5 Essential Tips for Mastering Specific Heat and Heat Capacity

Understanding and mastering specific heat and heat capacity is not just a fundamental part of physics and chemistry; it's a gateway to understanding thermal dynamics in real-world applications. Whether you're a student gearing up for a thermodynamics exam or an engineer working on energy-efficient systems, knowing these concepts can significantly enhance your analytical capabilities. Here's a detailed guide to help you master these topics:
1. Grasp the Basics: Defining Specific Heat and Heat Capacity


Specific heat © is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius or Kelvin. The formula for specific heat is:
[ c = \frac{Q}{m \Delta T} ]- Q - Heat added (or removed)
- m - Mass of the substance
- ΔT - Change in temperature
On the other hand, heat capacity © is the amount of heat energy needed to change the temperature of the entire sample of a substance by one degree. It is often given by:
[ C = mc ]💡 Note: Heat capacity is dependent on the mass of the substance, whereas specific heat is an intrinsic property that does not change with the amount of material.
2. Practice Calculations for Different Substances


Work through problems involving water, metals, and other common substances. Here are steps to follow:
- Identify the mass, initial and final temperatures, and the heat involved.
- Use the specific heat capacity values provided in tables or resources.
- Plug these values into the specific heat formula or heat capacity formula to solve for unknown variables.
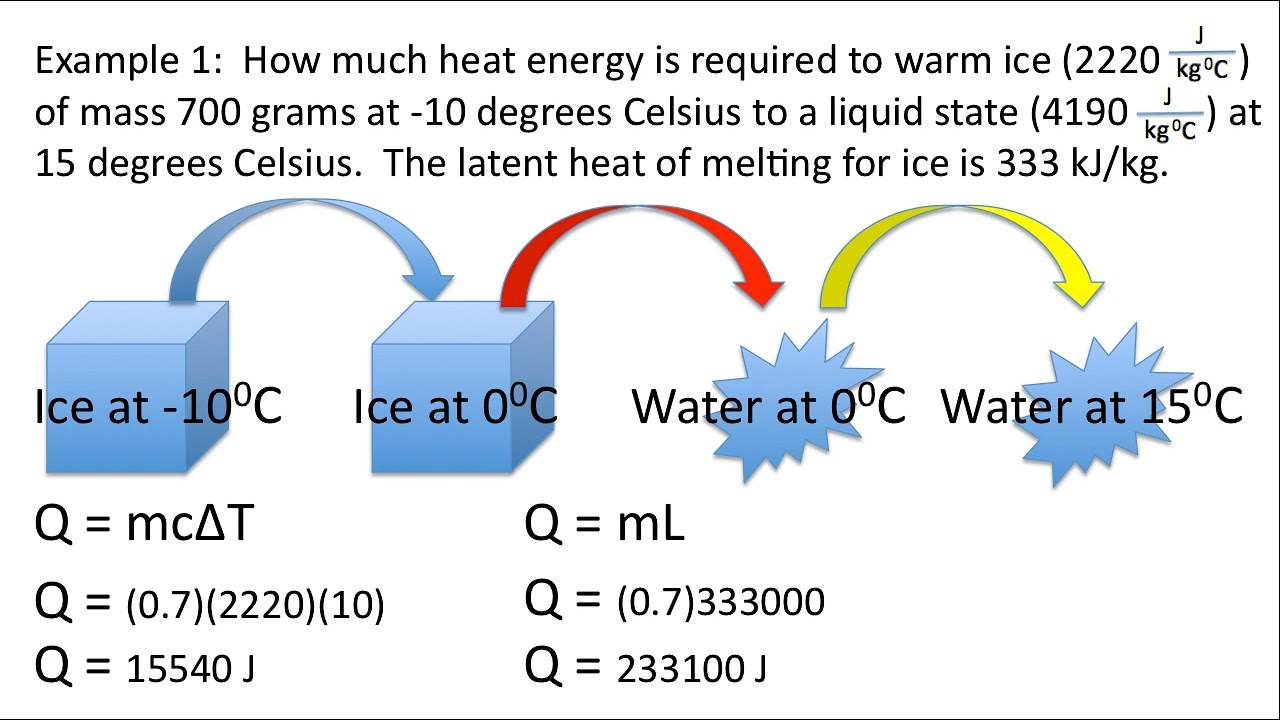
- Use latent heat values for phase changes like melting or evaporation. This involves the energy to change the phase at constant temperature, not to change the temperature itself.
- Be aware of how heat capacity changes with phase, which affects the energy calculations.
- Discuss how heat capacity affects the choice of materials in engineering projects, like insulating materials or heat sinks.
- Explore real-life scenarios where understanding specific heat is crucial, such as in thermal energy storage systems or cooling mechanisms in industrial applications.
- Analyze case studies involving specific heat in cooking, climate control systems, or geothermal energy utilization.
- Use simulation software like PhET Interactive Simulations or other physics engines to experiment with heat transfer and observe phase changes.
- Leverage online calculators to quickly verify your calculations or understand how variables interact.
- Study interactive graphs that show the relationship between heat, temperature, and phase transitions.
- Specific heat and heat capacity are pivotal for understanding how substances react to temperature changes.
- They have wide-ranging applications in science, engineering, and daily life.
- Practice with real-world examples and simulations to solidify your understanding.
📝 Note: Pay close attention to units. Specific heat can be given in J/(g·°C), kJ/(kg·K), or other units. Ensure all units are consistent for accuracy.
3. Understand the Phases and Phase Changes


When dealing with substances undergoing phase changes:
❗ Note: During phase changes, heat is added or removed, but the temperature does not change until the phase change is complete.
4. Incorporate Practical Applications

To make your learning real and applicable:
5. Engage with Digital Tools and Simulations

Modern technology offers an array of simulations and educational software to visualize and interact with these concepts:
🔧 Note: Interactive tools not only make learning enjoyable but also allow you to experience phenomena that might be difficult or unsafe to replicate in a classroom setting.
As you delve deeper into the world of specific heat and heat capacity, keep in mind these foundational principles:
By internalizing these tips, not only will you excel in academic assessments but also gain insights into thermal dynamics that can enhance your professional endeavors. The nuanced understanding of these concepts can drive innovations in energy efficiency, thermal management, and beyond.
What is the difference between specific heat and heat capacity?

+
Specific heat is an intrinsic property of a substance, indicating the heat needed to raise one unit of mass by one degree, whereas heat capacity is the energy needed to change the entire substance’s temperature by one degree, dependent on its mass.
Why is the specific heat of water higher than most other materials?

+
Water has a high specific heat due to its strong hydrogen bonding. It takes more energy to break these bonds and raise its temperature, making it an excellent coolant and heat storage medium.
How can I apply knowledge of specific heat in daily life?
+
Understanding specific heat helps in selecting materials for insulation, choosing cookware that distributes heat evenly, or understanding why some places have milder climates due to the proximity to large bodies of water.
Related Terms:
- Mass
- Specific heat capacity Worksheet pdf
- Specific heat Worksheet 1