5 Must-Know Facts: Egypt Engineering Empire Worksheet Answers
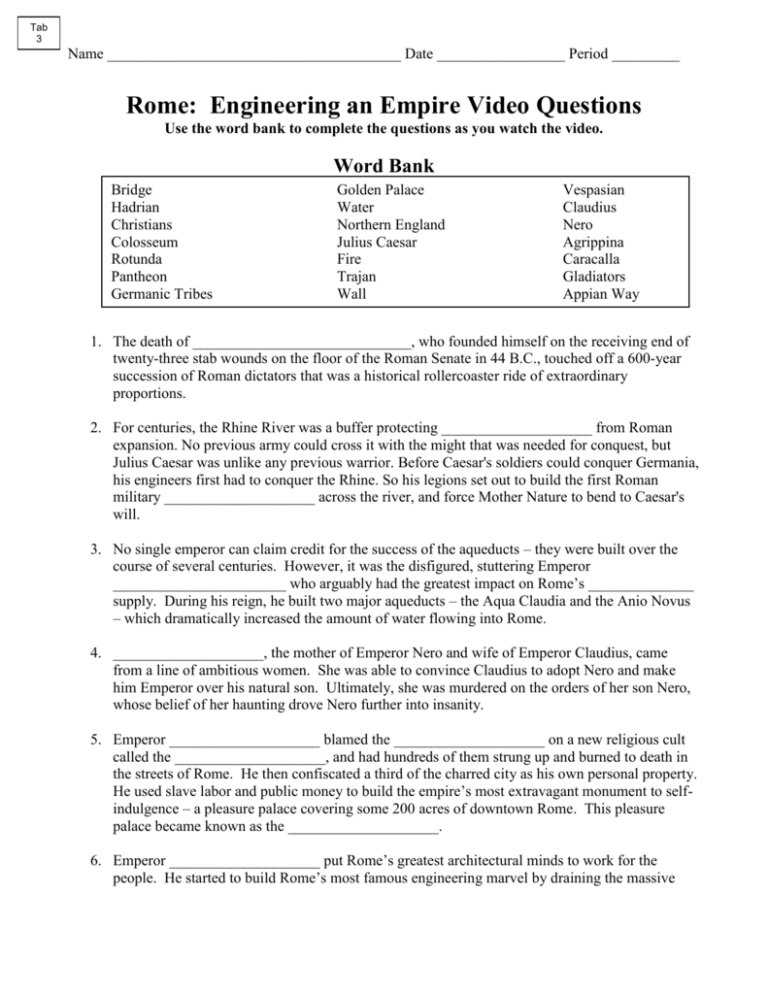
Ever wondered about the engineering marvels of ancient Egypt? From towering pyramids to the intricate irrigation systems, the Egyptians were pioneers in various fields of engineering. Whether you're a student of history, an enthusiast, or a teacher looking for reliable worksheet answers, this post will take you through five must-know facts about Egypt's engineering empire, helping you understand the genius behind their architectural and infrastructural achievements.
1. Pyramid Construction Techniques

The pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, are perhaps the most iconic symbols of Egyptian engineering. Here are some key facts:
- Materials Used: Limestone from local quarries was the primary material. The outer casing was made of polished Tura limestone which reflected sunlight and was visible from miles away.
- Transportation: Blocks were transported using sledges over sand or ramps. Recent theories suggest water may have played a role in moving these heavy blocks.
- Assembly: Despite popular myth, most blocks were laid by skilled workers, not slaves, with workers likely organized into highly specialized teams.
- Alignment: The pyramids’ sides are aligned almost perfectly north-south, with deviations less than 1⁄15 of a degree from true north.
- Height and Precision: The Great Pyramid was originally 146 meters tall and the precision in stone cutting and placement was down to mere millimeters.
2. Irrigation and Water Management

Water was the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, and their engineering in this aspect was crucial for agriculture:
- Nile River: They developed an extensive system of canals and basins to control the flooding of the Nile, capturing the fertile silt for farming.
- Shaduf: This simple yet effective device allowed for the irrigation of fields by lifting water from lower to higher elevations.
- Shurij: These were water wheels used to raise water, often seen in the Ptolemaic period, but the idea might have been Egyptian in origin.
- Basins and Levees: To manage floodwater, they constructed basins surrounded by levees to trap and distribute water evenly across fields.
💡 Note: The precision in water management allowed Egypt to cultivate crops throughout the year, making it one of the most fertile regions in the ancient world.
3. Mathematics and Surveying

The Egyptians had remarkable skills in mathematics and surveying which were essential for their engineering feats:
- Numerical System: Based on hieroglyphic numerals, they had a basic but effective system for calculations.
- Geometry: They were adept at using geometry for land measurement, a practice known as the rope stretcher where they used knots to measure distances.
- Precision: Their ability to lay out straight lines and right angles was crucial in pyramid construction and land division.
- Mathematical Papyri: Documents like the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus provide insights into their mathematical understanding.
📏 Note: The ancient Egyptians’ understanding of geometry was practical, contributing to both their architectural and agricultural advancements.
4. Architectural Innovations

The architectural achievements of Egypt were not limited to pyramids:
- Obelisks: These single-piece granite monuments were colossal feats of both engineering and artistry, weighing up to 500 tons.
- Columns: They developed various column styles, like the lotus, papyrus, and the Palmiform, for decorative and structural support.
- Temples: Structures like Karnak and Luxor demonstrate advanced building techniques, including hypostyle halls with massive columns.
- Forts: Constructing forts like those at Buhen along the Nile border show defensive engineering capabilities.
5. Transportation and Engineering

Ancient Egyptians were also advanced in transportation engineering:
- Ships: They built riverboats and larger ships for travel across the Mediterranean and Red Sea.
- Chariots: Egyptians eventually adopted and adapted the chariot technology from neighboring cultures.
- Causeways: They built ramps and causeways to facilitate the transport of construction materials.
- Quarry Operations: Techniques used in quarries to extract and shape massive blocks of stone for construction.
⛴️ Note: Transportation was crucial not just for trade but also for military campaigns and construction projects.
In delving into the Egypt Engineering Empire Worksheet Answers, we've uncovered some of the most fascinating aspects of how this ancient civilization engineered their world. From pyramid construction to sophisticated irrigation and beyond, the legacy of Egyptian engineering continues to awe and inspire. Their advancements in architecture, mathematics, and transportation have provided a foundation that subsequent civilizations built upon, showing just how ahead of their time the Egyptians were. This rich tapestry of engineering feats not only shaped their society but also left an enduring mark on the world stage.
How did the ancient Egyptians move heavy stone blocks for pyramid construction?

+
Ancient Egyptians likely used sledges, ramps, and possibly water to lubricate the surface, making it easier to slide the blocks into place. Some theories even suggest using counterweights and lever systems.
What was the purpose of the shaduf in Egyptian irrigation?

+
The shaduf was an ingenious device for lifting water from the Nile to irrigate higher fields, facilitating year-round agriculture.
Why were Egyptian pyramids aligned to cardinal points?

+
The precise alignment to the cardinal points could reflect religious beliefs, astronomical observations, or the use of magnetic compasses, though the latter is less likely.
Can you explain the importance of mathematics in Egyptian engineering?

+
Mathematics was crucial for surveying land after floods, calculating dimensions for buildings, and ensuring precise alignment in construction, which was vital for their engineering achievements.
What was unique about Egyptian shipbuilding?

+
Egyptians built ships for both river travel and sea voyages, using reed boats in the early periods and later adopting cedar for their durability. They also had advanced knowledge in using sails and navigation.