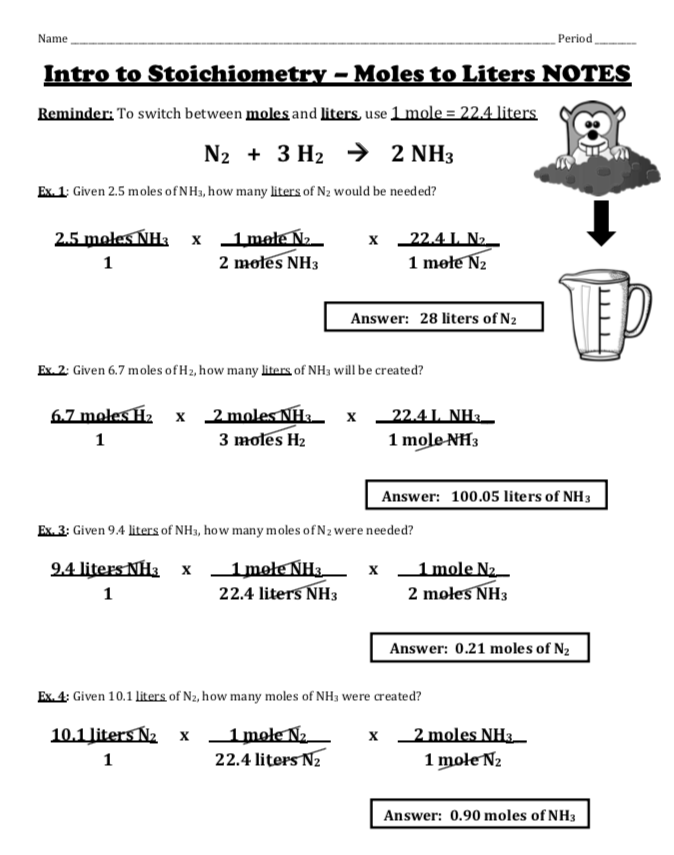
5 Must-Know Facts About Earth's Mountains

When you think of Earth's mountains, your mind might leap to the majesty of the Himalayas or the rugged beauty of the Rockies. But these geological marvels are much more than scenic vistas; they are dynamic entities that tell stories of Earth's history, climate change, and biodiversity. Let's dive into the 5 must-know facts about Earth's mountains:
Mountains Are Earth's History Book

From the oldest mountains, like the Barberton Greenstone Belt in South Africa (3.5 billion years old), to the newly formed mountains like the Hawaiian Islands (younger than 10 million years), mountains are like chapters of Earth's geological narrative:
- Orogenesis: The process of mountain building, which involves tectonic plate movements, folding, and faulting, has been instrumental in shaping mountain ranges over millions of years.
- Rock Types: Igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, each tell a different story about the past environmental conditions and events.
📘 Note: You can find the story of plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and even ancient climates by studying the rock formations within mountains.
Mountains Influence Climate

Far from being just passive features on the landscape, mountains actively engage in the global climate system:
- Barrier to Atmospheric Flow: They act as barriers to winds, creating distinct climate zones on either side of mountain ranges. An example is the Tibetan Plateau, which creates the monsoon rains in Southeast Asia.
- Altitude Effects: High mountain summits can have climates much different than surrounding lowlands. For instance, the climate on Mount Everest's peak would be classified as Arctic, despite its latitude.
Mountains Are Biodiversity Hotspots

Due to their vertical diversity, mountains host an incredible array of life forms:
- Elevation Zones: Each vertical zone has different temperature, humidity, and species adapted to these conditions.
- Isolation and Adaptation: Many species have evolved in isolation, leading to unique endemism, like the Mountain Gorillas of the Virunga Range.
🌱 Note: Conservation efforts often focus on mountain ecosystems due to their high levels of biodiversity and threats from climate change and human activities.
Economic and Cultural Significance

Mountains aren't just geological features; they are deeply woven into human life:
- Economic Value: Tourism, mining, hydroelectric power, and agriculture all thrive because of mountains. For instance, the Alps in Europe offer both skiing resorts and hydroelectricity.
- Cultural Heritage: From sacred peaks like Mount Kailash in the Himalayas to cultural traditions in the Andes, mountains are integral to local cultures and histories.
| Mountain Range | Economic Activity |
|---|---|
| Alps | Ski Resorts, Hydropower |
| Himalayas | Tourism, Trekking, Cultural significance |

Mountains Are Undergoing Change

As Earth's climate changes, mountains face threats from various sources:
- Glacier Retreat: With global warming, glaciers are melting at an accelerated rate, changing water availability for nearby populations.
- Human Impact: Mining, deforestation, and urbanization are altering mountain landscapes at an unprecedented scale.
🔍 Note: Researchers like those from the Glaciological Survey of Norway are monitoring glacier changes to better understand climate effects.
To wrap up, mountains are far more than just towering natural wonders. They offer us a glimpse into the past, shape our present, and are critical in understanding our future. Their influence on weather patterns, their rich biodiversity, their economic and cultural importance, and their susceptibility to change are key aspects we must appreciate to understand Earth's dynamic nature. By recognizing and conserving these natural wonders, we are ensuring not just their longevity, but also our own.
What causes mountains to form?

+
Mountains form due to orogenic processes like the collision of tectonic plates, volcanic activity, and the folding and faulting of the Earth’s crust.
How does climbing affect mountain ecosystems?

+
Climbing can disturb fragile ecosystems, leaving trash, polluting water sources, and impacting the flora and fauna that live at high altitudes.
Why are mountains important for water resources?

+
Mountains are often the source of rivers and lakes, providing essential fresh water to lower elevations through snowmelt, glaciers, and rain.
Can mountains predict future climate patterns?

+
Yes, by studying changes in mountain ecosystems, like glacier retreat and shifts in snow lines, scientists can infer trends about future climate change.
How do mountains impact weather and climate?

+
Mountains create rain shadows, influence wind patterns, and due to elevation changes, have various microclimates, which collectively affect regional weather and climate.