5 Key Answers for Nuclear Tech Worksheet

Embarking on the journey of understanding nuclear technology can be both fascinating and intimidating due to its complexity and significance in both peaceful applications and military contexts. Whether you're a student looking to ace your worksheet or someone intrigued by nuclear science, here are five key answers that should be covered comprehensively when exploring nuclear technology.
The Basics of Nuclear Reactions

- Fission: This involves splitting a heavy nucleus, such as uranium or plutonium, into two lighter nuclei. It's the primary process in nuclear power plants where the energy released is used to generate electricity.
- Fusion: The opposite of fission, fusion combines light nuclei to form a heavier one, releasing vast amounts of energy in the process. This is the reaction that powers the sun and is currently the focus of research for clean energy.
Nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions in that they involve changes in the nucleus, resulting in the transformation of elements, unlike chemical reactions where electrons are rearranged but the nuclei remain the same.
Energy from Nuclear Processes
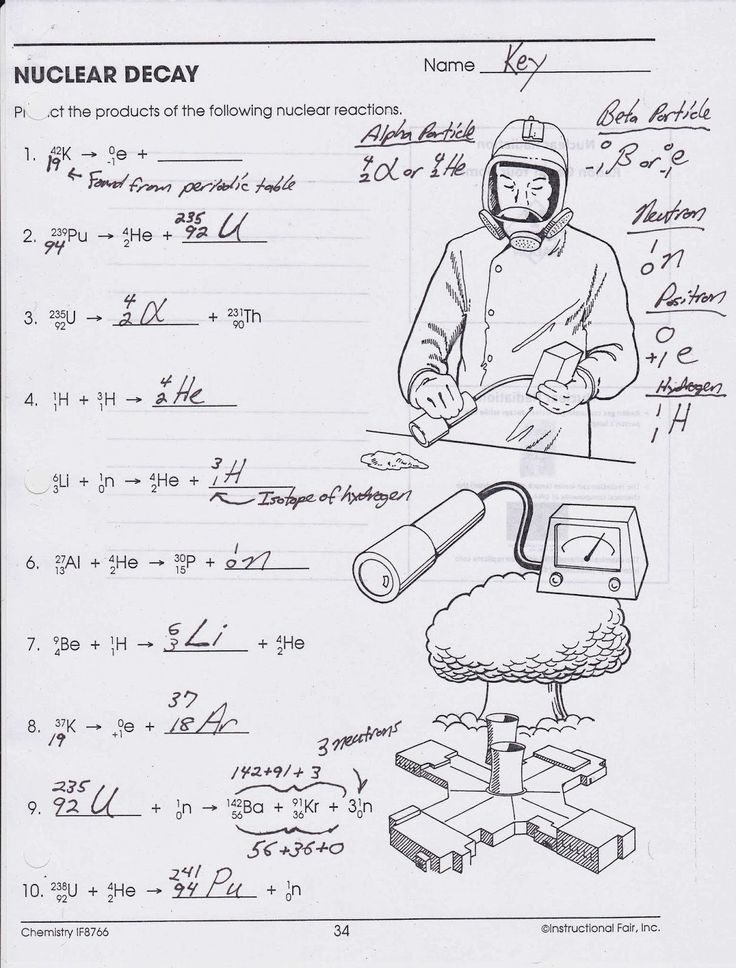
Nuclear reactions liberate energy by converting some of the nuclear mass into energy, following Einstein's famous equation, E=mc².
- Nuclear Power: Electricity generation through controlled nuclear fission. It's a major source of low-carbon energy around the world.
- Nuclear Weapons: Explosive devices that utilize either fission or fusion reactions for massive destructive power. Understanding their mechanisms is crucial for international security.
The energy output from nuclear reactions is exceptionally high due to the enormous energy density of nuclear fuel, making it an attractive source for sustainable energy.
Applications of Nuclear Technology

| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Energy | Generation of electricity, hydrogen production |
| Medicine | Cancer treatment, diagnostic imaging |
| Industrial | Sterilization, welding, analytical techniques |

⚛️ Note: Nuclear technology has medical applications, such as using radioactive tracers to diagnose conditions without invasive procedures, and therapeutic techniques like radiation therapy to treat cancers.
Nuclear Safety and Waste Management

Nuclear technology carries inherent risks, primarily from radiation exposure and the management of radioactive waste. Here's how these issues are addressed:
- Safety: Robust engineering designs, fail-safes, and strict regulatory oversight ensure the safe operation of nuclear facilities. Containment systems are built to prevent the release of radioactive material even in emergencies.
- Waste Management: Radioactive waste is categorized and managed according to its half-life and radiation intensity. Long-term storage solutions, like geological repositories, are employed for high-level waste, while lower-level waste undergoes treatment for volume reduction or decay.
Ethical and Societal Considerations

Beyond the scientific and technical aspects, nuclear technology brings forth significant ethical, environmental, and societal issues:
- Proliferation: The potential for misuse of nuclear materials to create weapons, a key concern in global disarmament and non-proliferation treaties.
- Environmental Impact: Long-term consequences of nuclear accidents, waste storage, and the benefits of low carbon emissions from nuclear power.
- Public Perception: Addressing public fears through transparent communication, safety measures, and engaging communities about the risks and benefits.
In conclusion, the study of nuclear technology is multifaceted, encompassing physics, engineering, policy, and ethics. Understanding nuclear reactions, the applications of nuclear energy, ensuring safety protocols, and considering the broader impacts on society are all crucial components. By diving into these aspects, you not only prepare for your worksheet but also engage with one of the most pivotal technologies shaping our world.
What is nuclear fission?
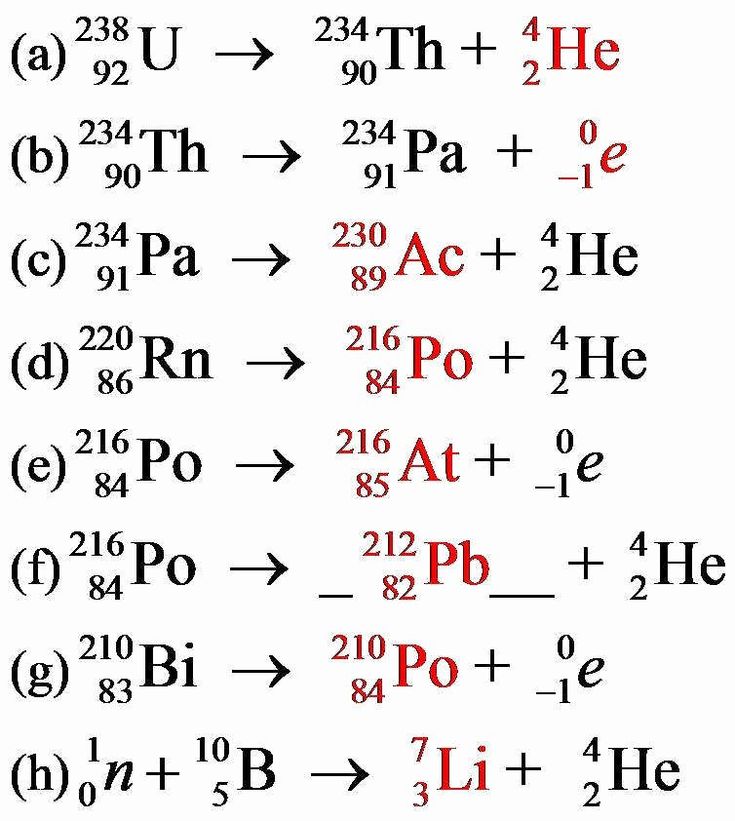
+
Nuclear fission is the process where a heavy nucleus, like uranium-235, absorbs a neutron and splits into two lighter nuclei, releasing energy, additional neutrons, and radioactive by-products.
How is nuclear fusion different from fission?

+
Nuclear fusion involves the merging of two light nuclei, typically isotopes of hydrogen, to form a heavier nucleus, like helium. It releases energy but requires extremely high temperatures and pressures, unlike fission which can be sustained at lower temperatures with the right setup.
What are the ethical concerns with nuclear technology?

+
Ethical concerns revolve around the potential for misuse in creating nuclear weapons, long-term environmental impact from accidents and waste disposal, and the economic accessibility of nuclear power to all countries, promoting a just energy transition.
How is nuclear safety managed in nuclear facilities?

+
Safety in nuclear facilities is managed through multiple layers of defense, including robust design features, redundant safety systems, stringent regulatory oversight, and thorough training for staff to respond to emergencies.




