5 Key Answers to Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheets
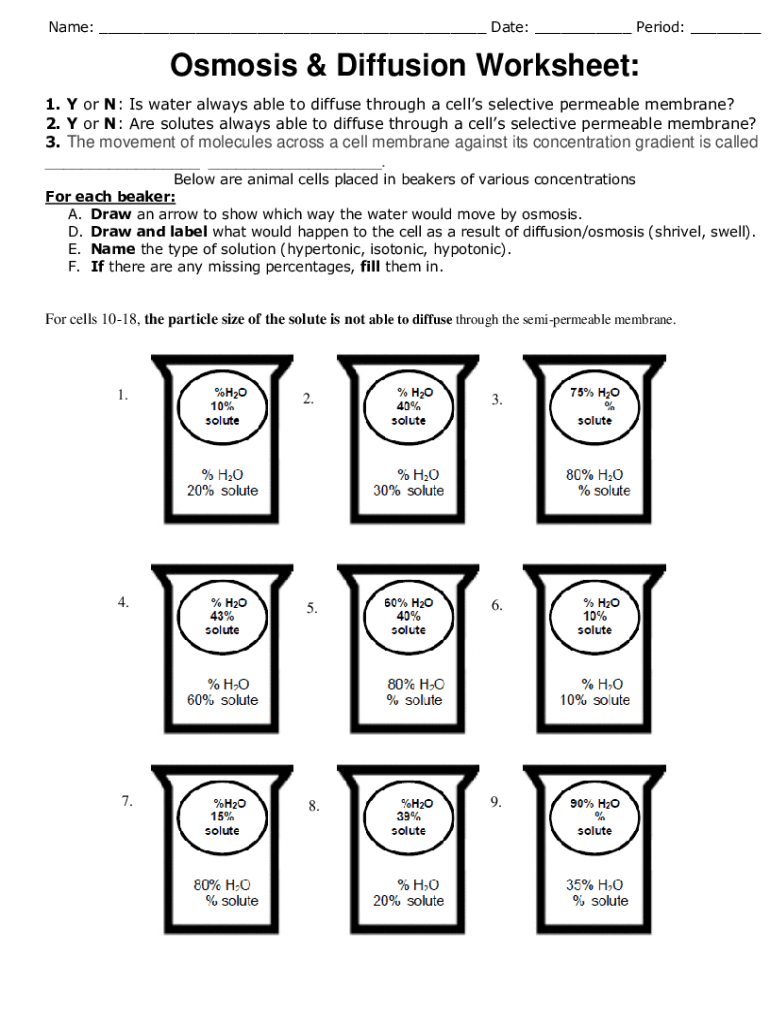
Understanding concepts like diffusion and osmosis can be a bit daunting for students, but with the right resources and explanations, these scientific phenomena become much easier to grasp. Here are five key answers to common questions on diffusion and osmosis worksheets:
What is the Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis?


Diffusion refers to the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. This process is driven by the random motion of molecules and does not require a membrane.
Osmosis, on the other hand, is the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration (hypotonic solution) to an area of higher solute concentration (hypertonic solution). This movement is also towards an equilibrium but involves water moving through a barrier that restricts the passage of solutes.
🧠 Note: Both processes aim to achieve an equilibrium, but the presence of a semi-permeable membrane is what defines osmosis.
Why Does Osmosis Happen?

Osmosis occurs due to the natural tendency of water to move across a membrane to equalize the solute concentration on both sides. Here are the primary reasons for this phenomenon:
- Equalization of Concentration: Water molecules naturally move in a way that balances the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane.
- Cellular Function: Osmosis is crucial for cells to maintain their turgidity and hydration, allowing them to perform their functions optimally.
- Pressure: Osmotic pressure plays a role, where the movement of water creates a pressure gradient that influences further osmotic flow.
💧 Note: Osmosis can affect the cell’s internal pressure, which can lead to either turgidity or flaccidity in plant cells or even cytolysis in animal cells if not managed properly.
What Factors Influence the Rate of Diffusion and Osmosis?

Several factors can influence the rate at which diffusion and osmosis occur:
| Factor | Effect on Diffusion | Effect on Osmosis |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration Gradient | Increases the rate when the difference is high. | Higher gradient increases water flow rate. |
| Surface Area | Greater surface area increases the rate. | More surface area for water to pass through increases the rate. |
| Temperature | Increased temperature speeds up molecular movement. | Higher temperature increases the kinetic energy of water molecules. |
| Pressure | Not typically a factor unless dealing with pressure gradients. | Pressure can oppose or enhance osmotic flow. |
| Presence of Membrane | Not a direct factor; diffusion happens through or around barriers. | The selectivity of the membrane affects osmosis rate. |
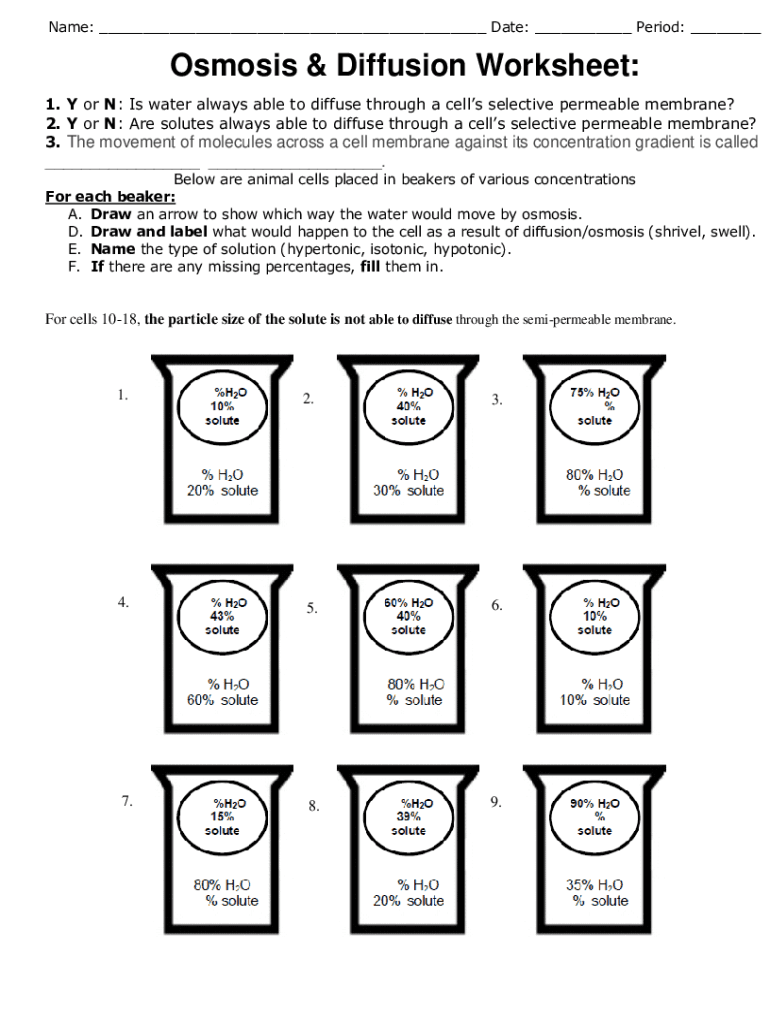
How Do These Processes Impact Living Organisms?

Both diffusion and osmosis play critical roles in the physiology of living organisms:
- Nutrient Uptake: Nutrients enter cells through diffusion, ensuring cells have the necessary resources for survival.
- Gas Exchange: Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across cell membranes to allow for respiration.
- Water Balance: Osmosis helps maintain osmotic pressure in cells, keeping them from bursting or shriveling.
- Plant Support: Turgor pressure caused by osmosis provides structural support to plants, keeping them erect.
Can You Explain Facilitated Diffusion?


Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport where substances move across cell membranes with the help of specific transport proteins. Here’s how it works:
- Substances like glucose or ions need transport proteins to move down their concentration gradient.
- These proteins act as channels or carriers, allowing molecules or ions that are too large or polar to pass through the lipid bilayer directly.
- This process does not require energy because it moves substances along their natural concentration gradient.
Facilitated diffusion is essential for substances that cannot readily cross the lipid bilayer to get into or out of the cell efficiently.
By understanding these processes, students can appreciate the complexity and efficiency of biological systems, where molecules move in an ordered yet seemingly chaotic dance to sustain life. The next time you face a worksheet on diffusion and osmosis, you'll have the tools to approach it with confidence and clarity, understanding the fundamental principles that govern these vital biological processes.
What causes plasmolysis in plant cells?

+
Plasmolysis occurs when plant cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, causing water to move out of the cell through osmosis, shrinking the cell membrane away from the cell wall due to loss of turgor pressure.
Why doesn’t facilitated diffusion require energy?

+
Facilitated diffusion involves the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient, which is a natural process that does not require the cell to expend energy. Energy is only used when moving substances against the gradient, as in active transport.
Can diffusion occur in solids?

+
Yes, diffusion can occur in solids, although at a slower rate than in liquids or gases. Solids like metals experience diffusion at high temperatures where atoms can move into available spaces, changing their properties over time.