5 Tips for Using a Protractor Correctly

In this article, we'll explore the essential techniques for effectively using a protractor. Whether you're a student, a DIY enthusiast, or simply someone looking to understand geometric shapes and angles, mastering the use of a protractor can enhance your precision in various projects.
1. Understanding Your Protractor

Before diving into the techniques, it's crucial to understand what a protractor is and its basic functions:
- Outer Scale: This scale measures angles from the right to the left, starting from 0°.
- Inner Scale: This one goes from left to right, also starting at 0°.
- Center Point: The middle point where all the angle measurements begin.
- Baseline: The straight edge used as the baseline for measurement.
📏 Note: Always ensure that the baseline of your protractor is aligned with one of the lines forming the angle you're measuring.
2. Measuring Angles

Measuring angles with a protractor is straightforward if you follow these steps:
- Place the Protractor: Position the protractor so that the center point is directly over the vertex of the angle. The baseline should align with one of the lines forming the angle.
- Read the Angle: Look at where the second line of the angle intersects with the protractor's scale. Use the outer or inner scale based on which direction you're reading:
- If you're measuring from the right side to the left, use the outer scale.
- If from left to right, use the inner scale.
- Record the Reading: Record the value where the angle line meets the scale. Make sure to note if it's an acute or obtuse angle.
3. Drawing Angles
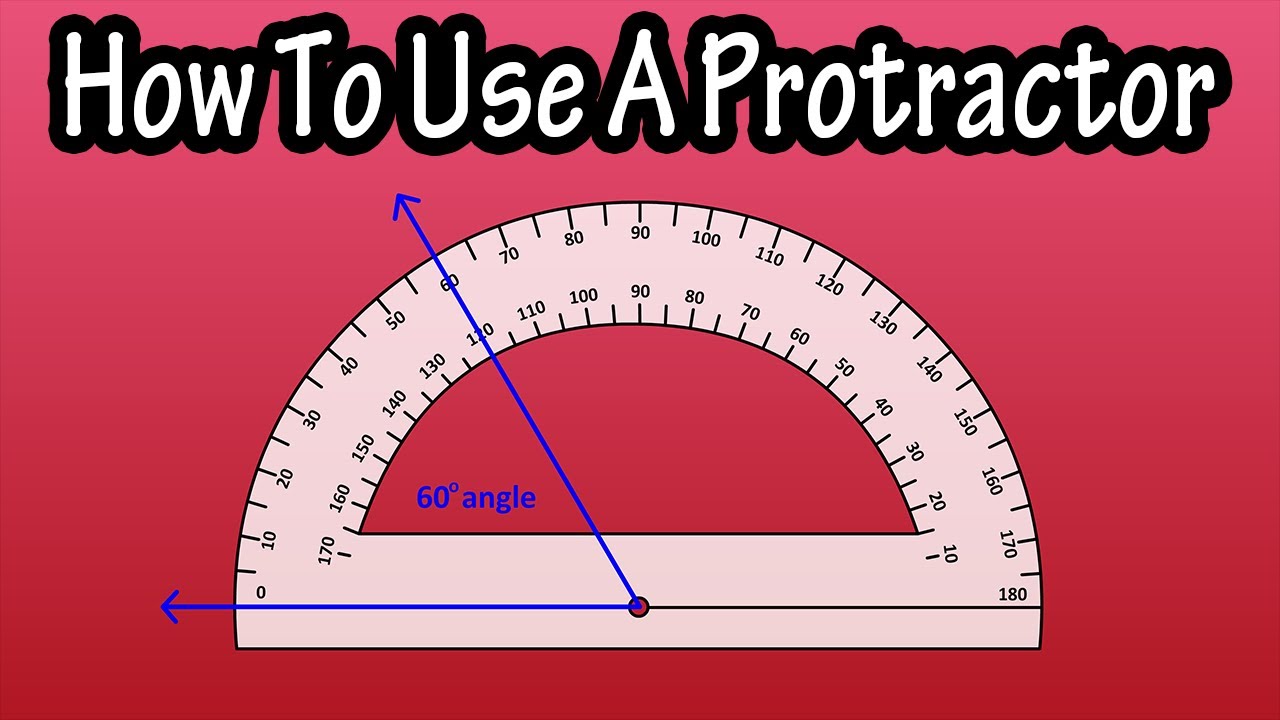
Drawing angles with a protractor involves these steps:
- Mark the Vertex: Draw a point on your paper where the angle's vertex will be.
- Align the Baseline: Lay the protractor over this point with the baseline running through it.
- Draw the Angle:
- For an acute angle (less than 90°), use the inner or outer scale depending on your preference.
- For an obtuse angle, you might need to use both scales to get a reading over 90°.
- Use the Center Point: From the vertex, draw a line following the arc of the angle you measured, ensuring it touches the scale at the intended angle.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Place protractor on vertex |
| 2 | Read angle from appropriate scale |
| 3 | Record the angle value |

4. Ensuring Accuracy

To ensure accuracy while using a protractor:
- Check Alignment: Ensure that the protractor is straight and the vertex is exactly at the center point.
- Read Carefully: When measuring angles, double-check to avoid misreading the scale.
- Use Right Proportions: If drawing an angle, use a ruler alongside the protractor to keep lines straight and even.
📐 Note: For very small angles or high precision work, consider using a smaller protractor or a digital angle gauge for better accuracy.
5. Advanced Techniques

For more complex tasks, here are some advanced tips:
- Bisecting an Angle: To bisect an angle, draw an arc from the vertex intersecting the lines of the angle, then connect the endpoints of these arcs to the vertex.
- Multiple Angles: If measuring or drawing multiple angles at once, ensure your protractor remains steady, or use multiple markings on the paper.
- Parallel Angles: For parallel lines, use the same angle measurement on both sides of a straight line.
In conclusion, mastering the use of a protractor can be a game-changer for anyone dealing with geometric shapes and angles. By understanding the tool, measuring and drawing accurately, ensuring alignment, and exploring advanced techniques, you can significantly improve your geometrical precision. Remember, practice makes perfect. Start with simple exercises and gradually incorporate these techniques into your everyday work to enhance your skills in geometry.
What if my protractor doesn’t have clear markings?
+
If your protractor lacks clear markings, consider using a digital angle finder or getting a better-quality protractor with more precise scales.
How can I measure angles larger than 180°?

+
For angles over 180°, subtract the measured angle from 360°. For example, if your angle measures 330°, the actual angle is 30°.
Can I use a protractor for curved lines?

+
Yes, but you’ll need to measure each segment individually or use a flexible protractor designed for curves.
Why do I need to know how to use a protractor?

+
Understanding protractors is essential for precise work in fields like engineering, construction, carpentry, and even in everyday tasks like interior decorating or DIY projects.
What’s the difference between an acute and an obtuse angle?

+
An acute angle is less than 90°, while an obtuse angle is between 90° and 180°. Knowing this helps in correctly measuring and interpreting angles with a protractor.



