5 Must-Know Answers for Phase Change Worksheet
Phase changes are fundamental to understanding the behavior of matter in different conditions. Whether it's the solid melting into liquid or a liquid evaporating into gas, each transition has its unique properties and implications. For students tackling a phase change worksheet, there are five crucial questions that often appear, each with their own depth and significance in the realm of physical science. Here, we will delve into these must-know answers to provide clarity and understanding.
Understanding the Nature of Phase Changes

A phase change is a transformation where a substance transitions from one phase of matter to another. These changes occur when a system experiences modifications in pressure, temperature, or other external conditions. Here are the essential phases of matter:
- Solid: The particles are tightly packed with fixed positions.
- Liquid: Molecules are closer but have more freedom to move around.
- Gas: Particles are widely spaced with high kinetic energy.
- Plasma: A hot, ionized gas with free electrons.
- Bose-Einstein Condensate: A state where particles at extremely low temperatures occupy the same quantum state.
1. What is the Relationship Between Heat and Phase Changes?

Heat plays a critical role in phase changes. Here’s how:
- Endothermic Processes: Heat is absorbed by the substance. Examples include melting (solid to liquid) and evaporation (liquid to gas).
🔥 Note: During an endothermic phase change, the temperature of the substance does not increase despite the addition of heat because it is used to overcome the intermolecular forces holding the particles together.
- Exothermic Processes: Heat is released when the substance changes phase. Examples are freezing (liquid to solid) and condensation (gas to liquid).
2. How Does Pressure Affect Phase Changes?

Pressure significantly influences phase transitions:
- Increasing pressure can cause a substance to solidify at a higher temperature than usual (e.g., making ice at room temperature).
- Conversely, decreasing pressure can make boiling points lower, as seen with high-altitude cooking.
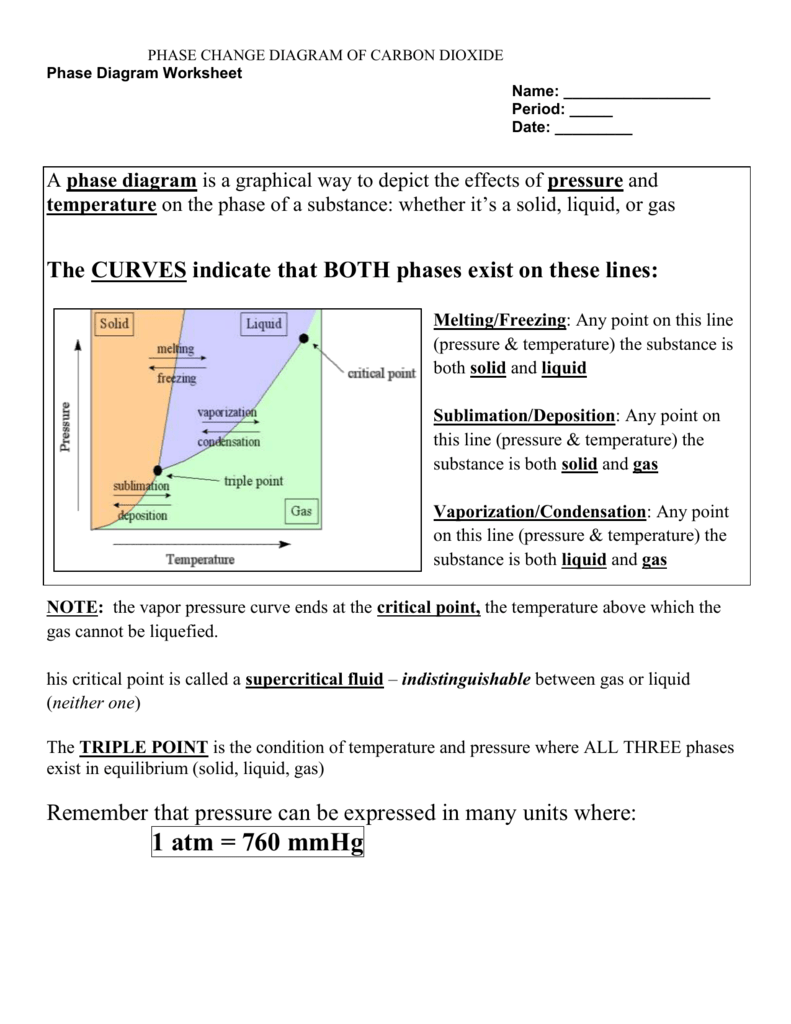
🔔 Note: Phase diagrams illustrate the conditions under which substances change phase at different pressures and temperatures.
3. What is Latent Heat?
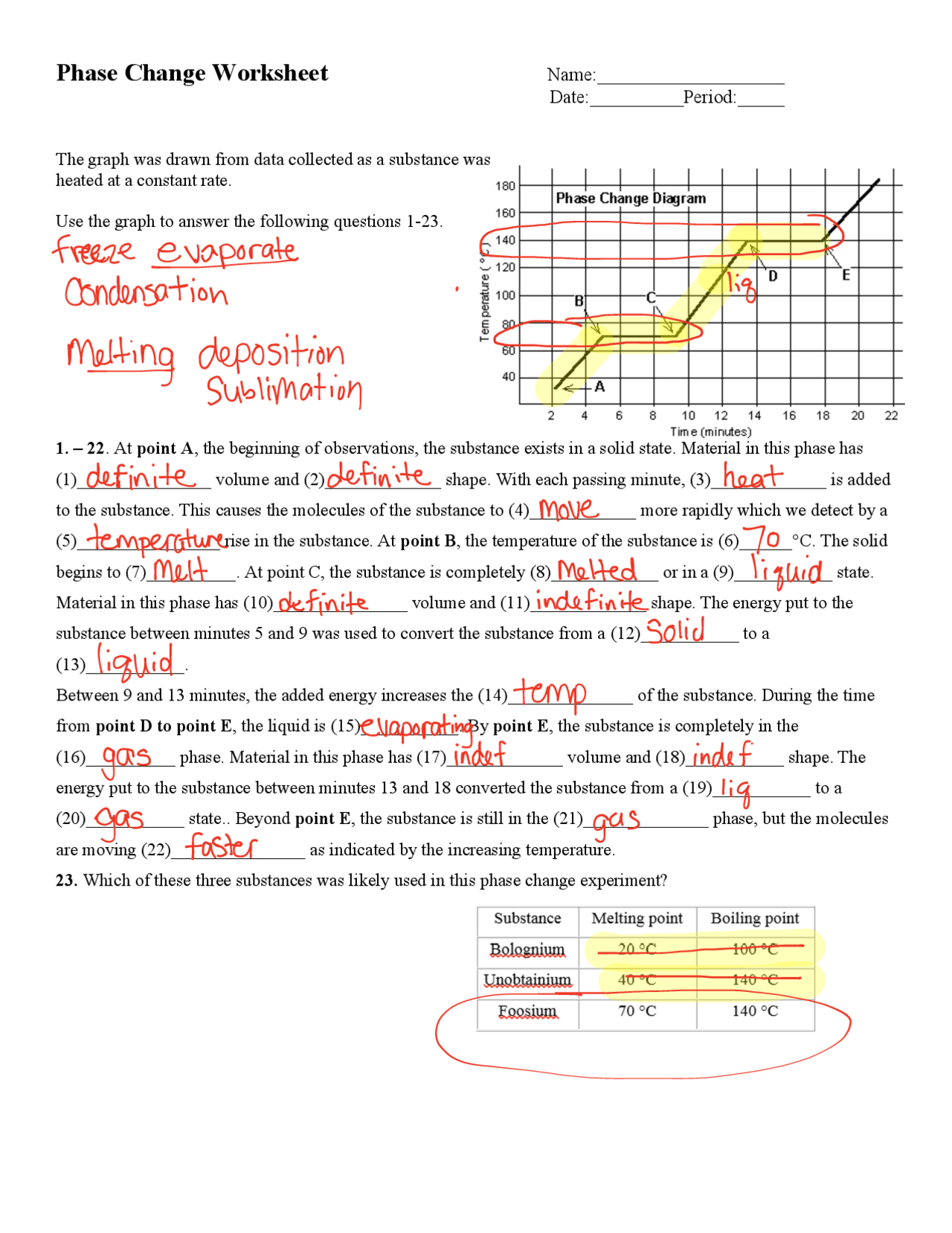
Latent heat is the energy required for phase changes without changing the temperature of the substance. Here are the two types:
| Type of Latent Heat | Description |
|---|---|
| Fusion | The heat needed to change a solid to a liquid at its melting point. |
| Vaporization | The heat needed to change a liquid to a gas at its boiling point. |

🔬 Note: This heat is hidden because there's no temperature rise during the phase transition, making latent heat an essential concept in thermodynamics.
4. Why Does Sublimation Occur?

Sublimation is the process where a solid changes directly into a gas without going through the liquid phase:
- It occurs at the substance’s triple point, where all three phases coexist in equilibrium.
- Factors like low pressure or specific temperatures can facilitate sublimation.
- Example: Dry ice (frozen carbon dioxide) sublimates at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
5. How Do Molecular Forces Affect Phase Changes?

The strength and nature of intermolecular forces determine how easily substances change phase:
- Strong Forces: Substances with strong intermolecular forces require more energy to change phase.
- Weak Forces: Substances like noble gases have weak forces, allowing for lower phase transition energies.
This understanding brings us to the heart of many physical phenomena, from water's unusual density changes upon freezing to the formation of frost on a chilly night.
Summing Up

In summary, phase changes involve transitions between different states of matter, each requiring a unique set of conditions to occur. By understanding the relationships between heat, pressure, latent heat, sublimation, and intermolecular forces, students can better navigate the complexities of phase change worksheets. Not only does this knowledge aid in solving problems, but it also provides a deeper appreciation for the world around us, where phase changes occur incessantly in various forms and contexts.
Why do some substances undergo sublimation?

+
Sublimation happens when a substance’s vapor pressure exceeds the pressure exerted on it at temperatures below its melting point. This is due to the substance’s molecular structure and external conditions, like low atmospheric pressure.
Can a substance change phase without changing its temperature?

+
Yes, during a phase transition, the temperature remains constant as the energy supplied or released is used to change the arrangement of particles, not their kinetic energy.
How can increasing pressure cause a substance to freeze?

+
By increasing pressure, you decrease the distance between particles, which can force them into a more ordered state (solid) at higher temperatures than usual. This phenomenon is called freezing under pressure.