Navy Officer Ranks Explained Simply

Navy Officer Ranks: A Comprehensive Guide
The naval ranks are a crucial aspect of the Navy’s hierarchical structure, defining the roles, responsibilities, and chain of command. Understanding the different ranks can be overwhelming, especially for those new to the Navy or considering a career in the maritime forces. In this article, we will delve into the world of Navy officer ranks, explaining each rank in detail, from the lowest to the highest.
Warrant Officer Ranks
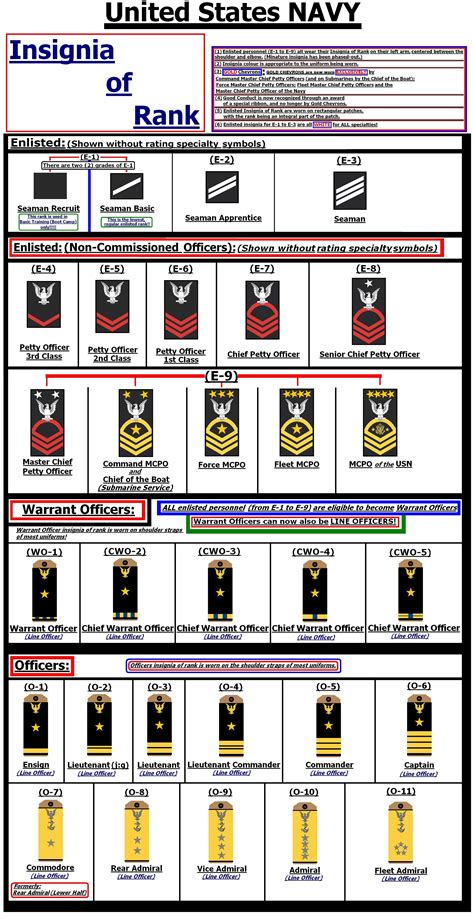
Warrant Officers (WOs) are technical experts in their field, holding a unique position between enlisted personnel and commissioned officers. They possess specialized skills and knowledge, often gained through years of experience and training.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CWO5): The highest warrant officer rank, CWO5s serve as technical experts and leaders in their field, often holding key positions in the Navy’s technical and operational sectors.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CWO4): CWO4s are experienced technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and expertise in their field.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CWO3): CWO3s are technical specialists who have achieved a high level of proficiency and serve as leaders in their field.
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): WO1s are entry-level warrant officers who have completed the necessary training and education to become technical experts in their field.
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned Officers are the leaders of the Navy, responsible for commanding ships, units, and personnel. They are divided into several categories, including Line Officers, Staff Corps Officers, and Limited Duty Officers.
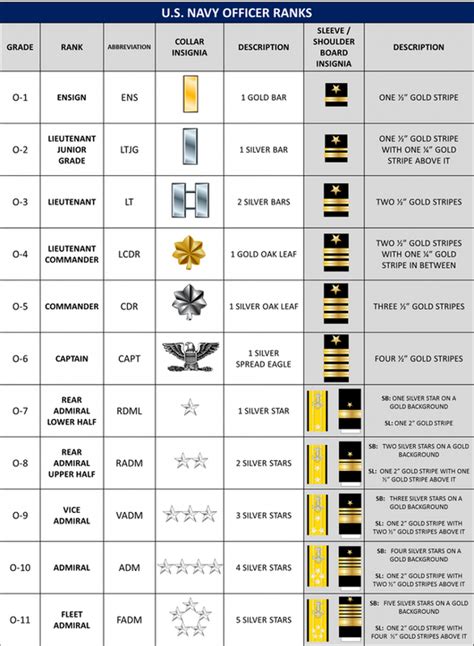
- Ensign (ENS): The most junior commissioned officer rank, Ensigns are typically recent graduates of the Naval Academy or Officer Candidate School.
- Lieutenant Junior Grade (LTJG): LTJGs are junior officers who have gained some experience and are working towards becoming more senior leaders.
- Lieutenant (LT): Lieutenants are experienced officers who have demonstrated leadership and technical skills, often serving as department heads or executive officers.
- Lieutenant Commander (LCDR): LCDRs are senior officers who have gained significant experience and are preparing for more senior leadership roles.
- Commander (CDR): Commanders are senior leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills, often serving as executive officers or commanding smaller units.
- Captain (CAPT): Captains are senior officers who have achieved a high level of leadership and technical expertise, often serving as commanding officers of larger units or in senior staff positions.
Flag Officer Ranks

Flag Officers are the most senior leaders in the Navy, responsible for commanding large units, fleets, and entire naval forces.
- Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (RDML): RDMLs are one-star admirals who have achieved a high level of leadership and technical expertise, often serving as commanders of smaller fleets or task forces.
- Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (RADM): RADM is a two-star admiral rank, typically serving as commanders of larger fleets or task forces.
- Vice Admiral (VA): VAs are three-star admirals who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills, often serving as deputy commanders of entire naval forces.
- Admiral (ADM): ADM is the highest rank in the Navy, typically serving as the Chief of Naval Operations or as a senior leader in the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
Special Titles and Positions

- Aviator: A specialized title for officers who have qualified as naval aviators.
- Submariner: A specialized title for officers who have qualified as submariners.
- Surface Warfare Officer: A specialized title for officers who have qualified as surface warfare officers.
- Naval Flight Officer: A specialized title for officers who have qualified as naval flight officers.
💡 Note: The ranks and titles listed above are specific to the United States Navy. Other navies may have similar ranks and titles, but with different designations and responsibilities.
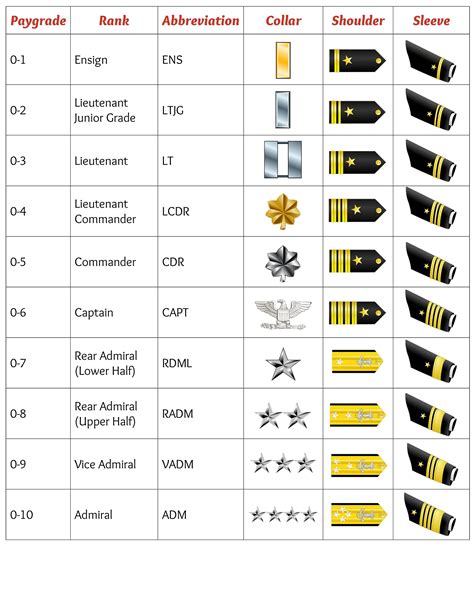
Officer Rank Insignia

| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Ensign | One gold bar |
| Lieutenant Junior Grade | One gold bar with a silver oak leaf |
| Lieutenant | Two gold bars |
| Lieutenant Commander | Two and a half gold bars |
| Commander | Three gold bars |
| Captain | Four gold bars |
| Rear Admiral (Lower Half) | One star |
| Rear Admiral (Upper Half) | Two stars |
| Vice Admiral | Three stars |
| Admiral | Four stars |

🔍 Note: The insignia listed above are for the United States Navy. Other navies may have similar insignia, but with different designs and colors.
In conclusion, understanding the Navy officer ranks is essential for anyone considering a career in the maritime forces or wanting to learn more about the Navy’s hierarchical structure. From Warrant Officers to Flag Officers, each rank plays a crucial role in the Navy’s operations and leadership. By recognizing the different ranks and their responsibilities, individuals can better appreciate the complexity and organization of the Navy.
What is the lowest officer rank in the Navy?
+
The lowest officer rank in the Navy is Ensign (ENS).
What is the highest officer rank in the Navy?
+
The highest officer rank in the Navy is Admiral (ADM).
What is the difference between a Warrant Officer and a Commissioned Officer?

+
Warrant Officers are technical experts in their field, while Commissioned Officers are leaders who command ships, units, and personnel.