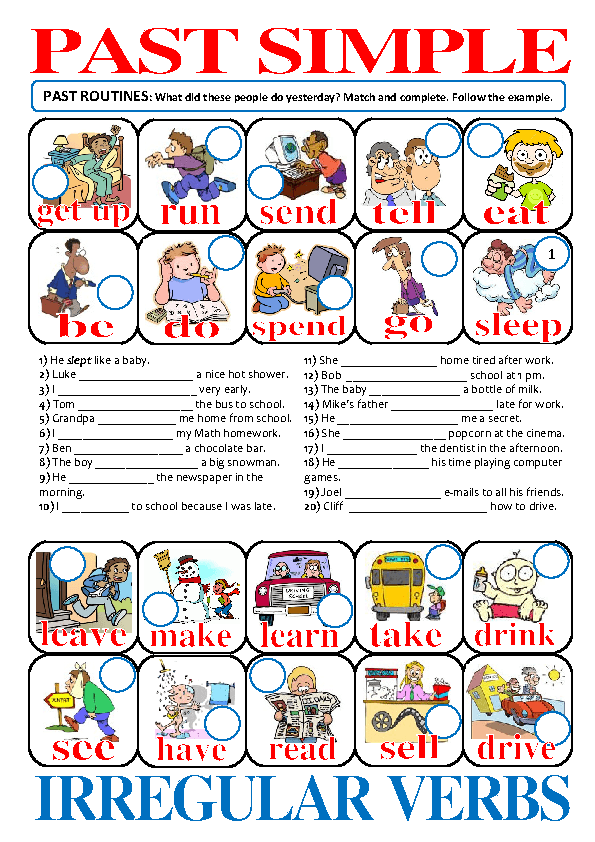
Simple Past Worksheet
The Simple Past tense, also known as the Past Simple, is fundamental in English grammar for describing actions or situations that happened and were completed at a specific time in the past. Learning how to use the Simple Past effectively is crucial for any English learner, whether you're aiming to improve your conversational skills or tackling complex narratives. This comprehensive guide will take you through the construction, usage, and common pitfalls when it comes to using the Simple Past tense.
Structure of the Simple Past

The Simple Past is formed differently for regular and irregular verbs:
- Regular Verbs: Add -ed or -d to the base form of the verb. For example, 'walk' becomes 'walked', 'love' turns into 'loved'.
- Irregular Verbs: These do not follow a standard pattern. Examples include 'go' becoming 'went', 'see' turning into 'saw'.
- Negative Form: Use 'did not' (or the contraction didn't) + the base form of the verb. E.g., "She didn't go to the party."
- Question Form: Start with 'Did' + subject + base form of the verb. E.g., "Did he see the movie?"
💡 Note: For negative sentences with 'be', use 'was not' or 'were not' instead of 'did not' + be.
Usage of the Simple Past

Here are some scenarios where the Simple Past tense is commonly used:
- To talk about completed actions in the past, where the time is known or implied. For example, "She visited London in 2019."
- Discussing past habits or general truths that were true but are no longer. E.g., "He smoked when he was younger."
- Narrating stories or retelling events. "The little girl lost her shoe."
- Describing a series of actions or events in the past. "First, we ate dinner, then we watched a movie."
Spelling Rules for Regular Verbs

Here are the rules to remember when adding '-ed' to regular verbs:
- Just add -ed if the verb ends in e. E.g., 'like' → 'liked'.
- If the verb ends in -y with a consonant before it, change the y to i and add -ed. E.g., 'carry' → 'carried'.
- If the verb has one syllable and ends in a consonant + a short vowel + a consonant (except 'w' and 'x'), double the last consonant before adding -ed. E.g., 'stop' → 'stopped'.
- Add -d if the verb already ends in 't' or 'd'. E.g., 'want' → 'wanted'.
Common Irregular Verbs

Learning irregular verbs can be tricky since they don't follow a predictable pattern. Here is a table of some common irregular verbs:
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| be | was/were | been |
| begin | began | begun |
| break | broke | broken |
| bring | brought | brought |
| do | did | done |

Pitfalls to Avoid

When using the Simple Past, there are several mistakes you should be aware of:
- Not using the correct form of the irregular verb.
- Overgeneralization of regular verb endings to irregular verbs. E.g., saying "He buyed the car" instead of "He bought the car."
- Using past tense inappropriately for actions still ongoing or not finished at the time of speaking.
- Confusion between 'was' and 'were'.
Exercises and Examples

Practice is key to mastering the Simple Past tense. Here are some examples:
- Positive Sentences: "Yesterday, I met with my old friend."
- Negative Sentences: "They didn't know about the event."
- Questions: "Did you remember to call your sister?"
To solidify your understanding, try converting present tense sentences into the Simple Past:
- Present: "She eats a lot of vegetables." Past: "She ate a lot of vegetables."
- Present: "We play soccer on weekends." Past: "We played soccer on weekends."
Incorporating these exercises into your daily practice can significantly improve your usage of the Simple Past tense.
👉 Note: When recounting past events, it's beneficial to mix the Simple Past with the Past Continuous to describe concurrent actions or to set scenes.
The Simple Past is a foundational aspect of English grammar, critical for clear communication about past events. Understanding its structure, usage, and common errors can immensely enhance your English proficiency. Regular practice, exposure to native speakers, and reading literature can further your grasp of when and how to apply this tense effectively. In storytelling, academic writing, or everyday conversation, the Simple Past allows us to share our experiences, lessons, and histories with others. Remember, while the rules are important, the context in which you use the Simple Past will often dictate its effectiveness in real-world communication.
Why is the Simple Past tense important in English?

+
The Simple Past allows you to clearly communicate actions, events, or states that occurred in the past. This is essential for narratives, historical recounts, and conversations about past experiences.
How can I learn irregular verbs?

+
Flashcards, verb conjugation apps, and consistent practice through reading and writing are excellent ways to learn and remember irregular verbs.
Are there any tricks to forming the past tense of regular verbs?

+
Yes, like doubling the final consonant or changing ‘y’ to ‘i’ before adding ‘-ed’. However, knowing the spelling rules for regular verbs can make forming the past tense easier.
Can I use Simple Past for actions that continue into the present?

+
No, for actions that started in the past and continue into the present, you would use the Present Perfect or the Past Continuous.
How do I know when to use “was” or “were”?

+
“Was” is used with singular subjects (I, he, she, it), while “were” is used with plural subjects (we, you, they) and with ‘you’ even in singular form.