5 Steps to Master Lewis Dot Structures for Ionic Bonds

If you're embarking on the fascinating journey through chemistry, learning how to draw Lewis dot structures for ionic bonds is a fundamental skill to master. These structures not only help in understanding the basics of chemical bonding but also form the foundation for more advanced topics in chemistry. Here, we'll explore the five crucial steps that will guide you in mastering Lewis dot structures for ionic bonds, ensuring your understanding is both deep and wide-ranging.
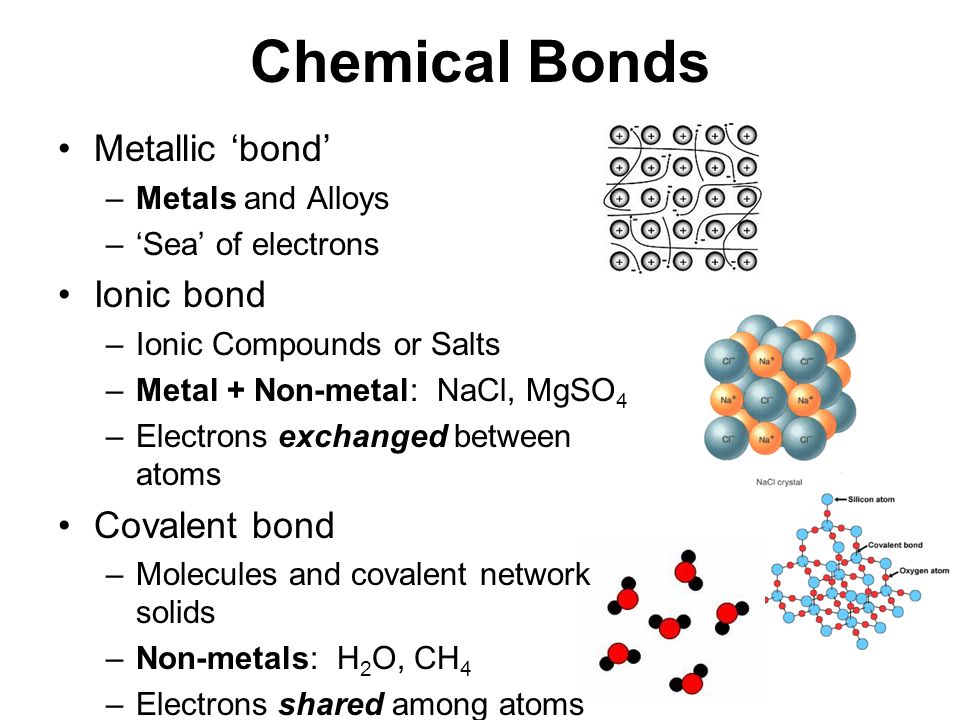
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Ionic Bonds

Ionic bonds occur when metals react with nonmetals, resulting in a transfer of electrons. Here’s what you need to grasp:
- Valence Electrons: These are the electrons in the outermost energy level, which are involved in bonding.
- Metal Atoms: Lose electrons to become cations (positively charged ions).
- Nonmetal Atoms: Gain electrons to become anions (negatively charged ions).

Step 2: Determine Valence Electrons

Before you start drawing, determine the number of valence electrons for each atom involved in the bond:
- Check the periodic table: The group number indicates the number of valence electrons for main group elements (1-8).
- Use the atomic number and electron configuration to confirm if needed.
Step 3: Draw Lewis Dot Structures

Now, let's move into drawing:
💡 Note: When placing dots around the element, use up to 4 pairs, ensuring single electrons first to facilitate electron transfer in ionic bonds.
Metals:

- Draw the element symbol.
- Place dots for the number of valence electrons:
- Place one dot at a time clockwise from the top until you’ve placed all valence electrons.
- If there are unpaired electrons, they will be involved in electron transfer.
Nonmetals:
- Draw the symbol.
- Place dots for the number of valence electrons, seeking an octet (8).
- Start pairing electrons after four single electrons are placed.

Step 4: Electron Transfer

Here's how to illustrate the transfer:
- Transfer electrons from metals to nonmetals.
- Metals will have their dots removed to reflect their new state as cations.
- Nonmetals will gain enough electrons to reach a full octet (8 electrons).
- Show this transfer using arrows between the symbols.
| Element | Lewis Dot Before | Lewis Dot After | Charge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium (Na) | Na• | Na+ | +1 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | :Cl: | :Cl:- | -1 |

⚠️ Note: The transfer of electrons ensures both atoms achieve an octet or stable electron configuration, which is crucial for understanding ionic bonding.
Step 5: Drawing the Ionic Compound

Combine your knowledge to depict the ionic compound:
- Place the cation (positive ion) on the left and the anion (negative ion) on the right.
- Draw the appropriate Lewis dot structures for each.
- Use brackets and charges to indicate the ionic compound formed.
Here's an example:

In summary, mastering Lewis dot structures for ionic bonds involves understanding the principles of electron transfer, recognizing valence electrons, and practicing the visualization of these transfers. By following these steps, you will be well on your way to visualizing how atoms interact in ionic bonding, which is fundamental to comprehending chemical reactions, the formation of salts, and many other chemical phenomena.
Why do metals lose electrons while nonmetals gain them?

+
Metals, which have low ionization energies, tend to lose electrons to achieve a stable, filled valence shell. Nonmetals, with high electron affinities, gain electrons to fill their valence shells, reaching the stable octet configuration.
Can ionic bonds form between two nonmetals?

+
Ionic bonds typically form between metals and nonmetals. However, very electronegative nonmetals like fluorine can sometimes form ionic bonds with other nonmetals if the conditions are right, like in the presence of a strong acid.
How do you determine the charge of an ion?

+
To determine the charge, look at the number of electrons lost or gained. For example, sodium loses one electron to become Na+, whereas chlorine gains one electron to become Cl-. The charge is the difference between the number of valence electrons and the number needed to reach a full octet.