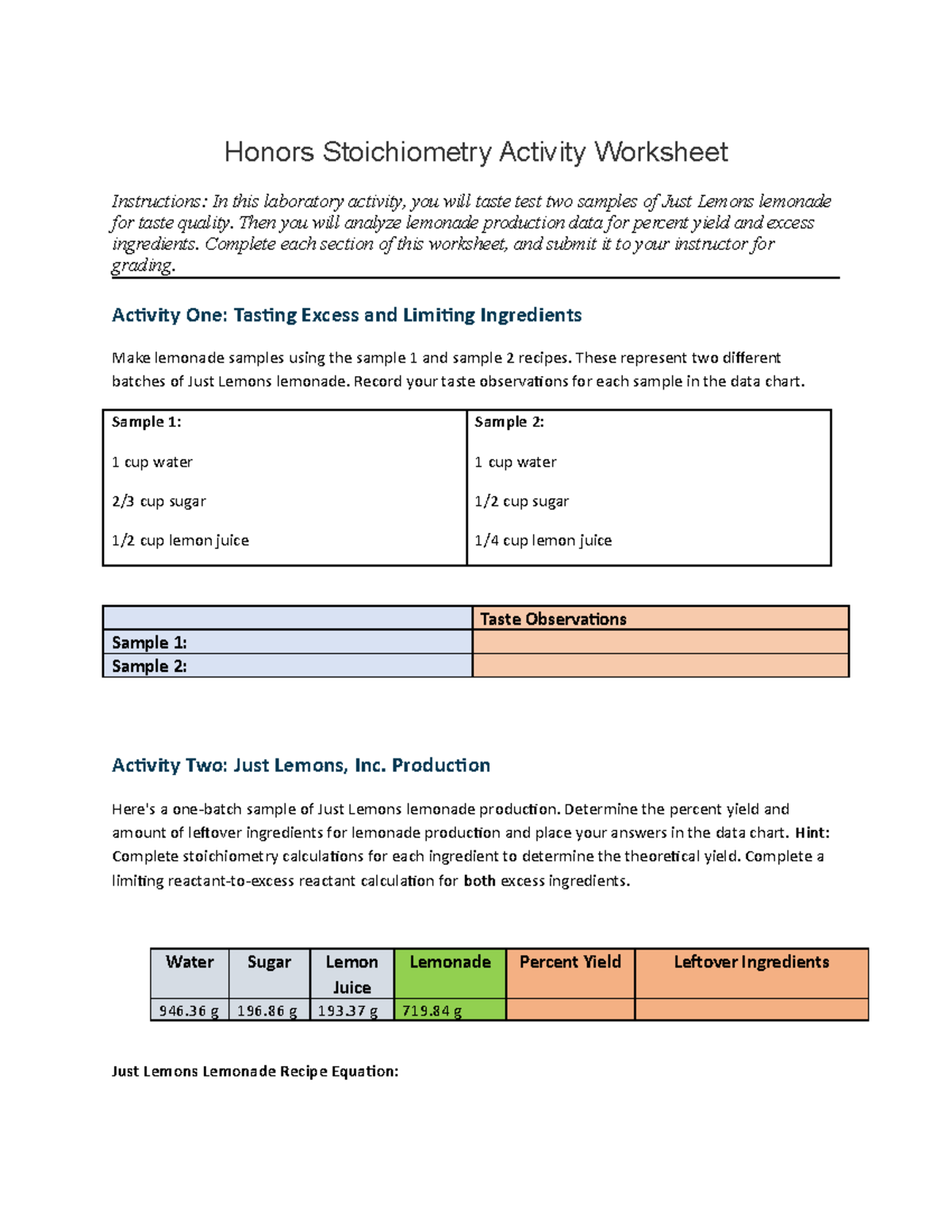
In reactions with multiple reactants, the limiting reactant is the one that runs out first, dictating how much product can form:
🔎 Note: The limiting reactant determines the yield of the product, while the excess reactant remains after the reaction is complete.
Percent Yield
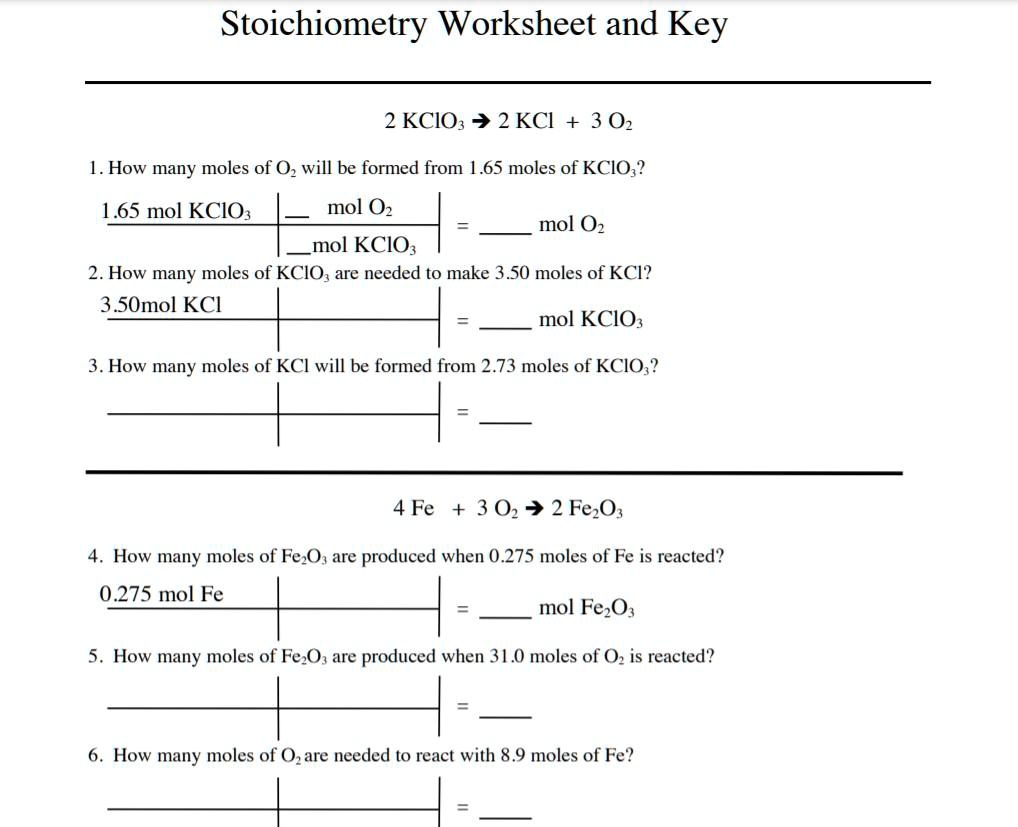
Theoretical yield vs. actual yield helps in understanding the efficiency of the chemical reaction:
- Theoretical Yield: The amount of product formed when the limiting reactant is completely consumed.
- Actual Yield: The amount of product actually obtained from the reaction.
- Calculate Percent Yield: (\frac{\text{Actual Yield}}{\text{Theoretical Yield}} \times 100\%)
Enhancing Your Stoichiometry Skills

To become proficient in stoichiometry, consider the following strategies:
- Practice Regularly: The more problems you solve, the more comfortable you'll become with the calculations.
- Understand Each Step: Don't just solve for the answers; understand why each step is necessary.
- Use Molar Ratios Effectively: These ratios are key to successful stoichiometry calculations.
- Check Your Work: Always review your calculations, checking for unit cancellation and correct significant figures.
What is stoichiometry?

+
Stoichiometry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It involves using balanced chemical equations to determine the amount of reactants required or the amount of products formed.
How can I find the limiting reactant?

+
To find the limiting reactant, calculate how much product each reactant would produce if it were consumed completely. The reactant that produces the least amount of product is the limiting reactant.
Why is percent yield important in stoichiometry?
+Percent yield compares the amount of product obtained in a reaction to the maximum amount theoretically possible. It provides insight into the efficiency of the chemical process, allowing chemists to improve reactions for better yield.