Mastering Dalton's Law with 5 Simple Worksheet Tips
In the world of chemistry, understanding the behavior of gases is crucial, and one of the fundamental laws that govern this behavior is Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures. Named after the chemist John Dalton, this law helps us predict the properties of gas mixtures. Today, we're diving into how you can master Dalton's Law with the help of five simple worksheet tips that will solidify your understanding and application of this principle.
Understanding Dalton’s Law

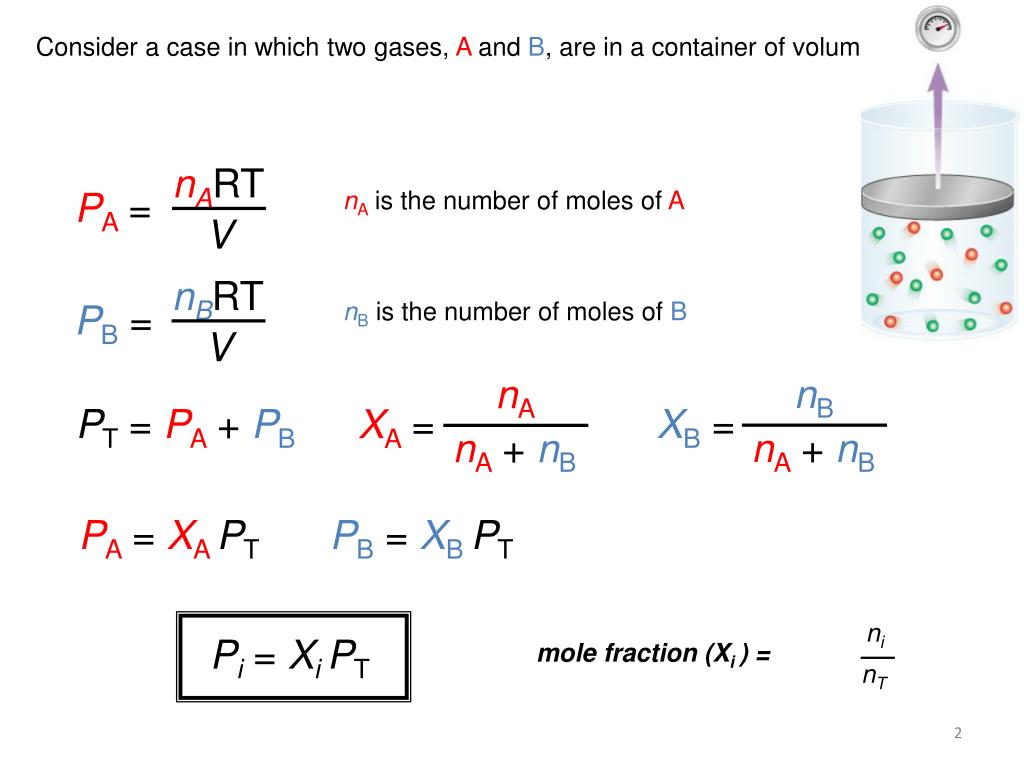
Dalton’s Law states that in a mixture of non-reacting gases, the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
- PTotal = P1 + P2 + P3 + … + Pn
Where PTotal is the total pressure of the mixture, and P1, P2, P3, …, Pn are the partial pressures of each component gas.
Tip 1: Visualize the Gas Mixtures

Start your worksheet exercises by drawing or imagining how different gases would mix. This visualization helps in:
- Understanding the concept of partial pressure
- Visualizing how each gas contributes to the total pressure

⚠️ Note: While gases can mix uniformly in reality, for conceptual clarity, picturing them as occupying separate regions can be helpful.
Tip 2: Use Equations Consistently

When you’re working on problems, keep the Dalton’s Law equation in mind:
- Always use the equation in its basic form: PTotal = P1 + P2 + P3 + … + Pn
- Remember to convert all pressures to the same units if they are given in different units
Practice converting units through worksheets to develop a solid understanding of how to apply the law uniformly.
Tip 3: Calculate Partial Pressures

Most often, you’ll be given the total pressure and the mole fractions of the gases. Here’s how to approach this:
- Use the equation: Pi = (Yi * PTotal), where Yi is the mole fraction of gas i, and Pi is its partial pressure.
This formula helps you calculate individual pressures from the total pressure, which is especially useful when dealing with mixtures where gases are not in an equal ratio.
📝 Note: Mole fractions are critical in determining partial pressures; always calculate or use provided mole fractions in your problems.
Tip 4: Understand the Concept of Volume

Since the partial pressure of each gas is proportional to its volume, understanding how volume changes affect partial pressures can enhance your worksheet solving:
- V1/Vtotal = P1/PTotal, this relationship is derived from Avogadro’s Law.
- When the volume changes, the partial pressures adjust accordingly, maintaining the ratio of individual volumes to total volume.
Recognizing this relationship can help in predicting pressure changes with volume adjustments in your worksheet exercises.
Tip 5: Apply Real-Life Scenarios

Finally, one of the best ways to master Dalton’s Law is to relate it to real-world applications:
- Respiration: How do partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide affect the breathing process?
- Scuba Diving: What happens to the pressure of various gases as a diver descends?
Incorporating these scenarios into your study can make theoretical exercises more tangible and engaging.
In sum, mastering Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures involves understanding the underlying principles, consistent practice with real-world applications, and a strategic approach to problem-solving through worksheet exercises. Each tip we've covered helps build a robust framework for dealing with gas mixture problems. By visualizing, using equations consistently, calculating partial pressures, understanding volume relationships, and applying the law to real-life situations, you'll find yourself adept at navigating through the complexities of gas behavior in mixtures. Remember that practice makes perfect, and the worksheets are your playground to experiment and solidify your understanding of this crucial law in chemistry.
Why is Dalton’s Law important?

+
Understanding Dalton’s Law helps predict the behavior of gas mixtures in various settings like in the atmosphere, industrial processes, and biological systems.
How do changes in temperature affect partial pressures?

+
Temperature changes can alter the total pressure due to the Ideal Gas Law, which in turn affects the partial pressures in proportion to their volume fractions.
Can Dalton’s Law be used for gases that react with each other?

+
Dalton’s Law assumes that gases in a mixture do not react chemically. If gases do react, the law does not apply directly as chemical reactions change the number and pressures of gases in the mixture.



