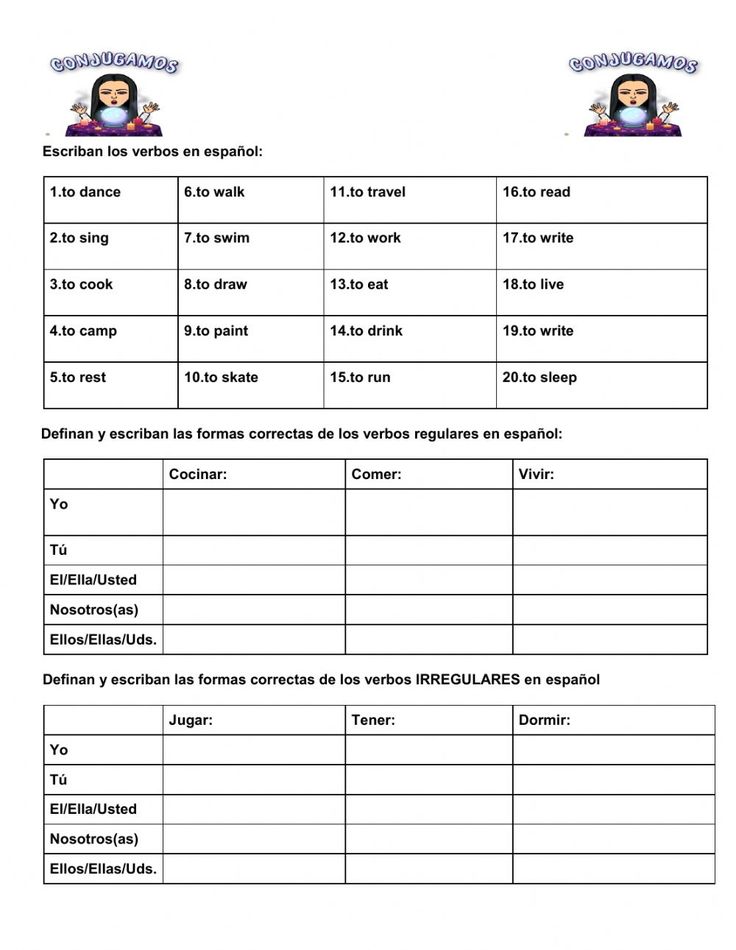
Spanish AR Verbs Worksheet Answers Revealed

Conjugating Spanish verbs can be a challenging yet fulfilling part of learning the language. Regular -ar verbs, with their predictable conjugation patterns, serve as a foundation for Spanish learners. This blog post delves into the answers for the Spanish AR verbs worksheet, providing clarity and a deeper understanding of how these verbs function across various tenses and moods. Whether you're just starting or need a refresher, we've got you covered with detailed explanations, conjugation charts, and practical examples.
Understanding Regular AR Verbs

Spanish verbs are categorized into three groups: -ar, -er, and -ir verbs, with -ar verbs being the most common. Understanding the conjugation patterns for these verbs is key because they follow a standard formula, making them easier to learn compared to irregular verbs. Here’s a brief overview:
- The root of the verb remains the same, only the endings change.
- Endings are determined by the subject pronoun and tense.
Present Tense Conjugation

To conjugate a regular -ar verb in the present tense, follow these steps:
- Remove the -ar ending from the infinitive form.
- Add the appropriate ending:
- Yo: -o
- Tú: -as
- Él/Ella/Usted: -a
- Nosotros/Nosotras: -amos
- Vosotros/Vosotras: -áis (mainly used in Spain)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes: -an
Here's a table to visualize the present tense conjugation of the verb "hablar" (to speak):
| Subject | Verb Ending | Conjugation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | -o | hablo |
| Tú | -as | hablas |
| Él/Ella/Usted | -a | habla |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | -amos | hablamos |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | -áis | habláis |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | -an | hablan |

⚠️ Note: Remember to adjust these endings according to the subject pronoun in question.
Preterite Tense Conjugation
The preterite tense describes actions completed in the past. Here’s how to conjugate regular -ar verbs:
- Remove the -ar ending.
- Add these endings:
- Yo: -é
- Tú: -aste
- Él/Ella/Usted: -ó
- Nosotros/Nosotras: -amos (same as the present)
- Vosotros/Vosotras: -asteis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes: -aron
Examples

- Yo trabajé: I worked.
- Tú cantaste: You sang.
- Ella tocó: She played (music/instrument).
🔍 Note: Notice how the nosotros form in the preterite is identical to the present for -ar verbs.
Future Tense Conjugation

Future tense conjugation for -ar verbs is simple and regular across all verbs:
- The infinitive verb itself is the stem, and we attach one of the following endings:
- Yo: -é
- Tú: -ás
- Él/Ella/Usted: -á
- Nosotros/Nosotras: -emos
- Vosotros/Vosotras: -éis
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes: -án
Examples

- Yo trabajaré: I will work.
- Tú cantarás: You will sing.
- Él tocará: He will play (music/instrument).
Worksheet Answers

Here are the correct answers for the Spanish AR verbs worksheet:
| Infinitive | Yo (present) | Tú (present) | Él/Ella/Usted (present) | Nosotros (present) | Vosotros (present) | Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes (present) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hablar | hablo | hablas | habla | hablamos | habláis | hablan |
| trabajar | trabajo | trabajas | trabaja | trabajamos | trabajáis | trabajan |
| cantar | canto | cantas | canta | cantamos | cantáis | cantan |
📝 Note: The worksheet focused on present tense, but the same patterns can be applied for other tenses once understood.
Recapitulating our journey through Spanish AR verb conjugation, we've covered the present tense, which lays the groundwork for understanding the language's structure. We then delved into the preterite tense, essential for expressing completed actions in the past, and briefly touched on the future tense for actions that will occur. The key takeaways are the simplicity and regularity of -ar verbs' conjugation, providing learners with a strong foundation to build upon. This exploration not only aids in mastering verb forms but also enhances your ability to communicate effectively in Spanish. Whether for travel, work, or personal growth, understanding Spanish AR verbs is a crucial step in your linguistic journey.
What are the most common AR verbs in Spanish?

+
Some of the most common regular -ar verbs include hablar (to speak), trabajar (to work), caminar (to walk), estudiar (to study), and cantar (to sing). These verbs are frequently used in everyday conversations.
How can I memorize verb conjugations easily?

+
Regular practice, flashcards, and contextual learning (using verbs in sentences) are effective strategies. Apps like Anki for spaced repetition, mnemonic devices, or songs can also help.
What are the differences between the preterite and imperfect tenses?

+
The preterite tense is used for actions completed at a specific point in the past (e.g., yo trabajé - I worked). The imperfect tense describes ongoing, habitual, or background actions in the past (e.g., yo trabajaba - I was working).