Codominance And Incomplete Dominance Worksheet Answer Key

Understanding the principles of inheritance in biology involves recognizing patterns such as codominance and incomplete dominance. These phenomena illustrate how traits are inherited and expressed differently from the classical Mendelian genetics. Here, we will delve into these genetic concepts, providing explanations, examples, and a detailed worksheet answer key to help grasp these intriguing aspects of genetics.
What is Codominance?


Codominance occurs when both alleles at a locus are expressed in the phenotype of an individual. This means neither allele is dominant over the other; instead, both contribute to the final trait:
- Blood Type: In humans, ABO blood groups exhibit codominance. When someone inherits one allele for the A blood group and one for the B blood group, their blood type is AB, where both A and B antigens are present on the red blood cells.
- Shorthorn Cattle: Roan cattle display this when they have patches of both red and white hair, reflecting the coat colors of both parents.
What is Incomplete Dominance?

In incomplete dominance, the heterozygote displays a phenotype that is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes. Here, neither allele completely masks the effect of the other:
- Snapdragons: A cross between a red-flowered snapdragon (RR) and a white-flowered one (WW) results in offspring with pink flowers (RW).
- Andalusian Fowl: When blue Andalusian fowl, which are heterozygous, are bred, the result includes black (BB), blue (BW), and white (WW) birds, with blue showing an incomplete dominance over both.
Codominance and Incomplete Dominance Worksheet

Below is a worksheet with questions related to codominance and incomplete dominance, followed by an answer key:
Worksheet
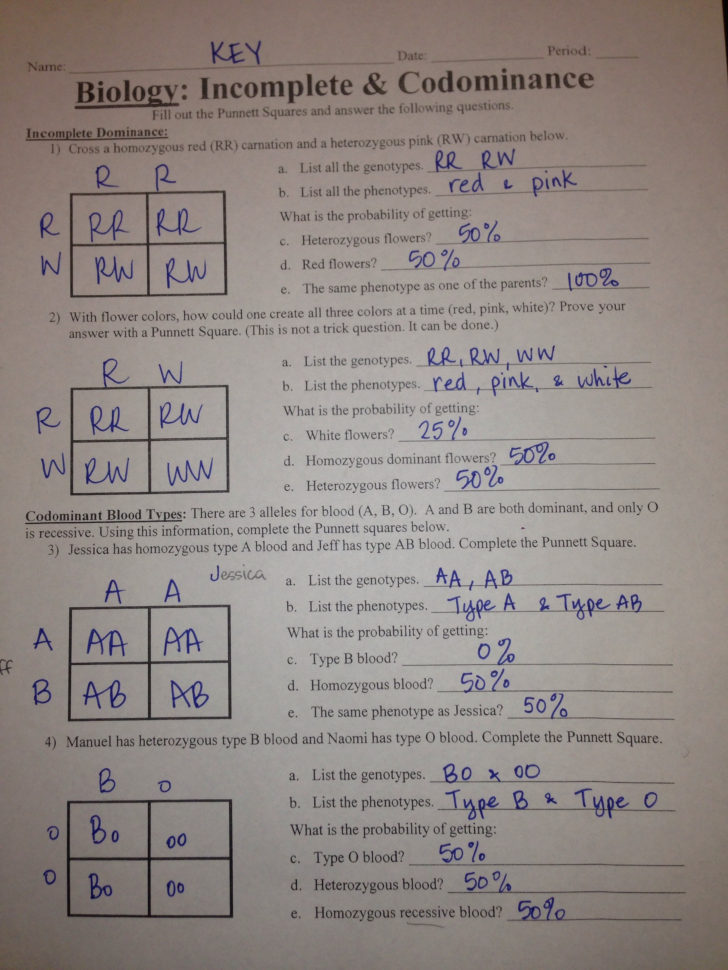
1. What are the phenotypes of the following matings for codominance in shorthorn cattle? - RR (red) x WW (white) - RW (roan) x RW (roan)
2. Snapdragon flowers follow incomplete dominance. What would be the phenotypes of the progeny from a cross between pink (RW) and white (WW) snapdragons?
3. A man with AB blood type marries a woman with B blood type whose father was type O. What are the possible blood types for their children?
Answer Key

1. Shorthorn Cattle:
- RR x WW: 100% RW (roan)
- RW x RW: 25% RR (red), 50% RW (roan), 25% WW (white)
2. Snapdragons:
- The phenotypes of the progeny will be 50% pink (RW) and 50% white (WW).
3. Blood Types:
- Possible blood types: A, B, AB, O. The woman's genotype must be BO (if B is from her father and she has type O, she must have inherited an O allele from her father). Therefore, the offspring can inherit:
- A from the man and B from the woman: AB blood type.
- A from the man and O from the woman: A blood type.
- B from both parents: B blood type.
- O from the woman and B from the man: O blood type.
🔍 Note: In the examples, ensure the punnett square is used to predict outcomes for traits.
📝 Note: Codominance and incomplete dominance are not the same, even though both deviate from Mendel's principles of dominance.
To sum up, codominance and incomplete dominance provide intriguing insights into how genetic material influences physical characteristics. Recognizing these patterns helps us understand the complexities of inheritance and genetic expression beyond simple dominance. This exploration not only enriches our knowledge of genetics but also illustrates the beautiful diversity found in nature, from the colors of flowers to human blood types.
What’s the difference between codominance and incomplete dominance?

+
With codominance, both alleles are expressed equally in the phenotype of the individual, like AB blood types. With incomplete dominance, a blend or intermediate phenotype occurs, like pink flowers from a cross between red and white snapdragons.
Can you give an example of codominance in humans?
+
The most common example in humans is the ABO blood group system, where individuals with the genotype IAIB have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells, leading to the AB blood type.
How can understanding these concepts help in genetic counseling?
+
Understanding codominance and incomplete dominance allows counselors to predict the likelihood of certain traits or genetic diseases being passed on, which can be crucial for informing individuals or families about potential health issues or characteristics in offspring.