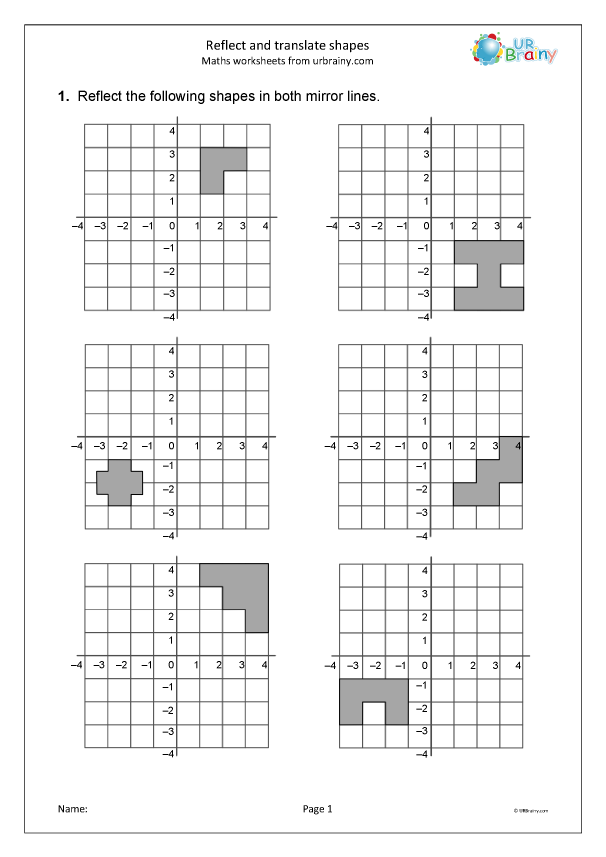
Point Slope Form Worksheet: Answers Included for Easy Learning

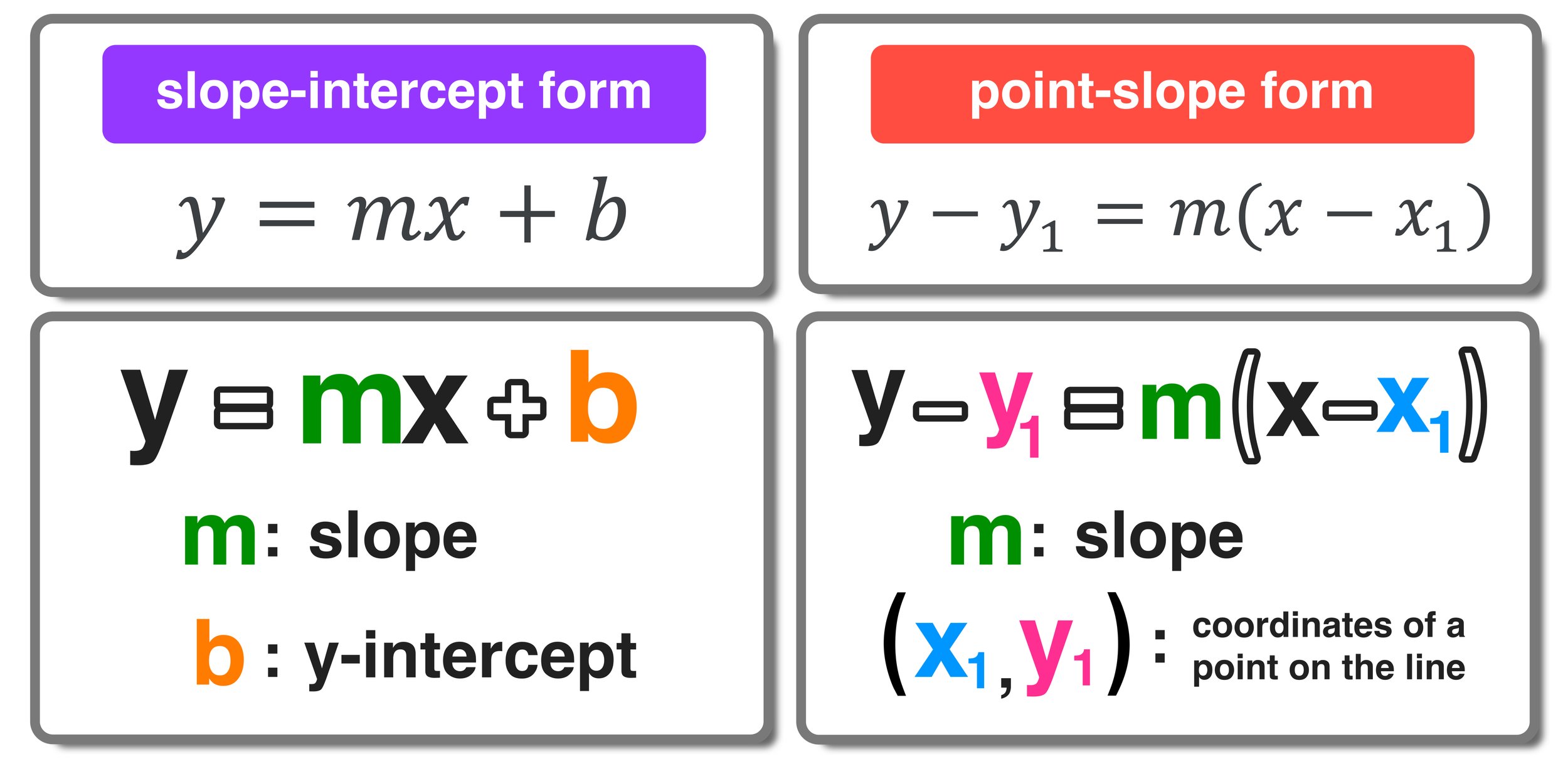
Understanding Point-Slope Form in Algebra
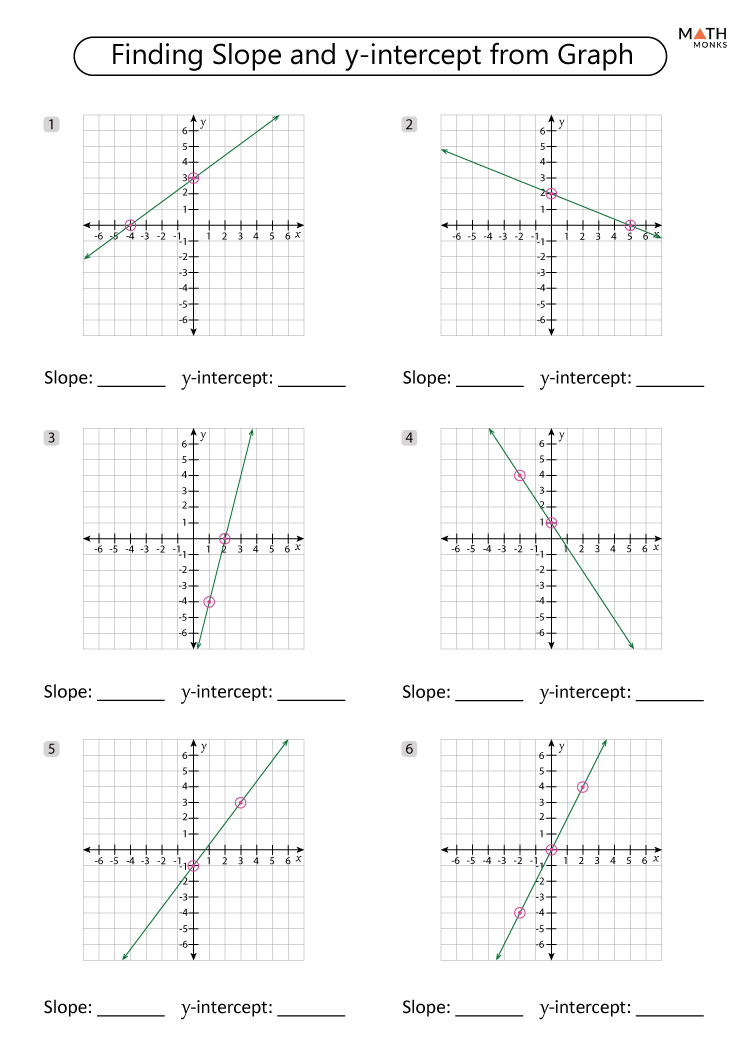
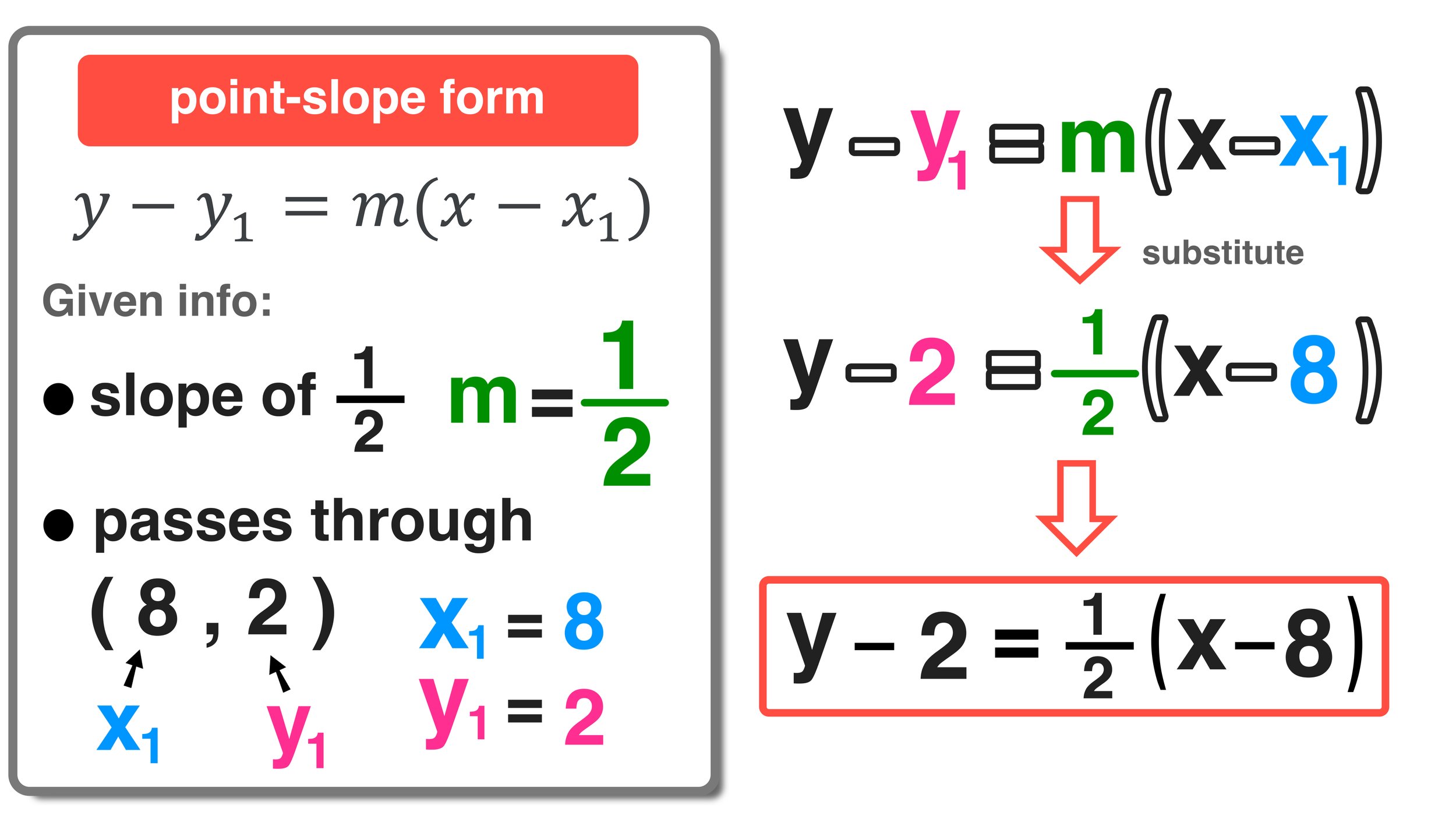
The point-slope form is a fundamental equation in algebra that describes a straight line when given a specific point on the line and its slope. It's expressed as:
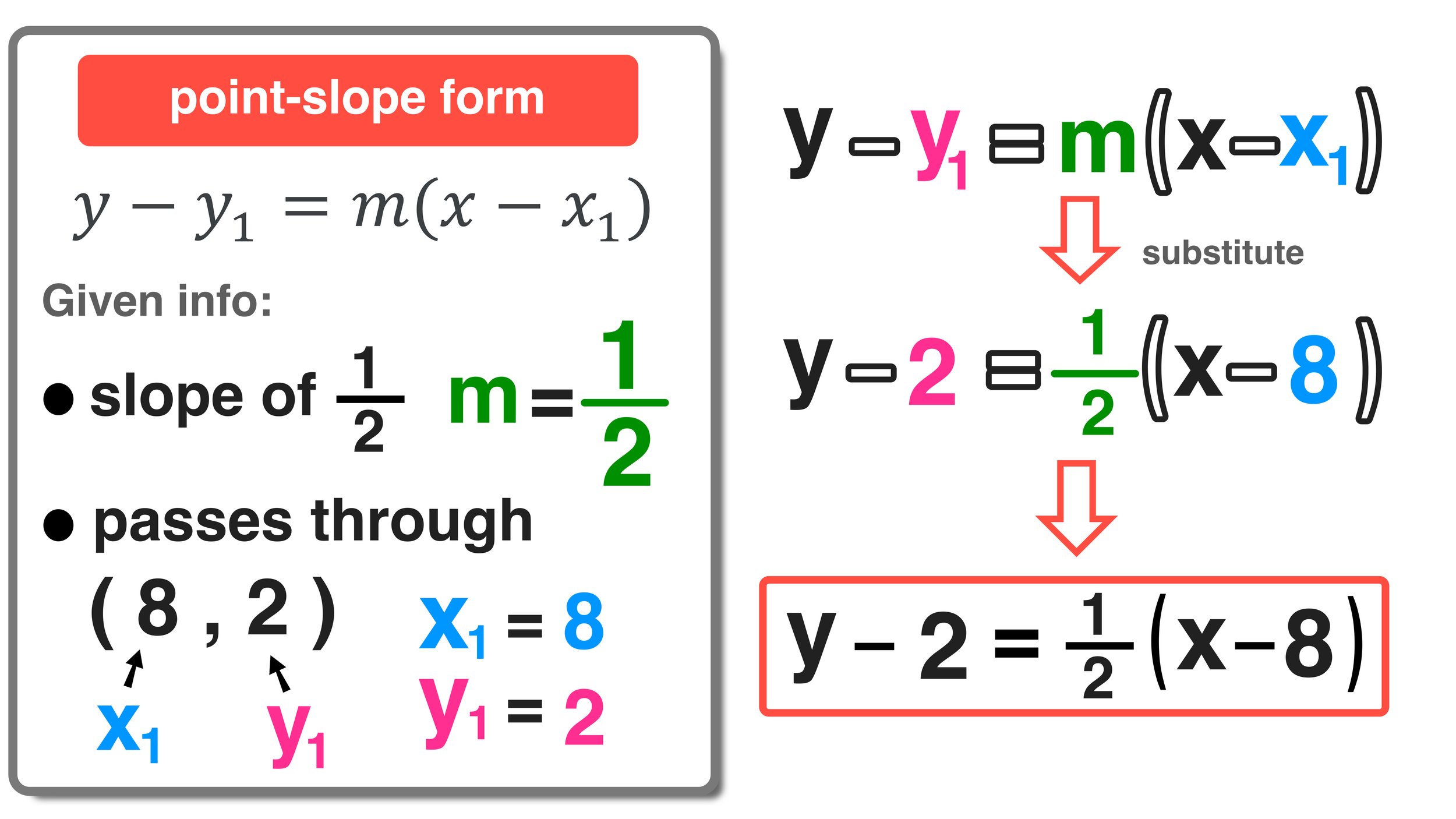
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
where m is the slope of the line, and (x1, y1) are the coordinates of a specific point on that line. This form of the equation is particularly useful when you want to find the equation of a line passing through a given point with a known slope.
Key Elements of Point-Slope Form

- The Slope (m): Represents the steepness or incline of the line. It tells you how much y changes with each unit change in x.
- The Point (x1, y1): A specific coordinate on the line. This point serves as an anchor, allowing us to define the equation's behavior at this exact location.
The Slope-Intercept Conversion

Converting from point-slope form to slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) involves isolating y on one side of the equation:
- Start with the point-slope equation: y - y1 = m(x - x1)
- Distribute m across the parentheses: y - y1 = mx - mx1
- Add y1 to both sides to isolate y: y = mx + (y1 - mx1)
💡 Note: The term (y1 - mx1) represents the y-intercept b.
Steps to Find the Equation of a Line
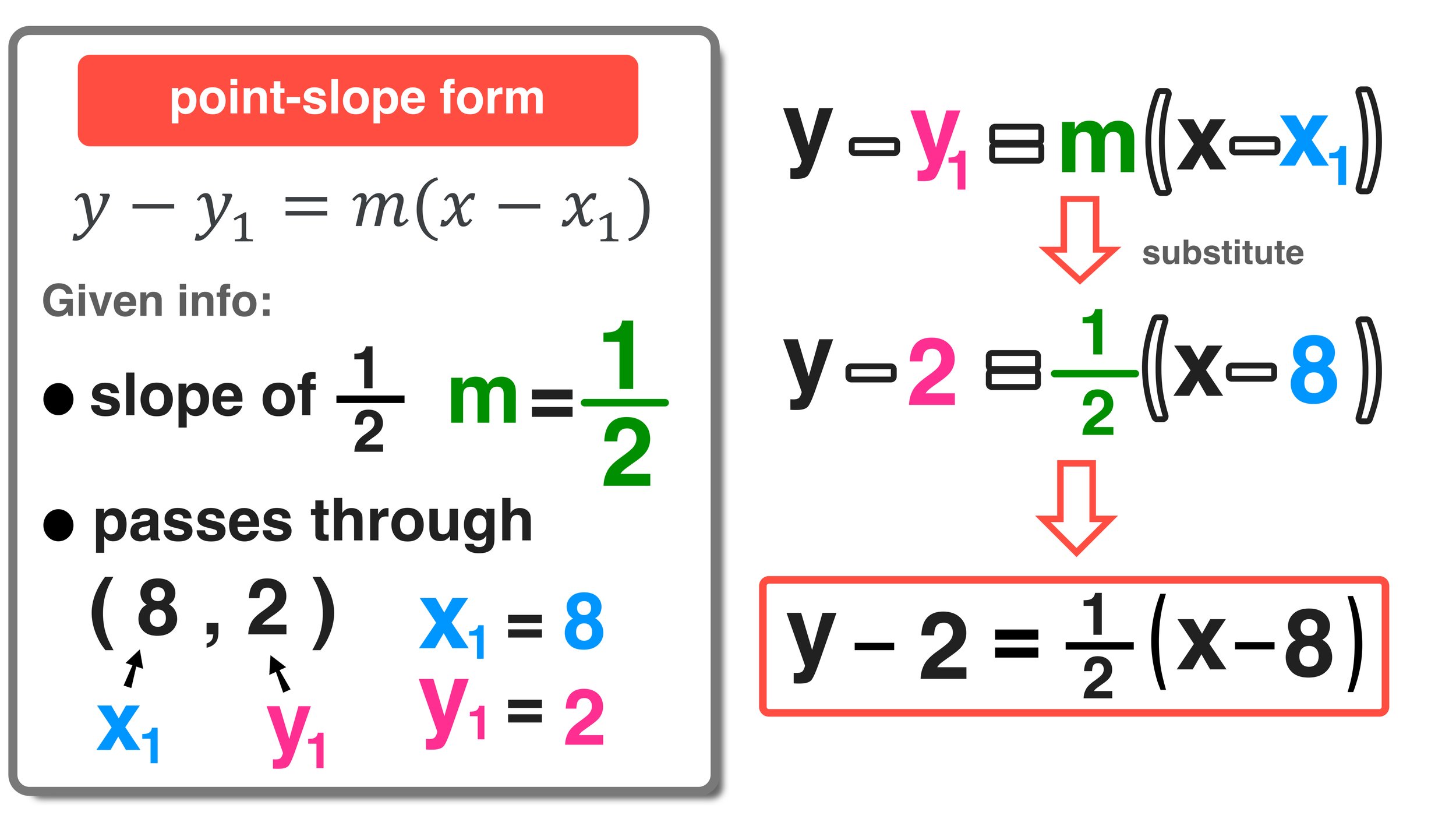
Finding the equation of a line using point-slope form requires you to follow these steps:
- Identify the slope (m): If you know the slope, use it. If not, you'll need two points to calculate it with the formula m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1).
- Select a point on the line: Choose any point through which the line passes. This point must include (x1, y1) for the equation.
- Apply the formula: Substitute the known values into the point-slope equation.
Example
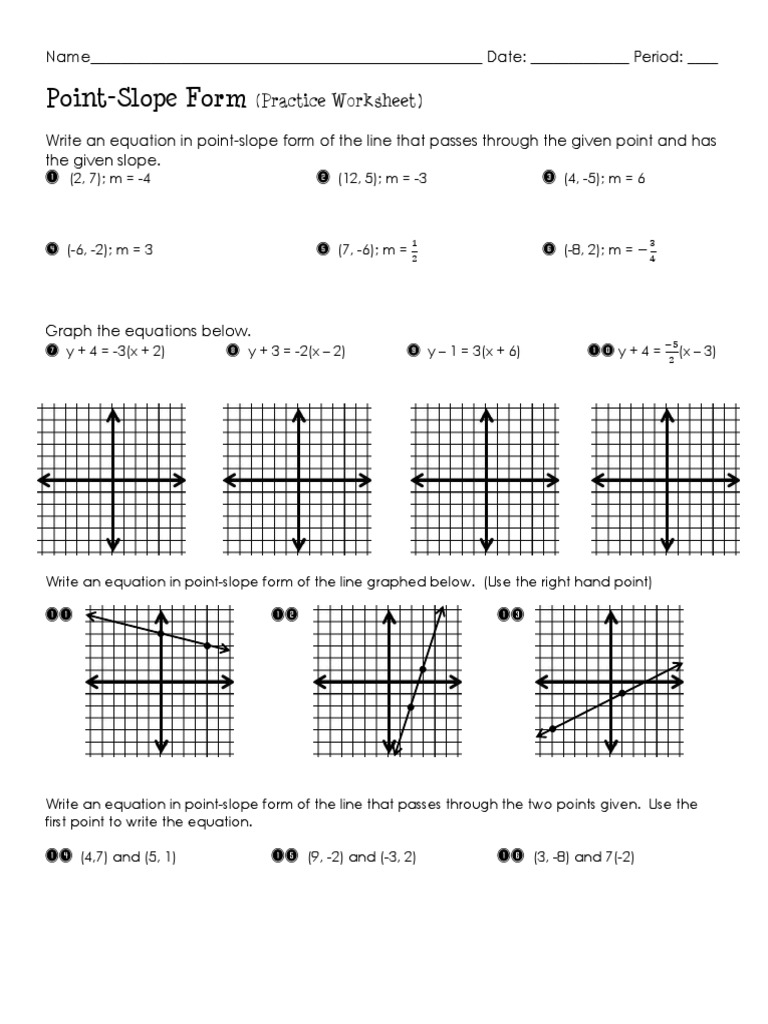
Suppose a line passes through the point (2, 4) with a slope of 3. To find its equation:
- Set up the equation: y - 4 = 3(x - 2)
- Distribute the slope: y - 4 = 3x - 6
- Isolate y: y = 3x - 2
Here, the slope is 3, the y-intercept is -2, and the equation in slope-intercept form is y = 3x - 2.
Practical Applications of Point-Slope Form
The point-slope form is particularly handy in situations where you need to:
- Quickly write the equation of a line given a point and slope
- Determine the equation of a line that is tangent to a curve at a point
- Analyze the change in slope over different segments of a line
In real-world scenarios, point-slope form is used in:
| Application | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Civil Engineering | Designing roads, paths, or drainage systems to ensure proper slopes for water flow |
| Computer Graphics | Calculating lines for drawing or movement algorithms |
| Finance | Modeling growth rates or depreciation of assets |
💡 Note: Even though these examples use point-slope form, many professional applications may eventually convert to other forms for easier use in their specific context.
Interactive Learning with Worksheets

Worksheets are an excellent way to reinforce understanding of point-slope form. Here's how you can engage with this concept through practice:
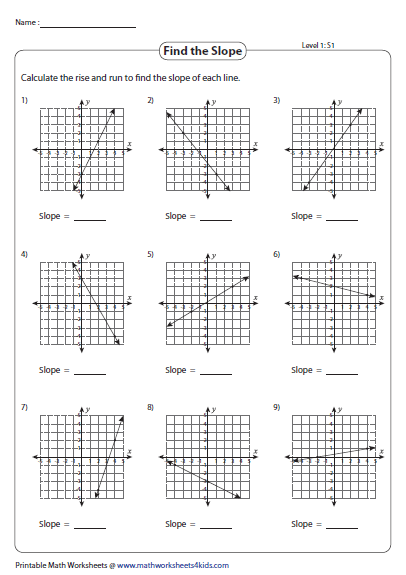
- Download and print the worksheet to start practicing. Here's an example of what the worksheet might look like:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the equation of the line that passes through (1, -3) with a slope of 2. | y + 3 = 2(x - 1) → y = 2x - 5 |
| What's the equation of the line with a slope of -1/2 that passes through (-2, 4)? | y - 4 = -1/2(x + 2) → y = -1/2x + 3 |
Answers to Worksheet

To help you check your work, here are the answers to the worksheet:
- Problem 1: y = 2x - 5
- Problem 2: y = -1/2x + 3
Remember, practice is key. Regularly working on these problems will enhance your confidence and proficiency in handling point-slope form equations.
The key takeaway from this exploration of point-slope form is its versatility and direct applicability in defining a line given only a point and its slope. By understanding how to convert from point-slope to other forms of linear equations, we not only improve our algebraic manipulation skills but also our ability to apply these concepts in practical scenarios.
What is the advantage of using point-slope form?
+
Point-slope form is especially useful when you’re given a point on the line and the slope of the line, making it easier to write the equation of a line quickly.
Can point-slope form be used for vertical or horizontal lines?
+
No, point-slope form isn’t suited for vertical lines, as their slopes are undefined. For horizontal lines, the slope is zero, so you’d use y = b form.
How do I convert from point-slope to slope-intercept form?

+
Distribute the slope through the parentheses and then add or subtract to isolate y on one side of the equation, yielding the slope-intercept form y = mx + b.
Why would I need to know the point-slope form in real life?
+
Point-slope form can be applied in various fields like engineering for design specifications, in physics to describe linear motion, or in economics to model linear relationships.
What common mistakes should I avoid when using point-slope form?
+
Common mistakes include incorrect substitution of the slope, misplacing the negative signs, and forgetting to distribute the slope when converting to slope-intercept form.