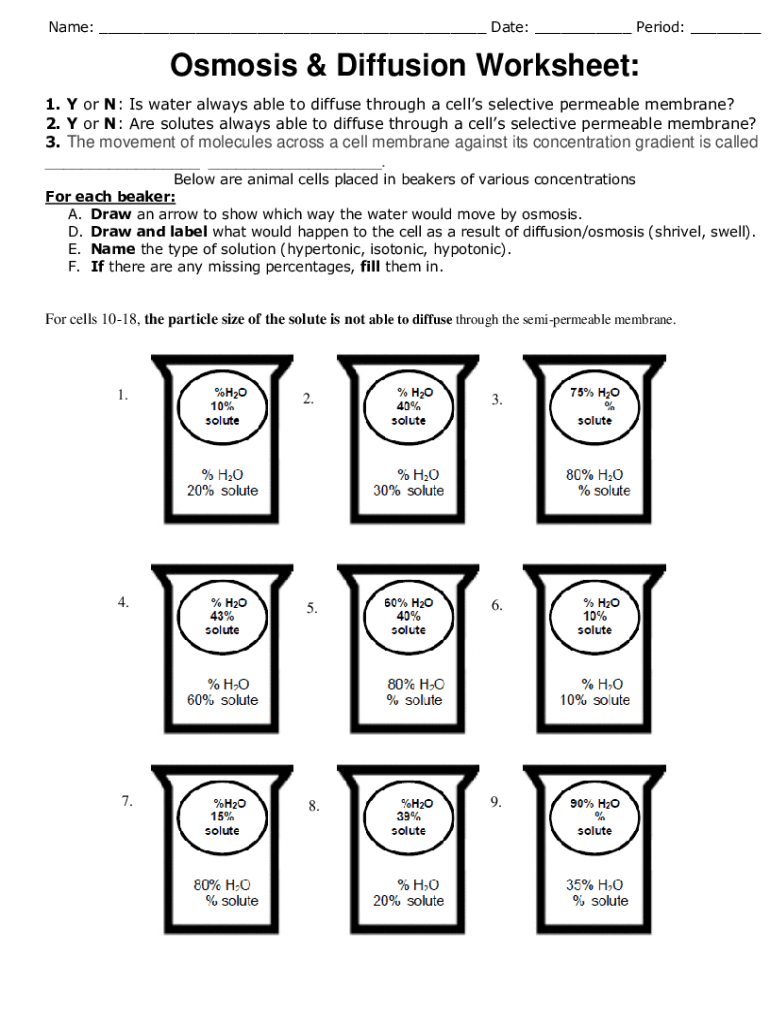
Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet Answers: 5 Essential Tips
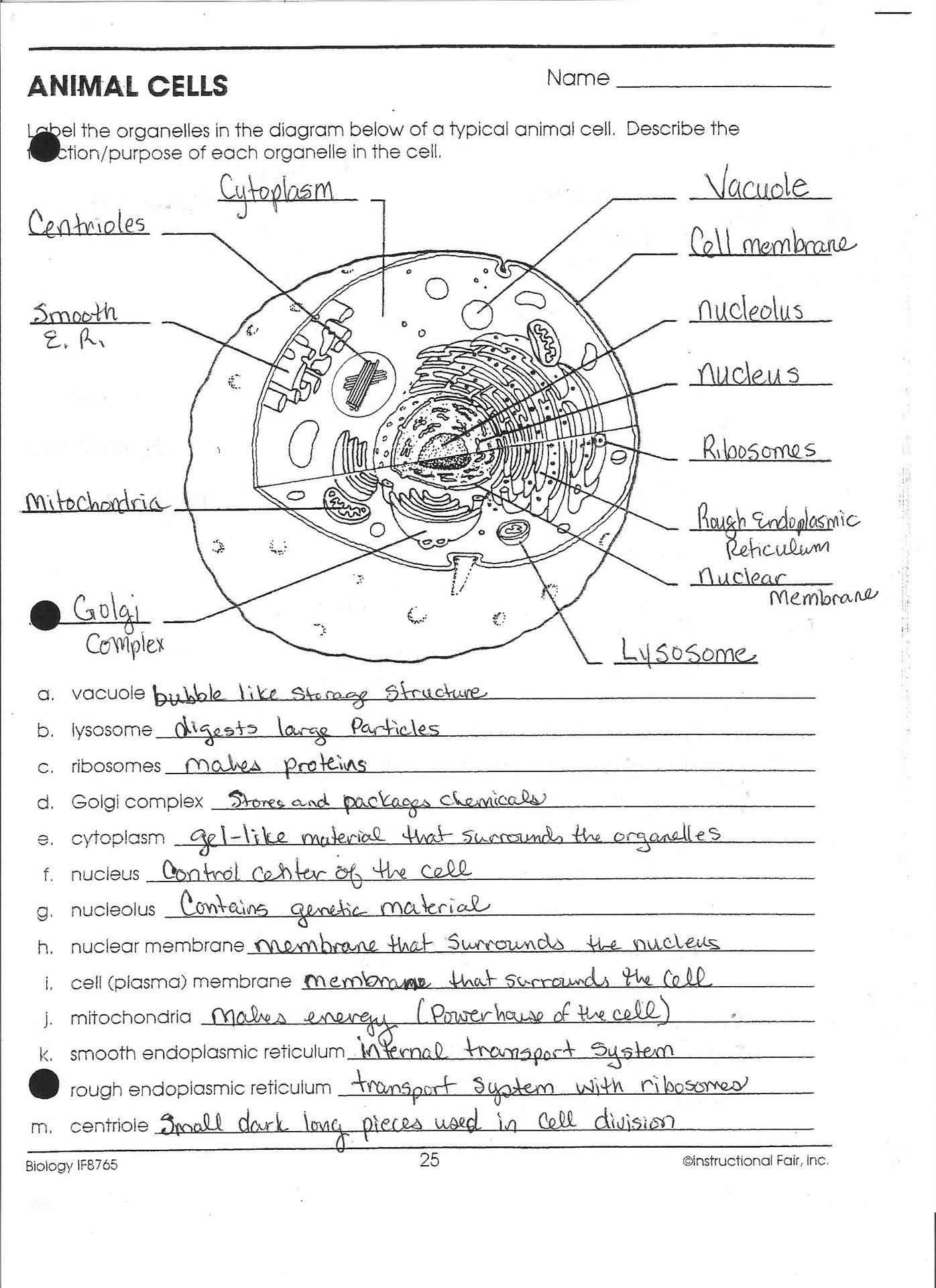
🌿 Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding plant cell diagram worksheets. Here, we dive into the essentials to help students excel in biology with clarity and insight.
Understanding Plant Cell Basics
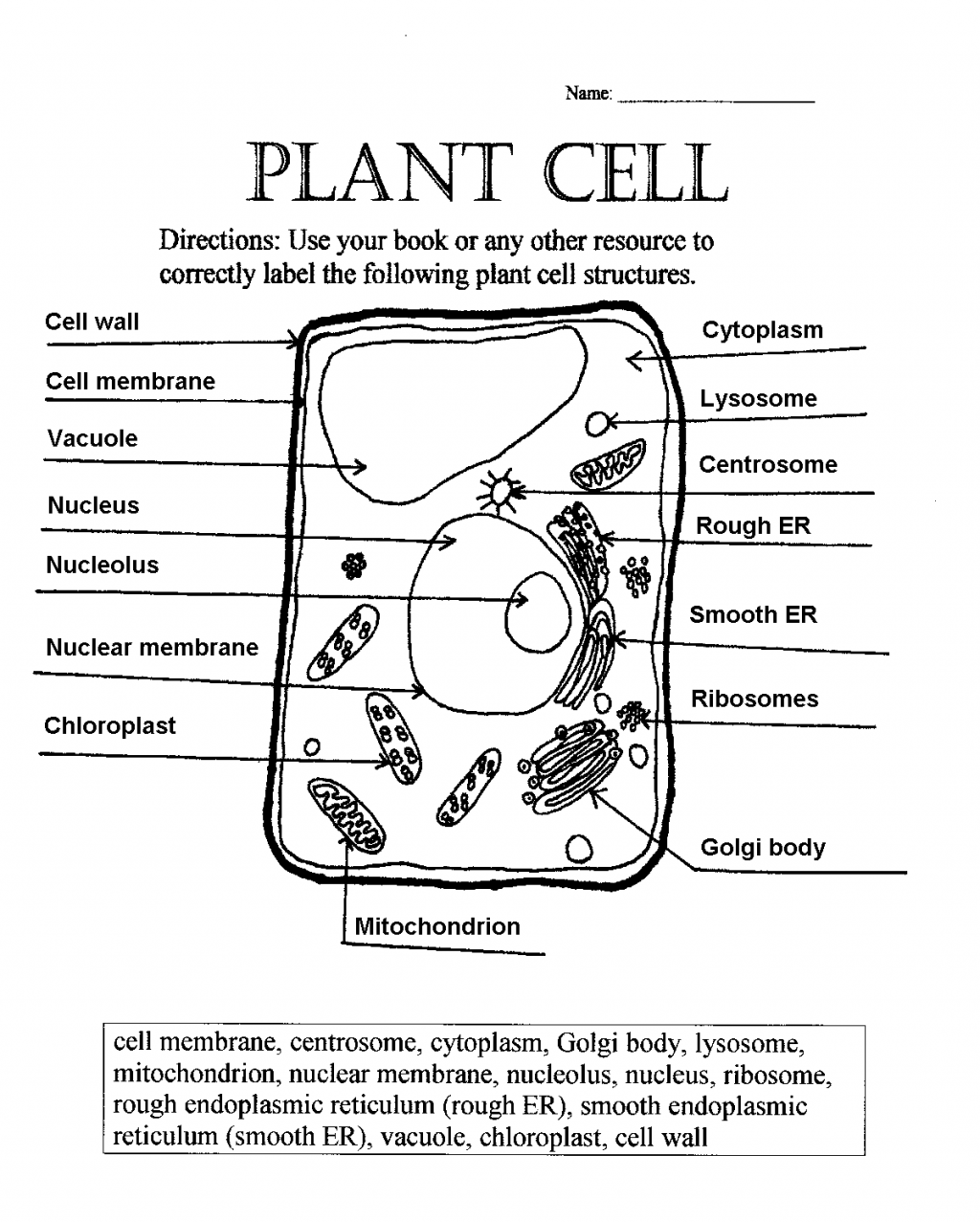
A plant cell, unlike an animal cell, has several unique organelles which are critical for its survival, growth, and function. These features include the cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole, each playing a significant role in the life of a plant.
- Cell Wall: This rigid outer layer provides structural support and protection.
- Chloroplasts: These are the powerhouses of photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
- Vacuole: The large central vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste products, maintaining turgor pressure within the cell.
🧪 Note: Understanding these key components is vital for distinguishing plant cells from animal cells and comprehending their function in a plant's ecosystem.
Components of a Plant Cell Diagram

When you're working through a plant cell diagram worksheet, it's helpful to have a clear understanding of what to look for:
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Large spherical organelle | Controls cellular activities |
| Cytoplasm | Jelly-like substance filling the cell | Medium for cell activities |
| Cell Membrane | Outer boundary of the cell | Regulates what enters and exits the cell |
| Cell Wall | Thick outer layer outside the cell membrane | Provides support and shape |
| Chloroplast | Oval-shaped organelles | Photosynthesis, energy production |
| Vacuole | Large membrane-bound space | Storage and cell expansion |
| Mitochondria | Small rod-shaped organelles | Energy production through cellular respiration |

📝 Note: Always check for clear labels in your diagrams to ensure you're correctly identifying and labeling the organelles.
Essential Tips for Completing Plant Cell Worksheets

1. Understand the Functions

Each organelle in a plant cell has a specific function. Knowing these roles will make labeling easier and help you to understand the interdependence of cell components.
2. Use Labels Clearly

Use clear, concise labels on your diagrams. Avoid cluttering the drawing with too much information. Here are some tips for labeling:
- Use arrows to point to specific organelles.
- Write labels in a consistent size and font for clarity.
- Ensure labels are close enough to the organelles but do not overlap with other labels or structures.
3. Analyze the Diagram Carefully

When completing worksheets, pay attention to the scale and positioning of organelles:
- Check if the organelles are drawn to proportion.
- Ensure the largest central vacuole is centrally placed.
- Observe the relative positions of chloroplasts, which are usually dispersed around the cell.
4. Learn to Identify Organelles by Shape and Function

Not all diagrams will be perfect or complete, so recognize the common features of organelles:
- The nucleus is often a large, central structure.
- Chloroplasts appear as small, oval, or disc-shaped structures with internal grana.
- Mitochondria can be identified by their distinctive rod-like shape.
5. Revise Plant Cell Differences

Remember the key distinctions between plant and animal cells:
- Plant cells have cell walls, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles, which animal cells lack.
- Plant cells are usually larger and have a more defined shape due to their cell walls.
🔍 Note: Understanding these differences is crucial for any biology student working on plant cell diagrams.
Final Thoughts

By now, you’ve learned the key components of plant cells and how to effectively analyze and complete plant cell diagram worksheets. Remember, clarity in labeling, understanding the function of each organelle, and recognizing the unique structures of plant cells are your best tools for success. Keep in mind the essential differences between plant and animal cells, and you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any plant cell worksheet with confidence and precision.
What’s the main difference between a plant cell and an animal cell?

+
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles, which animal cells do not have. These structures are essential for photosynthesis, structural support, and storage.
Why are chloroplasts important in plant cells?

+
Chloroplasts are crucial because they contain chlorophyll, which captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This process is vital for the plant’s growth and survival.
How do I label organelles in a plant cell diagram?

+
When labeling organelles, use clear arrows pointing to each organelle, place labels near but not overlapping structures, and ensure each label is legible and consistent in size and font.
What are some common mistakes in plant cell diagrams?

+
Common errors include misplacing organelles, drawing organelles out of proportion, or omitting key structures like the cell wall. Make sure to review your diagram carefully for these mistakes.