Lion King Ecology: 5 Key Worksheet Answers Revealed

Introduction to Lion King Ecology

The animated film "The Lion King" has captured the hearts of audiences worldwide, not only for its engaging story and compelling characters but also for its portrayal of the African savanna's intricate ecology. This ecosystem, as depicted in the movie, serves as a perfect canvas to explore real-world ecological principles. This article will delve into the critical aspects of Lion King's ecology through a worksheet, offering insights into the interactions, balance, and survival strategies within this iconic environment.
Ecological Interactions in the Circle of Life

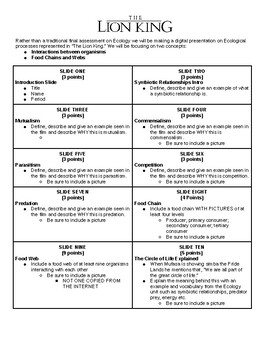
In "The Lion King," the Circle of Life is a central theme, illustrating the interconnectedness of all living things. Here are five key ecological concepts and their answers from a worksheet perspective:
1. Food Webs and Energy Flow

The Circle of Life showcases a food web where energy transfer occurs from one organism to another:
- Producers: Grasses and shrubs serve as primary producers, capturing solar energy.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores like antelopes, zebras, and giraffes feed on plants.
- Secondary Consumers: Carnivores like lions, cheetahs, and hyenas prey on these herbivores.
- Decomposers: Bacteria and fungi decompose dead matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil.
🌿 Note: Energy transfer is not 100% efficient, with around 10% of the energy being passed from one trophic level to the next.
2. Symbiotic Relationships

The film subtly shows various symbiotic relationships:
- Commensalism: Zazu and Mufasa, where Zazu benefits from the protection provided by the pride.
- Mutualism: Pumbaa and Timon share a relationship where both benefit from foraging and protection.
- Parasitism: The smaller, less prominent organisms in the savanna might be parasitic on larger hosts.
3. Niche and Habitats

Each character has a specific role and habitat:
- Lions: Apex predators, with prides controlling specific territories.
- Elephants: Engineers of the habitat, affecting the landscape and plant diversity through their feeding habits.
- Hyenas: Scavengers and occasional hunters, filling a niche that reduces waste in the ecosystem.
| Species | Niche | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Lion | Top Predator | Prides in savannas and grasslands |
| Elephant | Ecosystem Engineer | Varied, often near water sources |
| Hyena | Scavenger and Predator | Near lion prides, scavenging or hunting in packs |

4. Succession and Disturbance

The balance of the savanna can be disrupted:
- Wildfires: Natural events that clear out overgrown vegetation, promoting new growth for grazers.
- Drought: Leads to competition for resources, changing the dynamics among species.
- Overgrazing: Can result in habitat degradation, impacting the food web negatively.
5. Conservation and Human Impact

Although not directly addressed in the film, understanding conservation issues is key:
- Poaching: Illegal hunting disrupts the balance, with species like elephants suffering greatly.
- Habitat Loss: Conversion of savanna to farmland reduces available habitats.
- Conservation Efforts: Similar to real-life initiatives, protecting these ecosystems preserves biodiversity.
End Reflections
While "The Lion King" is a fictional narrative, it effectively highlights real ecological principles. From the importance of each organism's role in maintaining the Circle of Life to the challenges faced by ecosystems due to human activities, the film serves as a bridge between storytelling and science education. Through examining these worksheet answers, viewers can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and delicate balance of the African savanna, encouraging conservation awareness and action in real-world scenarios.
What is the Circle of Life?

+
The Circle of Life in ecology refers to the natural process where energy and nutrients are transferred between organisms in an ecosystem, maintaining a balance essential for survival.
Can you explain symbiotic relationships?

+
Symbiotic relationships are interactions between species that can be mutually beneficial (mutualism), beneficial to one and neutral to the other (commensalism), or beneficial to one at the other’s expense (parasitism).
Why is understanding the Lion King’s ecology important?

+
Understanding the ecology in “The Lion King” provides insights into how real ecosystems function, the importance of each species’ role, and the impact of disturbances and conservation efforts, which can inspire conservation action.