Right Triangle Area Worksheet: Fun Geometry Practice

Understanding the Basics of Right Triangles

Geometry, as a branch of mathematics, deals with shapes, sizes, and their properties, making it integral for understanding and navigating the world around us. Right triangles are a particular delight in this realm, thanks to their unique characteristics and the simplicity in calculating their properties. Today, we'll dive into the geometry of right triangles with an engaging and interactive right triangle area worksheet.
What is a Right Triangle?
A right triangle, or a right-angled triangle, is characterized by:
- One angle measuring exactly 90 degrees, denoted as the right angle.
- Two sides that form this angle, known as the legs or catheti.
- The longest side opposite the right angle, known as the hypotenuse.
Calculating the Area of a Right Triangle

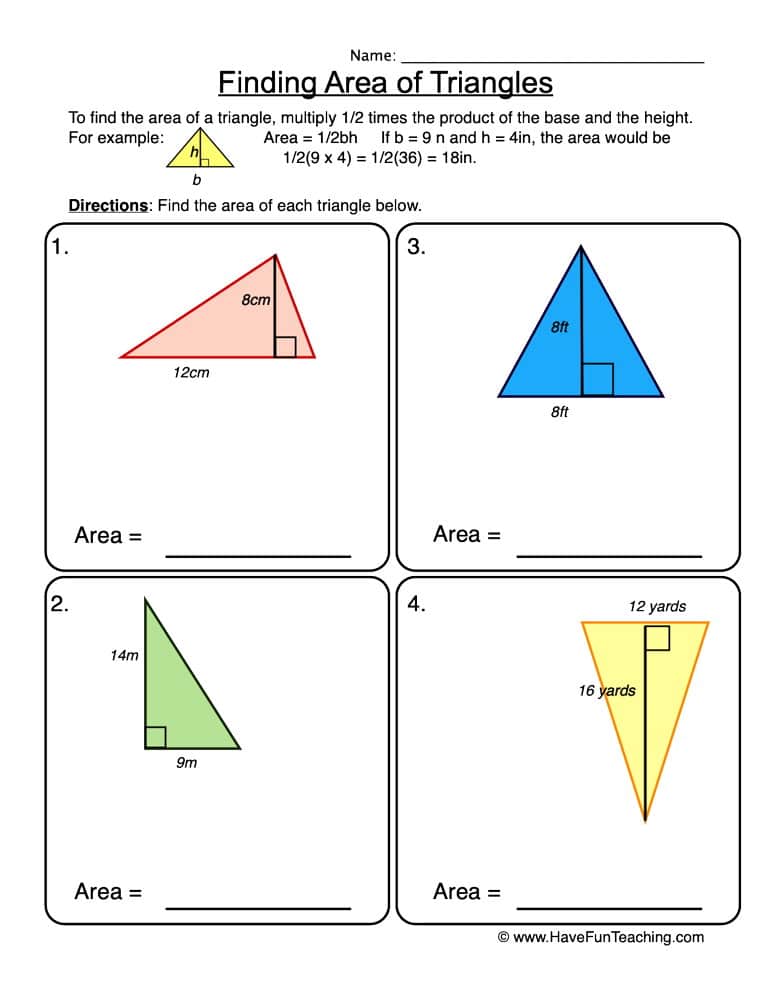
The area of a right triangle can be calculated using the formula:
Area = ½ * base * height
Here's how you can apply this:
- Identify the base and height. These are the two legs of the triangle.
- Multiply the base by the height.
- Divide the product by two.
Interactive Example:
Consider a right triangle with legs measuring 3 units and 4 units:
| Base (Leg 1) | Height (Leg 2) | Area Calculation | Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 units | 4 units | ½ * 3 * 4 = ½ * 12 | 6 square units |

📝 Note: When calculating the area, ensure the units are consistent for an accurate result.
Right Triangle Area Worksheet

Here are some practice problems to help solidify your understanding of calculating areas of right triangles:
- Calculate the area for a right triangle with a base of 5 units and a height of 12 units.
- Find the area if the two legs are both 6 units long.
- Determine the area when the base is 8 units and the height is 15 units.
You can try these by applying the formula, or for a more interactive experience, sketch the triangles on graph paper to visualize the calculations.
Practical Applications of Right Triangles
Understanding the area of a right triangle isn't just for classroom quizzes; it has numerous real-world applications:
- Construction: Architects and builders use right triangles to design and construct structures ensuring stability and alignment.
- Surveying: Land surveyors measure distances using right triangles formed by their instruments to calculate land area.
- Navigation: Pilots and sailors apply the principles of right triangles to plot their course and maintain accurate bearings.
The versatility of right triangles extends to graphic design, robotics, and even the digital world, where geometric algorithms play a crucial role in image processing and 3D modeling.
By the end of this post, you'll not only have sharpened your geometric calculation skills but also understood the relevance of these shapes in daily applications. Keep practicing, and you'll find geometry not just a subject to learn, but a fascinating lens through which to view the world.
What’s the most common mistake in calculating the area of a right triangle?

+
The most common mistake is forgetting to halve the product of the base and height. The formula requires you to divide by two after multiplying the base and height.
Can I use any side as the base when calculating the area?

+
Yes, you can use either leg of the triangle as the base, but the height must be the perpendicular distance from that base to the opposite vertex, forming a right angle.
How does knowing the area of a right triangle benefit construction?

+
In construction, understanding the area of right triangles helps in designing roofs, calculating the angle of inclination, and ensuring structural integrity where right angles are critical.



