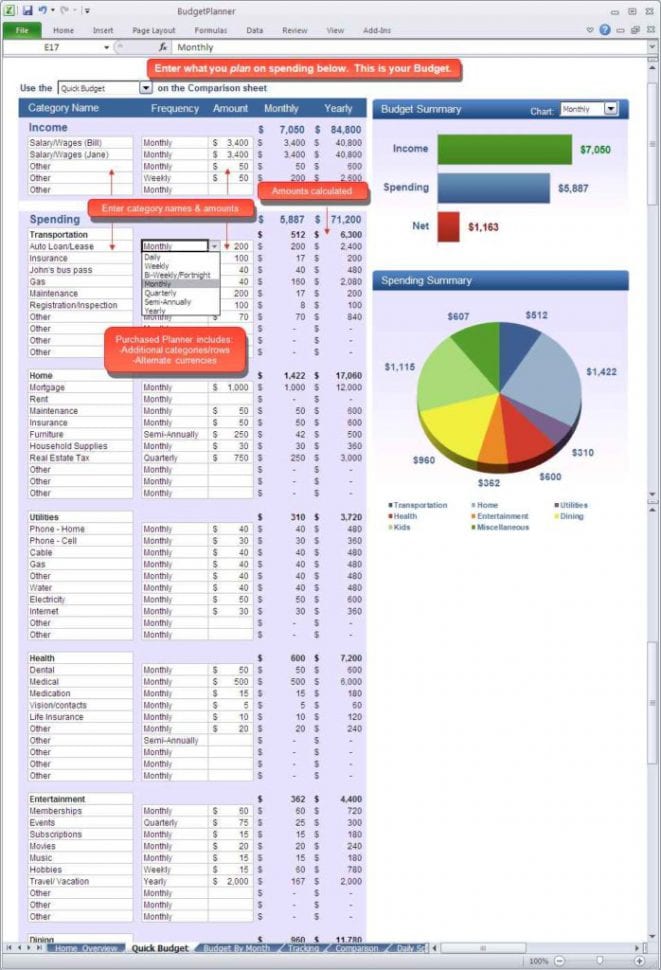
5 Steps to Master Naming Acids and Bases

Understanding how to name acids and bases is crucial for students, scientists, and enthusiasts of chemistry. Whether you're preparing for an exam or deepening your knowledge of chemical reactions, mastering this naming convention will streamline your learning and communication within the scientific community.
What are Acids and Bases?


In chemistry, an acid is typically a substance that produces hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water, often characterized by their sour taste and the ability to turn blue litmus paper red. Conversely, a base, sometimes called an alkali, is known for releasing hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in an aqueous solution, having a bitter taste, and turning red litmus paper blue. They are essential in many chemical processes, from industrial manufacturing to biological systems.
Steps to Naming Acids

Naming acids involves recognizing the anion and following a set of straightforward rules:
1. Identify the Anion

- Determine the name of the anion involved in the acid.
🔍 Note: Common anions like chloride, nitrate, sulfate, etc., form the basis for naming most acids.
2. Use Prefixes

- If the anion ends in -ide, replace it with -ic acid (e.g., chloride becomes hydrochloric acid).
- If the anion ends in -ate, use -ic acid (e.g., nitrate becomes nitric acid).
- If the anion ends in -ite, use -ous acid (e.g., nitrite becomes nitrous acid).
💡 Note: The prefix ‘hydro-’ is only used for acids containing hydrogen and a non-oxygen anion.
3. Add “Hydro” When Necessary

- When dealing with binary acids (hydrogen and one nonmetal), add hydro- at the beginning (e.g., HBr becomes hydrobromic acid).
4. Handle Polyanions
- For acids with polyatomic ions, skip the hydro prefix and follow the rules for -ate and -ite anions.
5. Check for Exceptions

- Keep in mind exceptions like acetic acid (from ethanoic acid) or common names like sulfuric acid.
Naming Bases

Naming bases is often less complex than naming acids, but here are the steps to follow:
1. Identify the Metal

- The name of the base often begins with the metal ion involved (e.g., sodium in NaOH).
2. Use the Hydroxide Suffix

- Bases that produce hydroxide ions when dissolved are given the suffix -hydroxide (e.g., NaOH is sodium hydroxide).
3. Handle Exceptions

- There are a few exceptions, like ammonia, which is technically not named as a hydroxide but is still considered a base.
Importance of Correct Naming

Knowing how to properly name acids and bases helps in:
- Communication: It allows for clear communication among scientists and researchers.
- Chemical Equations: Accurate names make writing chemical equations easier and more precise.
- Reactivity Predictions: Understanding the nature of acids and bases aids in predicting their chemical behavior.
- Safety: In laboratories and industries, correctly identifying substances ensures safe handling.
As you master these steps, you'll find that naming acids and bases becomes second nature. This proficiency will not only enhance your understanding of chemical reactions but also simplify the learning of more advanced topics in chemistry.
Why is it important to use proper chemical names?

+
Proper chemical names avoid confusion, promote clear communication, and are essential for accurately understanding and conveying chemical reactions and safety protocols.
What’s the difference between an acid and a base?

+
Acids are substances that release H+ ions when dissolved in water, whereas bases produce OH- ions or can accept protons. They have different chemical properties and reactions.
Can acids and bases be neutralized?
+Yes, when acids and bases react in the right proportions, they can neutralize each other, forming water and a salt.
How do you identify a polyatomic ion?
+Polyatomic ions are charged groups of atoms bonded together, like SO₄²⁻ (sulfate). You’ll recognize them by their charge and structure different from single atoms.
What happens if I misname an acid or base?
+Misnaming can lead to incorrect chemical reactions, misunderstanding of properties, and safety issues in experimental settings or industry applications.