Malcolm X vs MLK: Compare and Contrast Guide

Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X were two pivotal figures in the American civil rights movement, each with a unique approach and philosophy towards achieving racial equality. Their contrasting methods and ideologies not only shaped the movement but continue to influence discussions on race relations and civil rights today. In this guide, we will delve into the lives, beliefs, and strategies of Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X, offering a comparison and contrast to help readers understand their impact and legacy.
Early Life and Influences
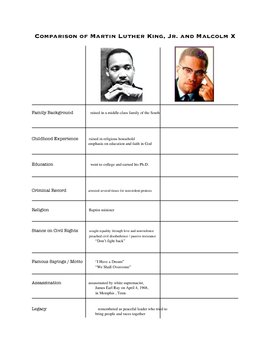
Martin Luther King Jr. was born on January 15, 1929, in Atlanta, Georgia. His family background played a crucial role in shaping his views on civil rights. King’s father, Martin Luther King Sr., was a pastor and an advocate for civil rights, providing a strong foundation for King’s involvement in the movement:
- Received theological education, eventually earning a PhD in systematic theology.
- Deeply influenced by Christianity, especially by the principles of love, non-violence, and forgiveness.
- The American Baptist Church and its philosophy of pacifism shaped his approach to civil rights activism.
Malcolm X, born Malcolm Little on May 19, 1925, in Omaha, Nebraska, faced a life starkly different from King’s:
- Experienced racism firsthand, including the murder of his father by white supremacists.
- Engaged in criminal activity early in life, which led to his imprisonment where he turned to the teachings of Elijah Muhammad and the Nation of Islam.
- His conversion to Islam during his time in prison provided a framework for understanding racial oppression in America.
Philosophies and Beliefs

The core philosophies of Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X were quite different, reflecting their backgrounds and personal experiences:
Martin Luther King Jr.

- Non-violence: King adopted a strict policy of non-violent resistance, inspired by figures like Mohandas K. Gandhi. He believed in love and peaceful protest to achieve civil rights.
- Integration: King advocated for a society where racial integration was the norm, emphasizing equality and unity among all races.
- Justice and Love: His vision was not only of racial equality but also of justice and love as the means to overcome hatred and racial division.
Malcolm X

- Self-defense and Separation: Initially, Malcolm X preached racial separation as a way to achieve true equality. He believed in self-defense, asserting that African Americans should defend themselves “by any means necessary.”
- Black Nationalism: He endorsed the idea of Black Nationalism, which focused on Black self-sufficiency, pride, and the right to determine their own destiny.
- Human Rights: Malcolm X also shifted his focus to human rights, arguing that the civil rights struggle was a broader issue of human rights, extending beyond America’s borders.
Strategies for Change

Both leaders employed different strategies to bring about social change:
Martin Luther King Jr.

- Civil Disobedience: King organized sit-ins, boycotts, and peaceful marches to protest against segregation.
- Speeches and Oratory: Known for his powerful speeches, King used rhetoric to inspire and mobilize people, like the “I Have a Dream” speech.
- Coalition Building: King worked to build alliances with various groups, including religious, political, and civil rights organizations.
Malcolm X

- Confrontational Tactics: Malcolm X often used provocative language and actions to challenge the status quo, advocating for direct confrontation.
- Community Organizing: He focused on building grassroots movements and self-help initiatives within the African American community.
- Media Savvy: Malcolm X understood the power of media and used it to spread his message, even when it was controversial.
Impact and Legacy

Both Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X left an indelible mark on American history:
Martin Luther King Jr.

- Legislation: His efforts were instrumental in the passage of landmark civil rights legislation like the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
- Global Influence: King’s philosophy of non-violent protest has inspired movements worldwide, from anti-apartheid in South Africa to the Civil Rights Movement in Northern Ireland.
- Cultural Legacy: His life and teachings continue to be celebrated annually on Martin Luther King Jr. Day in the United States.
Malcolm X

- Black Empowerment: Malcolm X’s emphasis on self-defense, self-respect, and Black Pride inspired a generation of activists, including the Black Panthers.
- Shifting Views: His change towards the end of his life, advocating for racial reconciliation and a broader understanding of human rights, influenced subsequent civil rights discourse.
- Cultural Impact: His autobiography remains a seminal work in American literature and has been adapted into films, continuing his legacy.
📝 Note: King’s philosophy of non-violence was not merely a strategy but a deeply held belief rooted in his Christian faith. Malcolm X's evolving views showed his openness to change and the complexity of his thoughts on race relations.
📝 Note: Their contrasting strategies often led to public tension, but many argue that their differing approaches ultimately complemented each other, pushing the movement forward from multiple fronts.
Today, understanding both Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X’s perspectives helps us appreciate the multifaceted nature of the civil rights struggle. Their legacies, while distinct, intersect in their pursuit of racial equality and justice. Martin Luther King Jr.'s work was foundational in bringing about legislative change, while Malcolm X's activism highlighted the need for Black empowerment and self-sufficiency. Their combined efforts led to profound shifts in American society, and their philosophies continue to inspire and guide activists around the world.
Did Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X ever meet?

+
Yes, Martin Luther King Jr. and Malcolm X met only once in person, briefly at a press conference during the Senate Civil Rights Debate in March 1964. Their meeting was documented, and although their public interactions were limited, their respective paths crossed in many indirect ways.
How did their personal experiences influence their civil rights approaches?

+
King’s upbringing in a stable, supportive, and religious family shaped his philosophy of non-violence and integration. Malcolm X’s early life of hardship, racism, and incarceration led him to initially embrace more radical and confrontational methods focused on self-defense and black nationalism.
What was the role of their speeches in the civil rights movement?

+
King’s speeches, like “I Have a Dream,” galvanized the nation and attracted widespread support, while Malcolm X’s fiery rhetoric challenged societal norms and inspired those who felt alienated by mainstream civil rights strategies. Both leaders used oratory as a powerful tool to communicate their vision.