Mitosis vs Meiosis: Worksheet Answer Key Revealed

What is Mitosis?

Mitosis is a fundamental cellular process that occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, characterized by the division of the parent cell into two identical daughter cells. This process is pivotal in growth, development, and repair in multicellular organisms.
Key Steps in Mitosis:
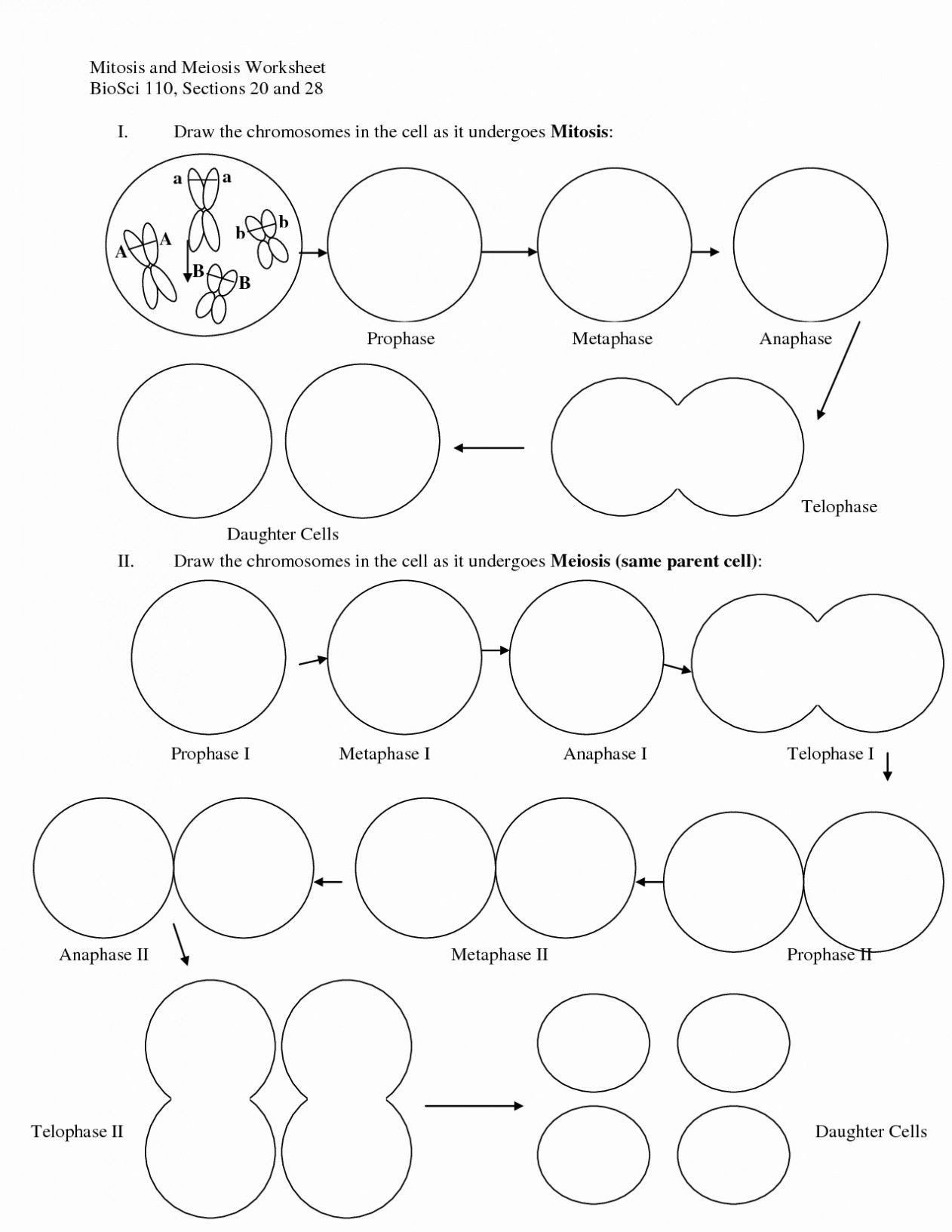
- Prophase: The chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane dissolves, and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
- Metaphase: The chromosomes align along the middle of the cell.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids are pulled apart and move to opposite poles.
- Telophase: Chromosomes de-condense, new nuclear envelopes form, and the cell prepares for cytokinesis.
- Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides, creating two separate daughter cells, each with an identical set of chromosomes.
What is Meiosis?

Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the production of gametes (sex cells) in sexually reproducing organisms. Unlike mitosis, meiosis involves two sequential divisions:
- Meiosis I: Consists of prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, and telophase I, leading to a reduction in chromosome number.
- Meiosis II: Similar to mitosis, it includes prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II, with no DNA replication between the two meiotic phases.
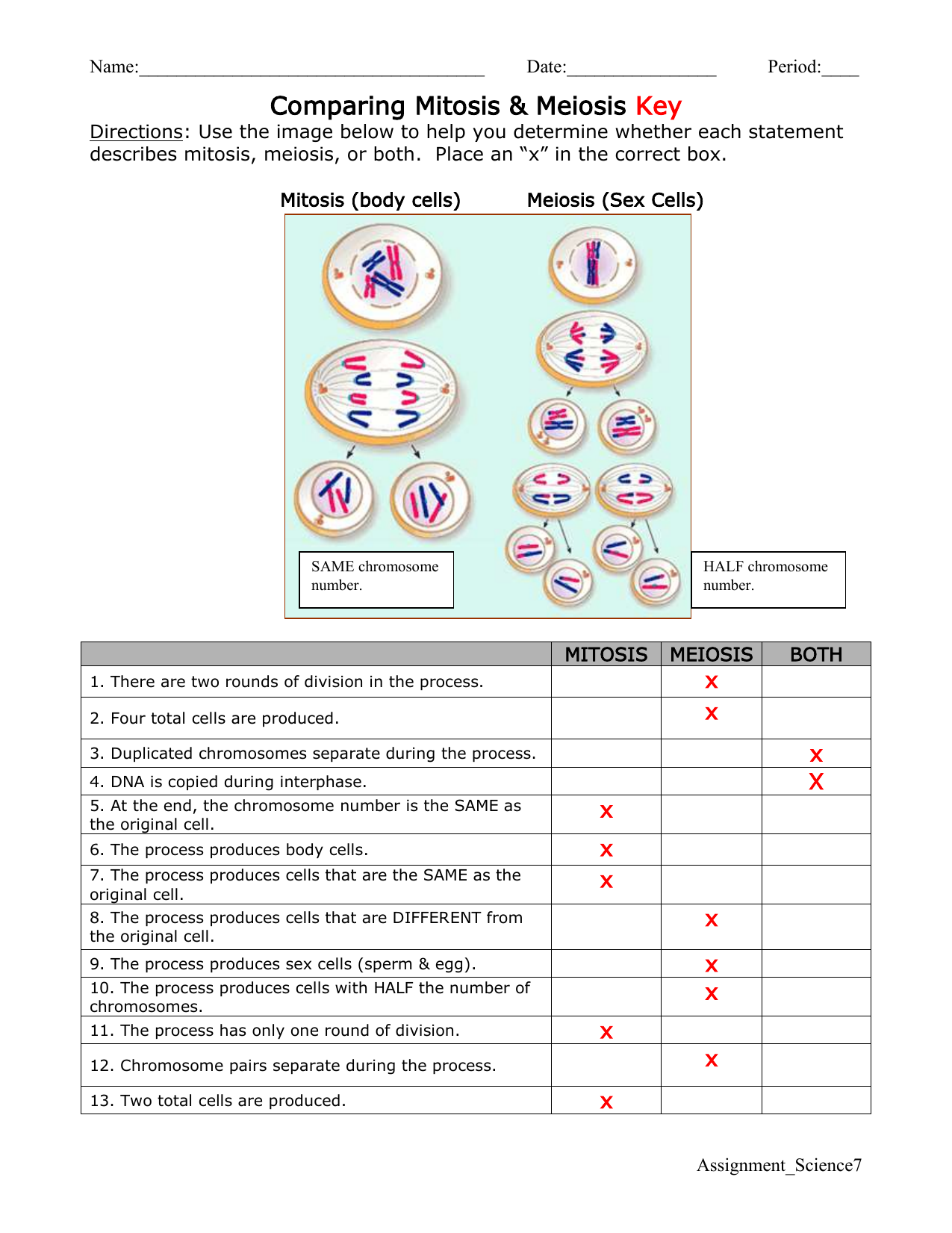
Here’s a comparative table to highlight the differences:
| Aspect | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Divisions | 1 | 2 |
| Daughter Cells Produced | 2 | 4 (in humans) |
| Chromosome Number in Daughter Cells | Same as parent cell (diploid) | Half of parent cell (haploid) |
| Genetic Variation | None (exact copies of parent cell) | High due to crossing over, random alignment during Metaphase I, and independent assortment |

Why Understand Mitosis and Meiosis?
Understanding these cellular processes is crucial for:
- Appreciating how life grows and repairs itself through mitosis.
- Recognizing the basis of genetic diversity and sexual reproduction via meiosis.
- Explaining abnormalities in cell division leading to diseases like cancer or genetic disorders.
🚀 Note: Each cell division type serves a unique purpose, yet both are interdependent for life processes.
Mitosis vs Meiosis: A Closer Look

Both mitosis and meiosis are modes of cellular division, but they serve different functions:
- Mitosis is about growth and repair. It ensures that the offspring cell is identical to the parent cell, thus maintaining genetic consistency in all cells of an organism.
- Meiosis, however, is about creating diversity. It is essential for sexual reproduction, as it introduces genetic variation through mechanisms like:
- Crossing over during prophase I of Meiosis I, where parts of homologous chromosomes are swapped.
- The random alignment of chromosomes during metaphase I, which leads to independent assortment.
Worksheet Answer Key for Mitosis vs Meiosis
Below, we provide answers to common questions in educational settings concerning the differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis:
1. How many daughter cells are produced from one parent cell in:
- Mitosis: 2
- Meiosis: 4
2. In which process do we see genetic variation? Why?
- Meiosis introduces genetic variation due to crossing over and independent assortment.
- Mitosis does not introduce new genetic variations; the daughter cells are clones of the parent cell.
3. What is the final chromosome number of the daughter cells compared to the parent?
- Mitosis: 2n (diploid) - Same as the parent cell.
- Meiosis: n (haploid) - Half of the parent cell's chromosome number.
Wrapping Up

In summary, mitosis and meiosis are both essential for cellular life but serve different roles. Mitosis ensures growth, repair, and the replacement of cells within an organism, while meiosis is the mechanism through which genetic diversity is generated, critical for evolution and the survival of species. Understanding the nuances between these processes not only aids in comprehending biological mechanisms but also provides insights into genetics and disease pathology.
What is the main purpose of mitosis?

+
Mitosis is primarily involved in growth, development, and the repair of tissues within an organism by producing identical copies of cells.
Why is genetic variation important in meiosis?

+
Genetic variation ensures that offspring have unique genetic profiles, allowing for adaptation, survival, and evolution of species.
What might happen if there is an error during either mitosis or meiosis?

+
Errors in mitosis can lead to uncontrolled cell growth or cancer. In meiosis, errors can result in gametes with incorrect numbers of chromosomes, leading to genetic disorders.
There we have it, a detailed explanation of mitosis and meiosis, their importance, and how they differ from each other. As you continue to explore biology, the intricate dance of cellular division will continue to amaze you with its complexity and its profound impact on life.