5 Tips for Mastering Lewis Structures: Essential Worksheet Guide

Understanding Lewis structures is fundamental for chemistry students who are looking to grasp the intricacies of molecular bonding. These diagrams serve as a visual representation of the valence electrons in a molecule, providing insight into its structure, polarity, and reactivity. Mastering the art of drawing these structures is not just about memorization; it requires a strategic approach. In this detailed guide, we will explore five indispensable tips for effectively learning and applying Lewis structures in your chemistry studies, with a special focus on worksheets that can enhance your learning experience.
1. Understand the Basics of Valence Electrons

Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which are involved in chemical bonding. Here’s how you can master this foundational step:
- Counting Valence Electrons: Learn to determine the number of valence electrons for different elements based on their group in the periodic table.
- Summing Electrons: When you’re drawing a Lewis structure for a molecule or ion, sum up all the valence electrons from each atom involved.
- Adjust for Ions: For ions, add or subtract electrons according to the ion’s charge. A positive charge means fewer electrons; a negative charge means more.
💡 Note: Transition metals have more complex electron configurations. Use your periodic table to check the common valence electron count for these elements.

2. Utilize Lewis Structure Worksheets for Practice

Lewis structure worksheets are an excellent tool for practice. Here are some ways to effectively use them:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice helps in reinforcing the concepts.
- Start Simple: Begin with diatomic molecules and ions with a few atoms, gradually moving to more complex structures.
- Identify Patterns: Notice how similar elements bond. For example, oxygen tends to form two covalent bonds in molecules like H2O.
| Element | Group | Number of Valence Electrons | Typical Bonding Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 | 1 single bond |
| Carbon | 14 | 4 | 4 single bonds or multiple bonds |
| Nitrogen | 15 | 5 | 3 bonds, 1 lone pair |

📝 Note: Use worksheets that provide a solution key or explanation to check your work and understand your mistakes.
3. Learn the Octet Rule and Its Exceptions
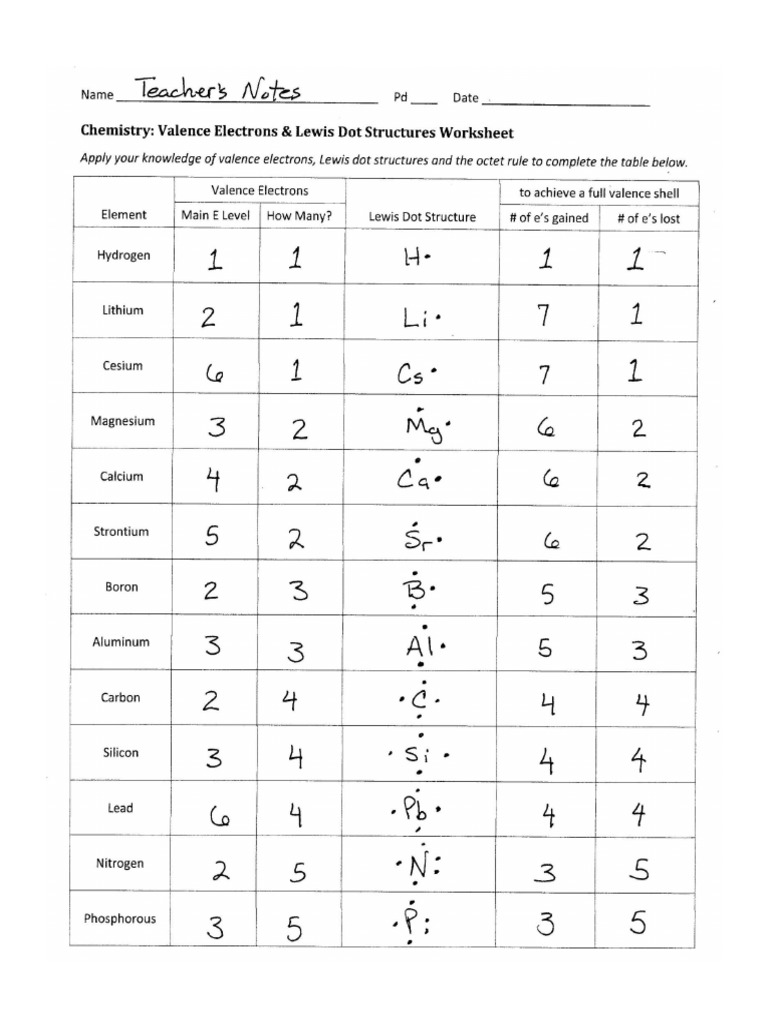
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons. Here’s how to approach this:
- Complete the Octet: Most atoms aim for an octet (8 electrons) to achieve stability.
- Hydrogen’s Duet: Hydrogen is an exception as it only requires two electrons (a duet) for stability.
- Beryllium and Boron: These elements often violate the octet rule, with Be preferring two bonds and B often bonding with three.
- Expanded Octets: Elements in the third row and beyond can have more than 8 electrons due to the availability of d-orbitals.
✅ Note: Be cautious with hypervalent compounds like SF6 where central atoms exceed the octet rule.
4. Master the Art of Formal Charge Calculation
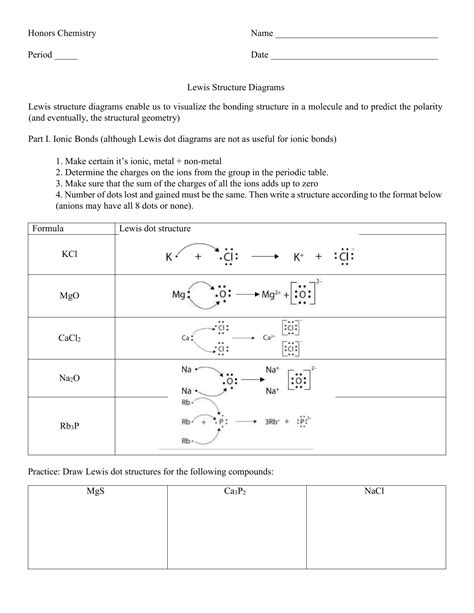
Formal charge is a method to determine the most likely Lewis structure by comparing electron distribution. Here are steps to calculate formal charge:
- Calculate: Use the formula: Formal Charge = [# of valence electrons] - [# of lone pair electrons] - 1⁄2[# of bonding electrons].
- Minimize: Choose structures with formal charges closer to zero.
- Check Common Charges: Some atoms often have formal charges. For instance, oxygen in an OH group often has a -1 charge.
⚗️ Note: Using formal charge can help identify resonance structures in complex molecules.
5. Recognize and Handle Resonance Structures

Resonance occurs when a molecule has multiple valid Lewis structures, each differing in electron arrangement but not in atom positions. Here’s how to manage this:
- Identify Resonance: Look for structures where electron pairs can move without changing atom positions.
- Draw Multiple Structures: When in doubt, draw different possible structures and use formal charges or molecular geometry to determine the most likely ones.
- Combine Structures: The actual structure of the molecule is often an average or hybrid of all resonance forms.
In summary, mastering Lewis structures involves understanding electron behavior, utilizing effective practice methods, grasping the octet rule and its exceptions, calculating formal charges, and recognizing resonance. These five tips are your roadmap to success in drawing accurate and informative Lewis structures. Incorporate these strategies into your chemistry studies, and you'll find yourself not only comprehending these structures but also solving related problems with greater ease.
What are valence electrons and why are they important in Lewis structures?

+
Valence electrons are the electrons in an atom’s outermost shell, which are involved in chemical bonding. They are crucial for Lewis structures as these diagrams show how these electrons are distributed within a molecule, indicating bonds and lone pairs.
How does the octet rule affect the drawing of Lewis structures?

+
The octet rule states that atoms prefer to have eight electrons in their outermost shell to achieve stability, which directly influences how we arrange electrons in Lewis structures to minimize formal charges and follow typical bonding patterns.
Why do we need to calculate formal charges?

+
Formal charges help in identifying the most plausible Lewis structure by showing how electron distribution occurs in a molecule. Structures with formal charges closer to zero are usually more stable.
What are resonance structures, and why are they important?
+
Resonance structures are different Lewis structures for the same molecule where electron pairs can move without changing atom positions. They are important because they indicate that the molecule’s structure is a hybrid of these forms, providing more accurate chemical behavior predictions.