5 Tips to Master Production Possibilities Curve Answers

Economics students often encounter a variety of analytical tools designed to explain the intricacies of how societies can efficiently allocate resources. Among these tools, the Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) stands out as a fundamental concept, serving as a graphical representation of the trade-offs between two goods or services. Understanding and mastering the PPC is crucial not only for academic success but also for grasping economic principles applied in real-world scenarios. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into five essential tips to help you master the answers related to the PPC.
Understand the Concept Thoroughly

Before diving into the specifics of PPC questions, it's vital to understand what the PPC represents:
- Scarcity: Resources are limited, forcing choices in production.
- Efficiency: Points on the curve signify maximum efficiency in resource use.
- Opportunity Cost: The cost of the next best alternative foregone.
Here are some questions you might encounter:
- Why does the PPC slope downward?
- What does a point inside the PPC indicate?
Understanding these basics will pave the way for a more insightful interpretation of PPC scenarios.

Identify Key Points and Trends
Mastering PPC answers involves identifying key points and interpreting the curve's shape:
- Concave Shape: Due to the law of increasing opportunity costs, the curve typically has a concave shape.
- Linear PPC: Indicates constant opportunity costs, which is less common but still possible.
- Outward Shift: Shows economic growth or technological advancements.
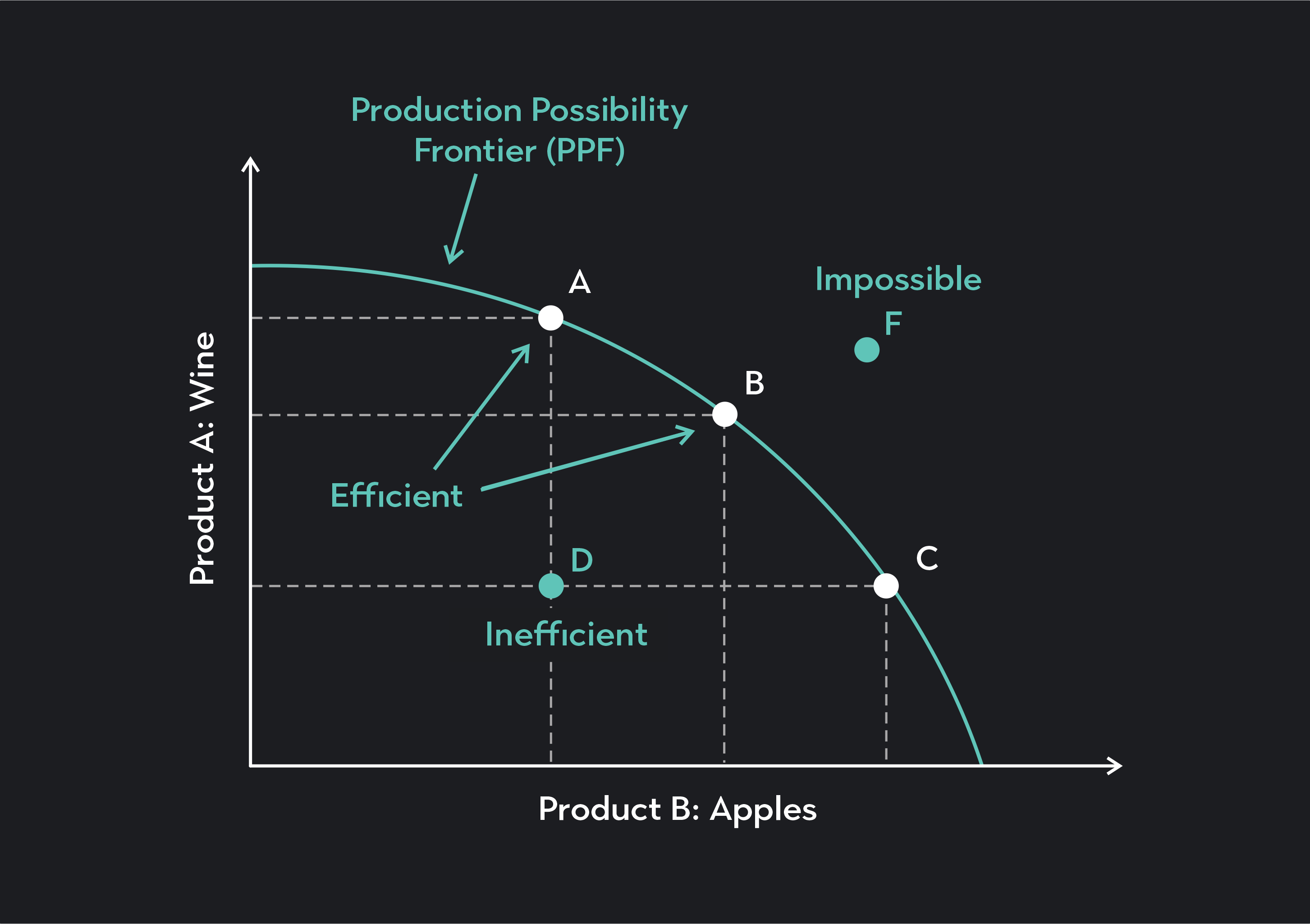
| Position on PPC | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| On the Curve | Maximum efficiency in resource allocation |
| Inside the Curve | Inefficient use of resources |
| Outside the Curve | Unattainable given current resources |
| Shift Outward | Economic growth or technological advancements |

💡 Note: Always consider the context when analyzing a PPC graph; some scenarios might deviate from these interpretations.

Analyze Opportunity Costs

One of the core concepts tied to the PPC is the opportunity cost:
- Opportunity cost increases as you move along the PPC, reflecting the trade-off between the two goods or services.
- The slope of the PPC at any point gives you the opportunity cost of producing more of one good in terms of the other.
- Understanding this dynamic helps in answering questions about production changes:
- How does the opportunity cost change as more of one good is produced?
- What are the implications of high opportunity costs for an economy?
💡 Note: Remember that opportunity costs reflect what you are giving up, which becomes more significant as you produce more of one good.

Apply to Real-World Scenarios

To truly master PPC answers, apply the concept to real-world situations:
- Examine national economic policies and how they affect the PPC.
- Understand the impact of technological progress or resource discovery on economic growth.
Here are some examples of questions:
- What happens to a country's PPC when there is a technological innovation in one industry?
- How does an increase in population affect a country's PPC?
💡 Note: Real-world applications require flexibility as economic models rarely capture all variables at play.

Practice with Different Curves

Consistent practice with various PPC scenarios will refine your understanding:
- Explore linear PPCs to understand constant opportunity costs.
- Work with PPCs that represent a single-good economy or multi-good economies.
- Engage with PPC questions that incorporate external factors like trade:
- How does trade expand the PPC?
- What shifts might occur when considering opportunity costs internationally?
Mastering PPC answers not only requires understanding the curve itself but also how it interacts with economic theory and real-world dynamics. Here's a wrapping up:
Mastering the Production Possibilities Curve (PPC) is a journey through the core economic concepts of scarcity, efficiency, opportunity cost, and growth. By understanding the PPC thoroughly, identifying key points and trends, analyzing opportunity costs, applying the concept to real-world scenarios, and practicing with diverse curve scenarios, you'll be well-equipped to tackle any PPC question. Remember, the PPC is more than just a graph; it's a window into understanding economic choice, trade-offs, and the path to sustainable development. As you progress in your studies, let these tips be your guide to unlocking the complexities of economic analysis and decision-making.
Why does the PPC curve have a concave shape?

+
The PPC has a concave shape due to the law of increasing opportunity costs, where resources are not equally efficient in producing all goods. As you move along the curve, producing more of one good requires sacrificing increasingly larger amounts of the other good.
What does a point on the PPC curve indicate?

+
A point on the PPC curve indicates an efficient use of resources where the economy produces the maximum possible output of both goods, given the current resources and technology.
How does an economy grow, and how is this reflected in the PPC?

+
Economic growth, due to technological advancements or an increase in resources, shifts the PPC outward, allowing for higher production levels of both goods than previously possible.