Plant Structure and Function Worksheet: Interactive Learning

Delving into the study of botany opens up a fascinating world of complex structures and functions unique to plant life. Whether you're a seasoned botanist, a student beginning your journey, or simply someone with a green thumb, understanding how plants are built and how they work can be both intriguing and educational. This blog post dives into the intricacies of plant structure and function through an interactive worksheet approach, designed to enhance your learning experience by engaging with the material hands-on.
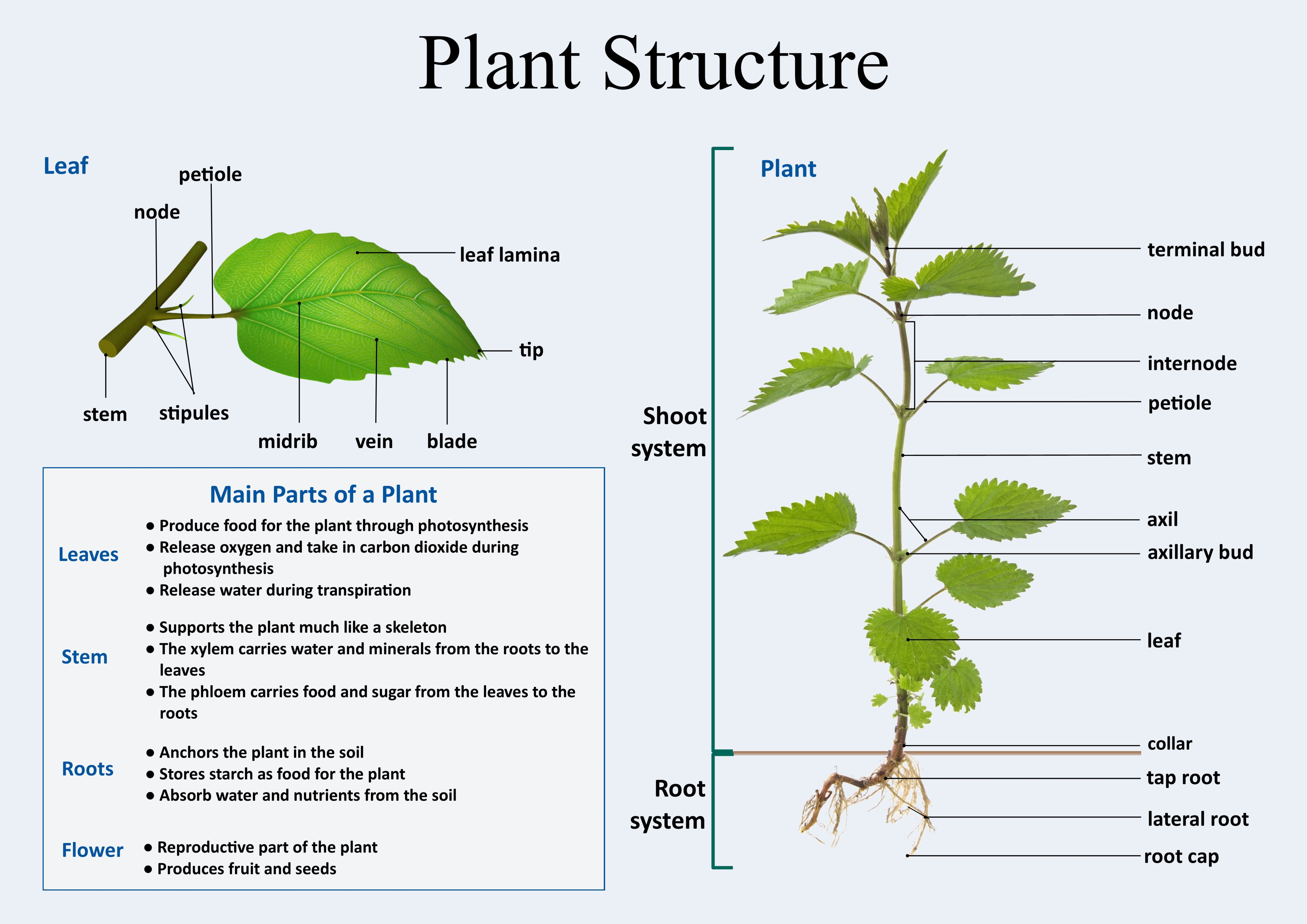
Understanding Plant Structure


To effectively learn about plant function, it's imperative first to grasp their anatomy. Here's how you can break down the structure of a typical plant:
- Roots: The underground part of the plant responsible for anchoring, water and nutrient absorption, and storage.
- Stems: The supportive pillars that transport water, nutrients, and sugars between roots and leaves.
- Leaves: The primary sites for photosynthesis, gas exchange, and transpiration.
- Flowers: Reproductive structures attracting pollinators and facilitating seed production.
- Fruits: Mature ovaries containing seeds for plant reproduction.
- Seeds: The embryo encased in a protective coat that has the potential to grow into a new plant.
| Plant Part | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Root System | Water absorption, nutrient uptake, and anchoring the plant. |
| Shoot System | Photosynthesis, support, and reproduction. |
| Leaves | Photosynthesis and gas exchange. |
| Flowers | Reproduction via pollination. |

🔍 Note: This table offers a simplified overview of plant parts, but some plants might have specialized structures with variations in function.
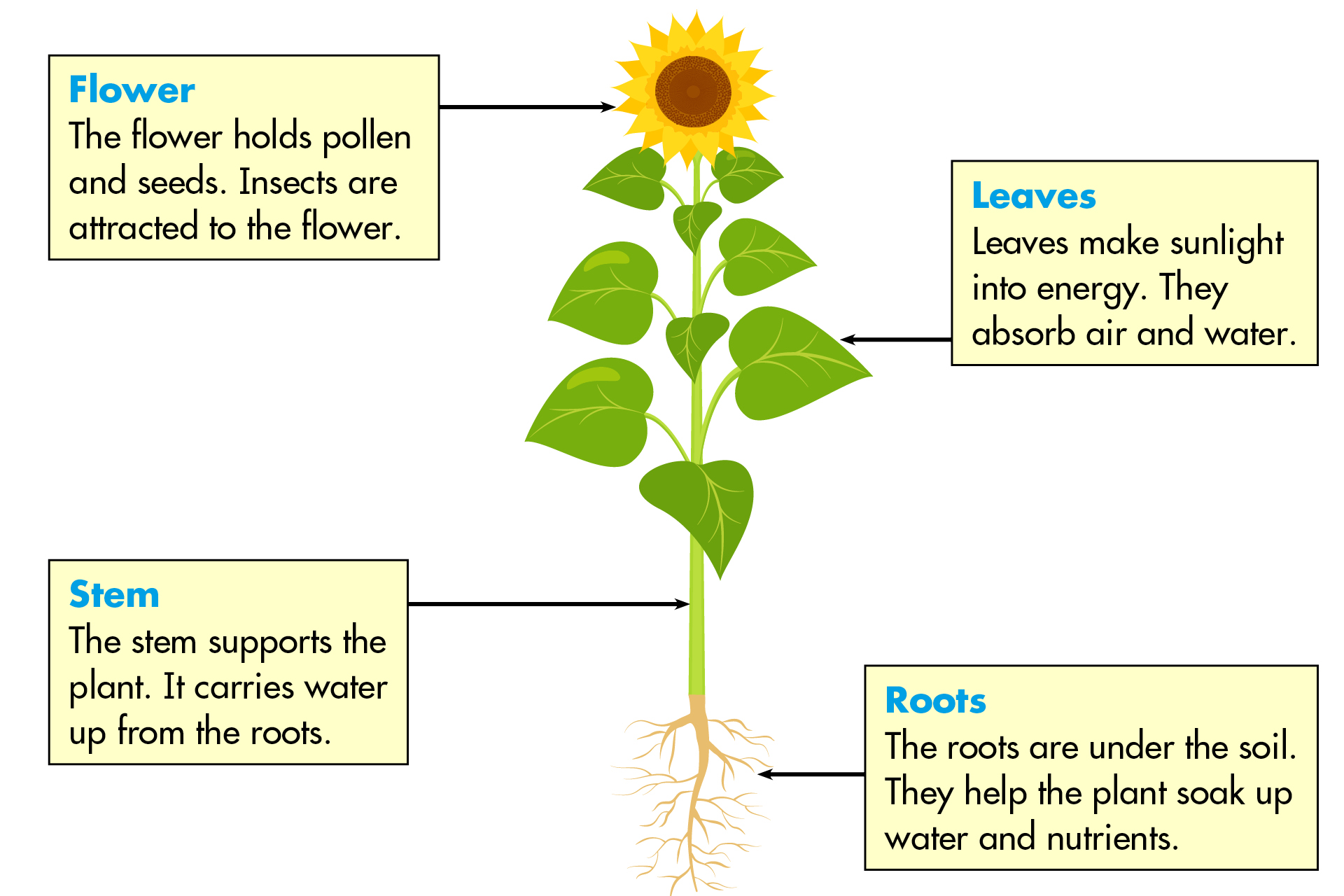
The Function of Plant Parts

Each part of the plant performs specific functions that are critical for its survival and reproduction:
- Roots: Apart from absorption, roots stabilize plants in the soil, preventing erosion and providing support.
- Stems: They transport substances through vascular tissue, support the leaves, flowers, and fruits, and may also store nutrients.
- Leaves: They are solar energy collectors, converting sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- Flowers: Attract pollinators, develop into fruits, and ensure seed dispersal for the next generation.
💡 Note: Environmental conditions can influence these functions, such as how some plants adapt to drought or nutrient-poor soils by altering root structures.
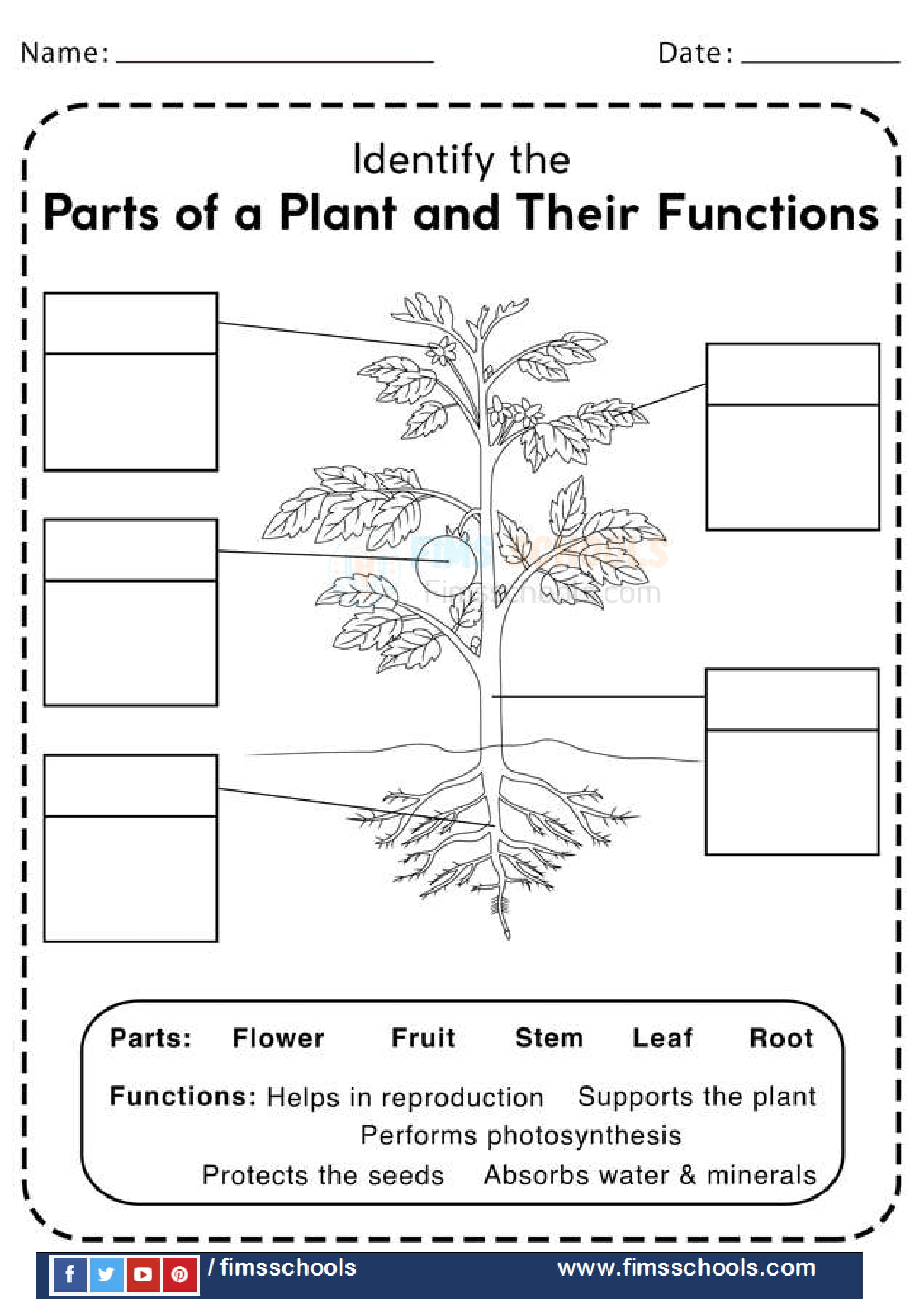
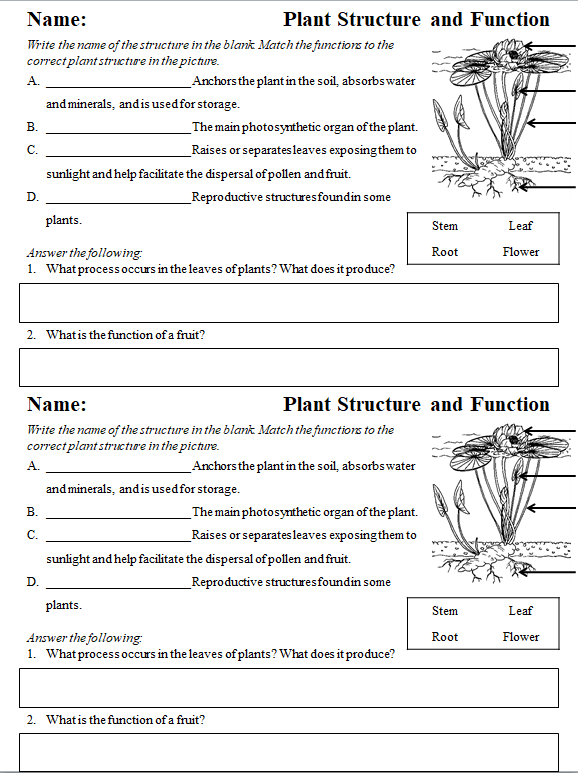
Interactive Learning with Plant Structure and Function Worksheets


Interactive worksheets provide an engaging way to delve into plant science. Here’s how you can make the most of them:
- Fill in the Blanks: Use worksheets with blanks to encourage recall and understanding of plant parts and their functions.
- Labeling Diagrams: Labeling different parts of a plant diagram helps in visual learning and memory retention.
- Matching Exercises: Match plant structures to their roles, reinforcing the connection between structure and function.
- Short Answer Questions: Encourage critical thinking with questions about how plants adapt to different environments.
Incorporating Experiments in Your Learning
Interactive learning extends beyond worksheets. Here are some experiments to bring plant structure and function to life:
- Observing Roots: Set up a container with a transparent side to watch root growth and development.
- Transpiration Rate: Conduct experiments to measure the rate of water loss from different plant species.
- Photosynthesis Demonstration: Use simple setups to show how leaves produce oxygen in the presence of light.
🌱 Note: While these activities are fun, they also emphasize the practical application of botanical principles.
When reflecting on the myriad of ways plants adapt to their environments, it's awe-inspiring to consider how they've evolved to survive and thrive. From the intricate root systems that delve deep into the earth, searching for life-sustaining water and nutrients, to the elaborate designs of leaves that maximize sunlight absorption, plants exemplify nature’s elegance and efficiency. This interactive journey through plant structure and function not only deepens our understanding but also fosters a connection with the natural world. By engaging in this knowledge through hands-on activities, one learns not just the theory but the dynamic interplay between the plant and its environment, enriching both our understanding and appreciation of these living wonders.
How do roots function beyond absorption?

+
Roots also play a crucial role in anchoring plants, preventing erosion, and even storing food reserves, especially in species like carrot and beet.
Why are leaves so important for plant survival?
+
Leaves are vital for photosynthesis, which is how plants convert light energy into chemical energy, producing food for themselves and oxygen for all living creatures. They also regulate gas exchange and manage water loss through transpiration.
Can plants survive without flowers?

+
Yes, while flowers are essential for sexual reproduction, some plants can reproduce asexually through vegetative propagation, which does not require flowers. However, they play a significant role in many plants’ life cycles for attracting pollinators and ensuring genetic diversity.
What is the significance of the stem in plant structure?
+
Stems support leaves, flowers, and fruits, elevating them to receive sunlight, they transport water, nutrients, and sugars between roots and leaves, and can also store food.



