Plotting Points Made Easy: Interactive Worksheet Guide
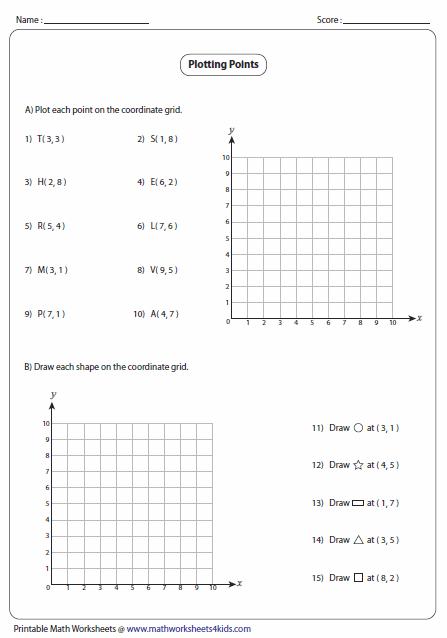
The art of plotting points on a graph is fundamental in various fields such as mathematics, science, engineering, and even in daily life applications like map-reading or data analysis. Whether you're a student learning the basics or a professional looking to enhance your graphing skills, understanding how to plot points accurately can significantly simplify complex tasks. In this interactive worksheet guide, we'll dive into the essentials of plotting points, offer step-by-step instructions, and introduce techniques to make the process not just easy but also fun and educational.
Why Plotting Points Matters

Plotting points is more than just a mathematical exercise. Here are a few reasons why it's crucial:
- Visualization: It helps in visualizing data, making patterns, trends, and outliers more apparent.
- Communication: Graphs and charts are a universal language for sharing information.
- Problem Solving: Many complex problems in physics, engineering, and data science require plotting data points to find solutions.
- Memory and Cognitive Skills: The spatial reasoning developed from plotting points aids in memory retention and cognitive skills.
Interactive Plotting Tools

Before we delve into the step-by-step guide, let's explore some interactive tools that make plotting points both engaging and efficient:
- Desmos: An excellent online graphing calculator with an interactive environment for plotting points.
- Geogebra: A dynamic mathematics software system for all levels of education which includes plotting capabilities.
- Microsoft Excel: Widely used for plotting data points with various chart options.
Plotting Points: A Step-by-Step Guide

1. Understand Your Coordinates
A coordinate system, typically a Cartesian coordinate system, is used to locate points on a plane. Here’s what you need to know:
- The x-axis runs horizontally, with positive values to the right and negative to the left.
- The y-axis runs vertically, with positive values upwards and negative downwards.
- Each point (x, y) represents the intersection of these two coordinates.
2. Setting Up Your Graph

Choose your plotting tool or draw your graph:
- Set the scale: Determine the range of your axes to fit your data. For instance, if plotting the weather over a week, your x-axis could range from 1 to 7, while your y-axis might cover temperatures.
- Label your axes: Clearly label each axis with the variable name and its scale. E.g., ‘Days’ on the x-axis and ‘Temperature in Celsius’ on the y-axis.
3. Plotting Individual Points

Now, let’s plot some points:
- Identify the coordinates for each point, e.g., (3, 2).
- Move along the x-axis to find ‘3’, then move up to ‘2’ on the y-axis.
- Mark the point where these two values meet with a dot.
📝 Note: Ensure you use a clear, small dot or a mark that’s easily visible but doesn’t overcrowd your graph.
4. Joining the Dots

Depending on your data:
- If it’s continuous, like a trend line, connect the points with a line.
- For discrete data or to highlight points, leave the dots unconnected.
- If you’re showing a range or an error margin, consider using bars or a confidence interval.
🌟 Note: Joining points with a line can help in identifying trends, but remember, not all data should be connected.
5. Annotate Your Graph

Add labels, titles, and legends:
- Add a title to your graph to specify what it represents.
- Label each point if necessary. If there are too many, consider color-coding or a legend.
- Include a legend if using multiple series of data or different symbols for different categories.
In conclusion, the ability to plot points accurately and efficiently opens up a world of problem-solving, analysis, and communication through visual representation. Whether you’re using traditional methods or interactive tools, the key is understanding the basics of coordinate systems, setting up your graph correctly, and plotting your points with precision. This guide aims to empower you with the knowledge and techniques to make plotting points an enjoyable and productive task.
What are the common mistakes when plotting points?

+
Common mistakes include misreading coordinates, not setting the correct scale, or incorrectly connecting points. Ensuring accurate axis labeling and consistent dot size can prevent misinterpretation.
Can plotting points be automated?

+
Absolutely. Many software tools, like Excel, Google Sheets, or plotting software like Matplotlib in Python, can automate plotting by accepting data inputs and generating graphs accordingly.
How can I make my plots more visually appealing?

+
Consider:
- Using color wisely to differentiate data sets.
- Including a descriptive title and clearly labeled axes.
- Adding visual elements like gridlines for readability.



