H-R Diagram Worksheet Answers: Boost Your Astronomy Knowledge
In the vast expanse of the night sky, understanding stars is not just a matter of curiosity but a key to unlocking the mysteries of our universe. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram, one of the most important tools in astronomy, serves as a stellar map that helps us classify and comprehend the life cycles, luminosity, temperature, and other vital characteristics of stars. This blog post is designed to equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the H-R Diagram, providing detailed answers to the typical worksheet questions you might encounter.
Understanding the H-R Diagram

The H-R Diagram plots stars according to their:
- Luminosity (intrinsic brightness) on the vertical axis.
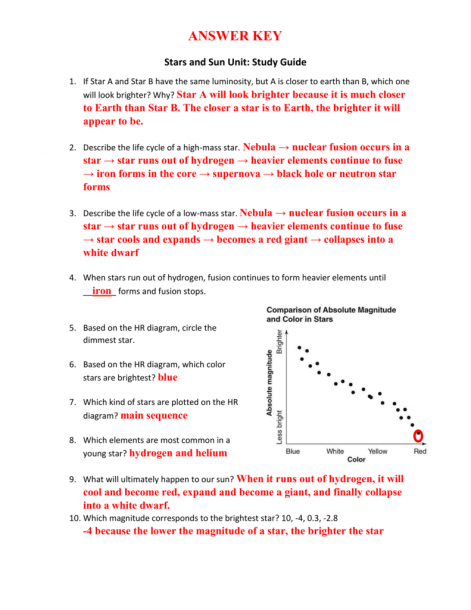
- Effective temperature or spectral type on the horizontal axis.
Here's how to read the H-R Diagram:
- Spectral Class (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) represents star color and temperature. O stars are the hottest and bluest, while M stars are the coolest and reddest.
- Luminosity Class indicates the size and stage of the star. Roman numerals from I to V describe stars from supergiants to main-sequence stars.
| Spectral Class | Temperature Range (K) | Luminosity Class | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 30,000-60,000 | 1 (supergiants) | Theta Orionis C |
| B | 10,000-30,000 | I, II, III (giants), V (main sequence) | Rigel |
| A | 7,500-10,000 | V, VII (white dwarfs) | Sirius |
| F | 6,000-7,500 | V, VII | Canopus |
| G | 5,200-6,000 | V | The Sun |
| K | 3,700-5,200 | III, V | Arcturus |
| M | 2,400-3,700 | I, III, V | Betelgeuse |

Answering H-R Diagram Worksheet Questions

Let's delve into common worksheet questions related to the H-R Diagram:
1. Star Characteristics

Question: “A star has a spectral class of F5 V. What can you infer about its temperature and luminosity?”
Answer: An F5 V star lies in the F class on the main sequence of the H-R Diagram. It indicates:
- Temperature: Approximately 6,600 K, considering F5 is in the middle of the F range.
- Luminosity: Moderate compared to the Sun, but still within the main sequence, meaning it has not started fusion of heavier elements yet.
⭐ Note: Stars on the main sequence burn hydrogen into helium in their cores, which determines their position on the H-R Diagram.
2. Evolution of Stars

Question: “Explain the life cycle of a star like our Sun on the H-R Diagram.”
Answer: The Sun’s evolution can be traced as follows:
- Main Sequence: It is currently fusing hydrogen into helium, positioned in the center of the H-R Diagram.
- Subgiant Branch: After hydrogen is exhausted in the core, the Sun will expand and cool, moving to the right and up on the H-R Diagram.
- Giant Branch: The Sun will then swell to become a red giant, with luminosity increasing dramatically.
- Horizontal Branch: Helium fusion will stabilize it, moving the Sun left on the H-R Diagram.
- Asymptotic Giant Branch: Further expansion occurs as outer layers are lost, moving up again.
- Planetary Nebula: The core will shrink and heat up, while shells of gas are ejected.
- White Dwarf: Finally, it becomes a hot but dim white dwarf at the lower left of the H-R Diagram.
3. Comparing Stars

Question: “How does the H-R Diagram help compare a supergiant and a main sequence star?”
Answer:
- Supergiant: Appears in the top left quadrant, indicating high luminosity and relatively high temperature. Supergiants are massive stars in the late stages of evolution.
- Main Sequence Star: On the diagonal band, representing the majority of stars that are fusing hydrogen, with a wide range of luminosities and temperatures.
The H-R Diagram visually separates these classes by their stark differences in evolutionary stages, sizes, and intrinsic brightness.
In conclusion

Studying the H-R Diagram can give astronomers invaluable insights into the characteristics and life cycles of stars, providing a fundamental understanding of stellar evolution. By plotting stars’ positions on this diagram, we can discern their past, present, and potential future, connecting the dots of cosmic history. Remember, the journey through the H-R Diagram is not just about learning a tool; it’s about engaging with the fundamental processes that shape the stars and, ultimately, our universe.
What does the vertical axis of the H-R Diagram represent?

+
The vertical axis represents the luminosity, or how intrinsically bright a star is.
Can you find the mass of a star from the H-R Diagram?

+
Not directly. However, mass can be indirectly inferred from the star’s position on the main sequence or through observing binary star systems.
Why are there so many stars on the main sequence?

+
Stars spend the majority of their lives on the main sequence, fusing hydrogen into helium. This is the longest phase in a star’s lifetime, hence the large number of stars observed there.
How does the H-R Diagram change over time?

+
The H-R Diagram itself doesn’t change, but as stars evolve, their positions move within it. Therefore, what we see over time is the movement of stars as they evolve from one phase to another.
Are all white dwarfs cooler than main sequence stars?

+
Although white dwarfs are smaller and less luminous than main sequence stars, they can be hotter due to the rapid contraction of their cores.