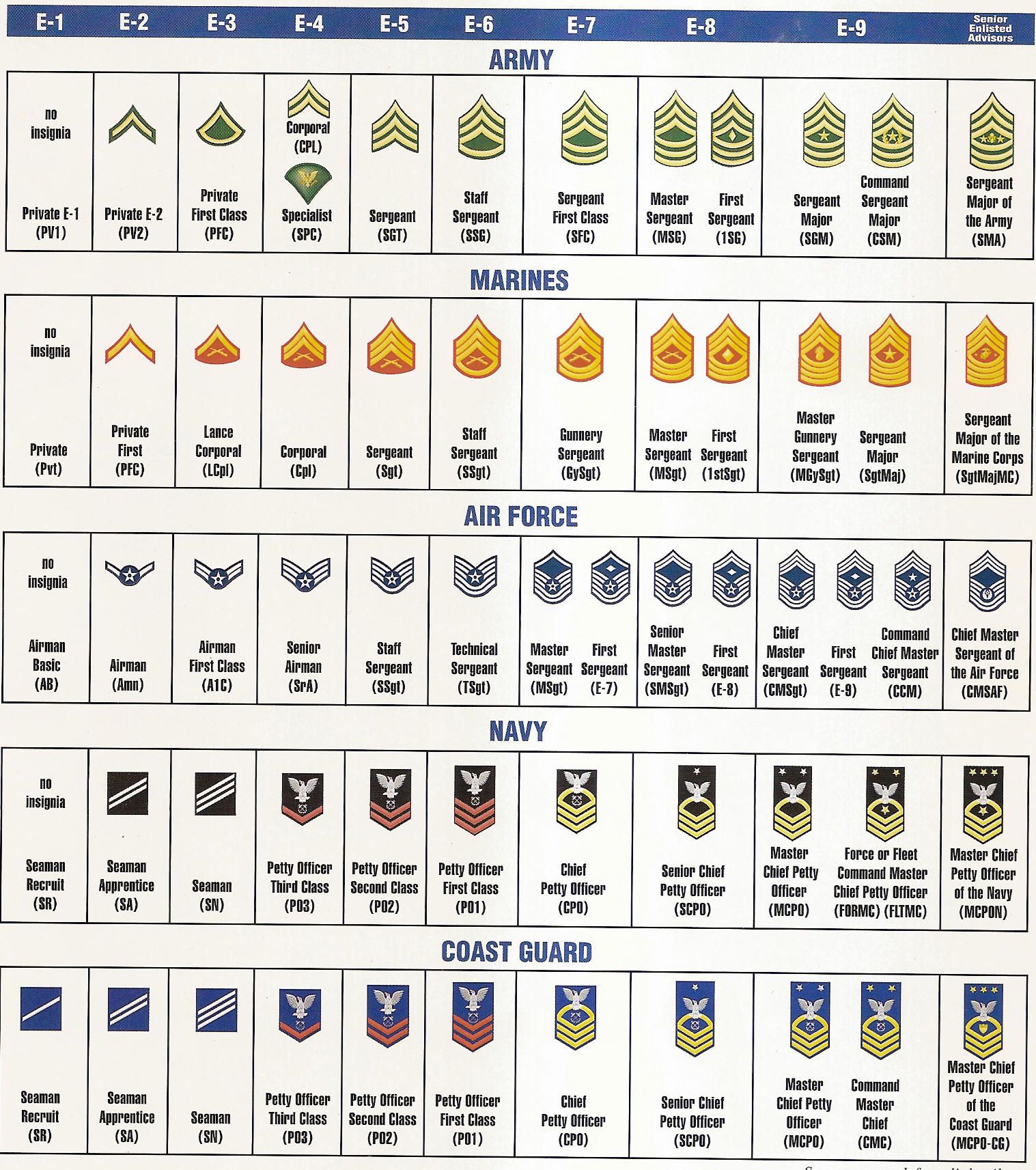
11 Navy Officer Ranks in Order
Navy Officer Ranks: A Comprehensive Guide

The Navy is a vital part of any country’s defense system, and its officer ranks play a crucial role in maintaining the discipline, organization, and effectiveness of the naval forces. In this article, we will explore the 11 Navy officer ranks in order, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of the responsibilities, requirements, and career progression for each rank.
Understanding Navy Officer Ranks
Before we dive into the specifics of each rank, it’s essential to understand the basics of Navy officer ranks. The Navy uses a combination of commissioning sources, including the United States Naval Academy, Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (ROTC), and Officer Candidate School (OCS), to recruit and train its officers. The officer ranks are divided into three main categories: junior officers, senior officers, and flag officers.
Junior Officer Ranks
Junior officers are the entry-level officers in the Navy, responsible for leading small teams and executing specific tasks. The junior officer ranks in order are:
1. Ensign (O-1)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, commissioning through OCS, ROTC, or the Naval Academy
- Responsibilities: Basic division officer, assists in leading a team of sailors
- Career progression: Typically serves as a division officer on a ship or at a shore-based facility
2. Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 18-24 months of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a team of sailors, may serve as a department head or executive officer on a small ship
- Career progression: May serve as a department head or executive officer on a larger ship or at a shore-based facility
3. Lieutenant (O-3)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 3-5 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a department or division on a ship or at a shore-based facility, may serve as an executive officer on a large ship
- Career progression: May serve as an executive officer on a large ship or as a department head at a shore-based facility
Senior Officer Ranks
Senior officers are experienced leaders who have demonstrated exceptional skills and dedication to the Navy. The senior officer ranks in order are:
4. Lieutenant Commander (O-4)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 6-10 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a department or division on a large ship or at a shore-based facility, may serve as an executive officer on a carrier or large amphibious ship
- Career progression: May serve as an executive officer on a carrier or large amphibious ship or as a department head at a shore-based facility
5. Commander (O-5)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 10-15 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a department or division on a carrier or large amphibious ship, may serve as a commanding officer on a small ship
- Career progression: May serve as a commanding officer on a large ship or as a department head at a shore-based facility
6. Captain (O-6)
- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 15-20 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a department or division on a large ship or at a shore-based facility, may serve as a commanding officer on a large ship
- Career progression: May serve as a commanding officer on a carrier or large amphibious ship or as a department head at a shore-based facility
Flag Officer Ranks
Flag officers are the most senior leaders in the Navy, responsible for making strategic decisions and leading large organizations. The flag officer ranks in order are:
7. Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (O-7)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 20-25 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a task force or a group of ships, may serve as a deputy commander of a fleet
- Career progression: May serve as a deputy commander of a fleet or as a department head at a shore-based facility
8. Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (O-8)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 25-30 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a fleet or a group of task forces, may serve as a commander of a naval component
- Career progression: May serve as a commander of a naval component or as a department head at a shore-based facility
9. Vice Admiral (O-9)

- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 30-35 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads a fleet or a group of naval components, may serve as a deputy chief of naval operations
- Career progression: May serve as a deputy chief of naval operations or as a department head at a shore-based facility
10. Admiral (O-10)
- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 35-40 years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads the Navy as the Chief of Naval Operations, may serve as the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff
- Career progression: May serve as the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff or as a department head at a shore-based facility
11. Fleet Admiral (O-10)
- Requirements: Bachelor’s degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 40+ years of commissioned service
- Responsibilities: Leads the Navy as the senior-most officer, may serve as a special advisor to the President
- Career progression: May serve as a special advisor to the President or as a department head at a shore-based facility
Conclusion
The Navy officer ranks are a complex and nuanced system, with each rank requiring a specific set of skills, experience, and education. From the junior officer ranks to the flag officer ranks, each officer plays a critical role in the success of the Navy. By understanding the responsibilities, requirements, and career progression for each rank, individuals can better navigate their own careers and make informed decisions about their future in the Navy.
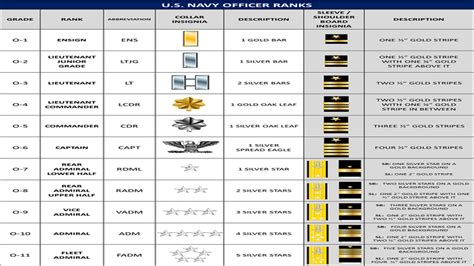
Table: Navy Officer Ranks at a Glance
| Rank | Abbreviation | Requirements | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ensign | O-1 | Bachelor's degree, commissioning through OCS, ROTC, or the Naval Academy | Basic division officer, assists in leading a team of sailors |
| Lieutenant Junior Grade | O-2 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 18-24 months of commissioned service | Leads a team of sailors, may serve as a department head or executive officer on a small ship |
| Lieutenant | O-3 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 3-5 years of commissioned service | Leads a department or division on a ship or at a shore-based facility, may serve as an executive officer on a large ship |
| Lieutenant Commander | O-4 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 6-10 years of commissioned service | Leads a department or division on a large ship or at a shore-based facility, may serve as an executive officer on a carrier or large amphibious ship |
| Commander | O-5 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 10-15 years of commissioned service | Leads a department or division on a carrier or large amphibious ship, may serve as a commanding officer on a small ship |
| Captain | O-6 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 15-20 years of commissioned service | Leads a department or division on a large ship or at a shore-based facility, may serve as a commanding officer on a large ship |
| Rear Admiral (Lower Half) | O-7 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 20-25 years of commissioned service | Leads a task force or a group of ships, may serve as a deputy commander of a fleet |
| Rear Admiral (Upper Half) | O-8 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 25-30 years of commissioned service | Leads a fleet or a group of task forces, may serve as a commander of a naval component |
| Vice Admiral | O-9 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 30-35 years of commissioned service | Leads a fleet or a group of naval components, may serve as a deputy chief of naval operations |
| Admiral | O-10 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 35-40 years of commissioned service | Leads the Navy as the Chief of Naval Operations, may serve as the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff |
| Fleet Admiral | O-10 | Bachelor's degree, completion of OCS or ROTC, and 40+ years of commissioned service | Leads the Navy as the senior-most officer, may serve as a special advisor to the President |

FAQ Section
What is the lowest Navy officer rank?
+The lowest Navy officer rank is Ensign (O-1).
How long does it take to become a Navy Admiral?
+Typically, it takes 35-40 years of commissioned service to become a Navy Admiral.
What is the difference between a Commander and a Captain in the Navy?
+A Commander (O-5) leads a department or division on a carrier or large amphibious ship, while a Captain (O-6) leads a department or division on a large ship or at a shore-based facility.