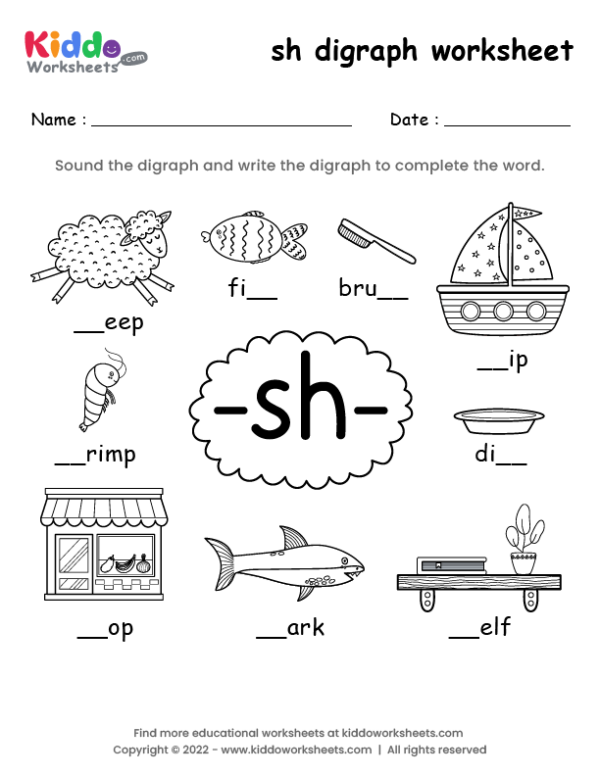
Skeletal Homeostasis: Mastering Calcium Balance Worksheet
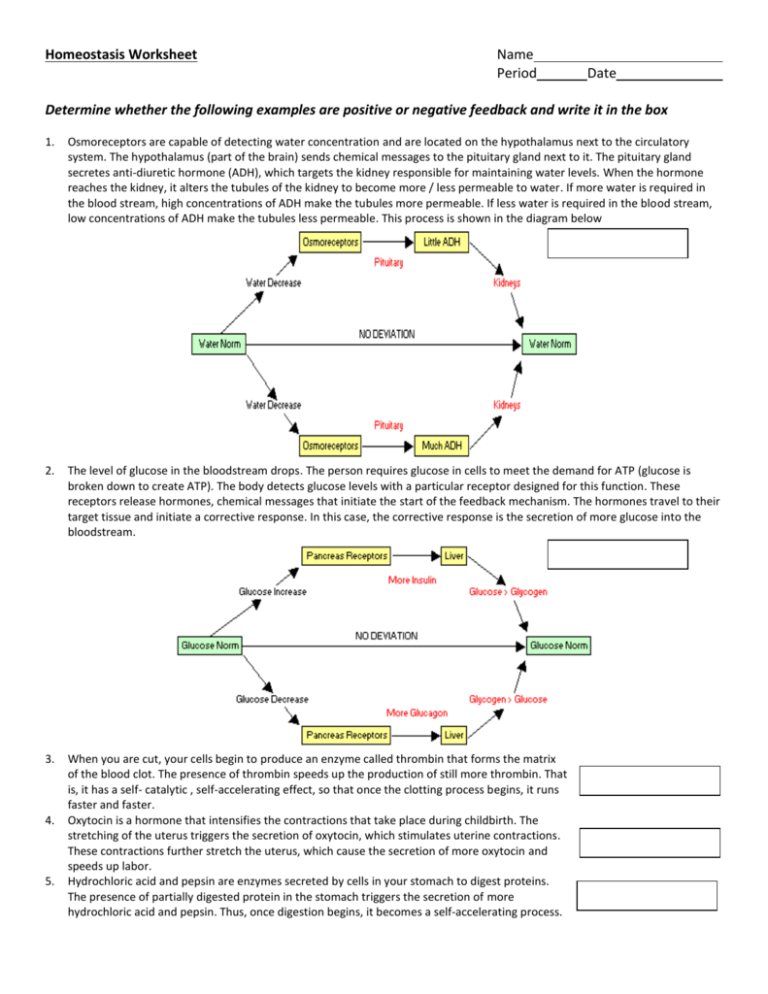
Calcium balance is a crucial aspect of maintaining skeletal homeostasis. This process involves a delicate interplay between absorption in the intestines, deposition in bones, resorption from bones, and excretion via the kidneys. For individuals interested in health, fitness, or those studying biology, understanding how to master calcium balance can provide insights into preventing bone diseases like osteoporosis, enhancing physical performance, and maintaining overall health.
Why Calcium Balance Matters


Calcium is essential not just for bone health but also for nerve function, muscle contraction, blood clotting, and enzyme activity. Here’s how calcium balance works:
- Intestinal Absorption: This is where dietary calcium is first encountered by the body, and vitamin D plays a pivotal role in this process.
- Bone Deposition: Calcium is stored in bones, where it not only strengthens the skeletal system but also acts as a reservoir for maintaining serum calcium levels.
- Bone Resorption: When dietary intake is insufficient, bones release calcium into the bloodstream, a process regulated by hormones like parathyroid hormone (PTH).
- Renal Excretion: Excess calcium is excreted by the kidneys to avoid hypercalcemia, with the hormone calcitonin helping in this regulation.
Understanding Calcium Intake

| Source | Calcium Content (mg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | 415 |
| Cheese (Cheddar) | 307 |
| Milk | 299 |
| Kale | 177 |
| Broccoli | 62 |

Vitamin D, calcium’s co-nutrient, enhances absorption by increasing the expression of proteins involved in this process. Here’s how to optimize your calcium intake:
- Choose dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt for their high calcium content.
- Incorporate leafy greens such as kale and broccoli, which provide calcium along with other nutrients beneficial for bone health.
- Utilize fortified foods like cereals, juices, and soy products, especially if you have dietary restrictions.
- Get adequate sunlight exposure for vitamin D synthesis or consider supplements if necessary.
Regulation of Calcium Levels

Calcium balance isn’t just about intake; it’s also about how the body regulates this vital mineral:
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): Increases bone resorption and kidney reabsorption of calcium to elevate serum calcium levels.
- Vitamin D: Increases calcium absorption from the gut and decreases kidney excretion.
- Calcitonin: Lowers blood calcium levels by inhibiting bone resorption and promoting urinary excretion.
🏋️ Note: Physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises, can stimulate bone formation, reducing bone resorption by increasing the mechanical stress on bones.
Managing Calcium Balance for Skeletal Health

Here’s how one can manage their calcium balance effectively:
- Ensure Adequate Intake: Meet daily calcium requirements through diet or supplements.
- Balance Absorption and Excretion: Enhance absorption by maintaining optimal vitamin D levels, while being mindful of renal function.
- Monitor Bone Health: Regular bone density scans (DEXA) can help assess bone health and calcium status.
- Exercise Wisely: Include exercises that stimulate bone formation like weight lifting or resistance training.
- Manage Dietary Factors: Consider the impact of other nutrients like magnesium and vitamin K on bone health.
The journey towards mastering calcium balance involves understanding and optimizing several interconnected processes. By focusing on diet, supplementation, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can significantly influence their skeletal homeostasis, ensuring stronger bones, improved physical performance, and a healthier life overall. This intricate system requires a balanced approach, where each aspect contributes to maintaining calcium levels that support essential bodily functions.
Why is it important to have an adequate calcium intake?

+
Calcium is crucial for bone health, muscle function, nerve signaling, and more. Without enough calcium, bones can weaken, leading to conditions like osteoporosis, and various bodily functions might suffer.
Can you get too much calcium?

+
Yes, excessive intake can lead to hypercalcemia, which can cause kidney stones, constipation, and even impair absorption of other minerals like iron and zinc.
What are natural ways to improve calcium absorption?

+
Enhancing calcium absorption can be achieved by increasing dietary vitamin D, which is naturally produced by the body through sunlight exposure or can be obtained from foods like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs. Additionally, regular physical activity and a balanced diet with sufficient protein and minerals like magnesium can support calcium absorption.