JROTC Ranks Explained
Introduction to JROTC Ranks

The Junior Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (JROTC) is a federal program sponsored by the United States Armed Forces in high schools across the country. The program is designed to teach high school students the value of citizenship, leadership, and service to the community. One of the key aspects of JROTC is its ranking system, which is modeled after the United States military ranking system. Understanding the different JROTC ranks is essential for both cadets and parents to navigate the program effectively.
Cadet Ranks in JROTC

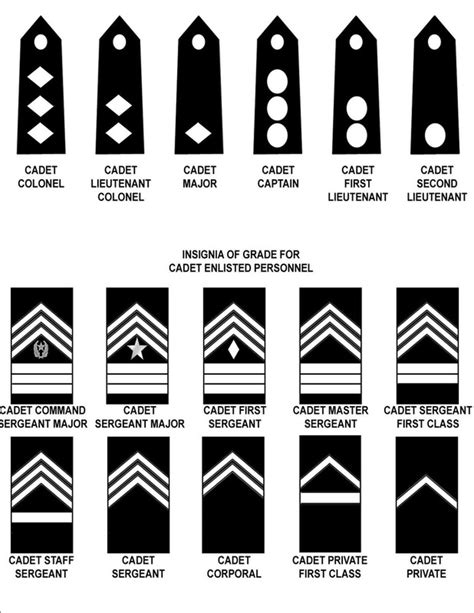
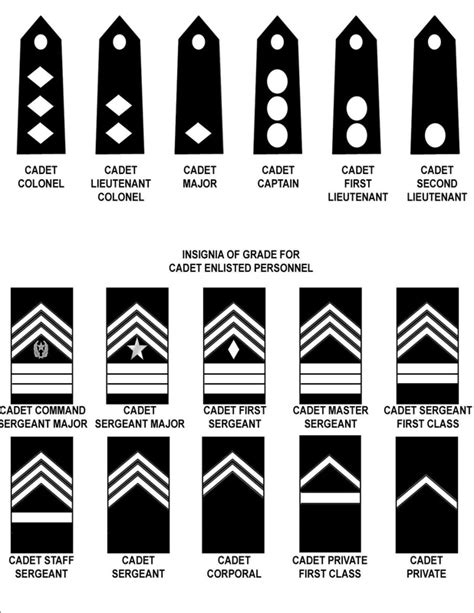
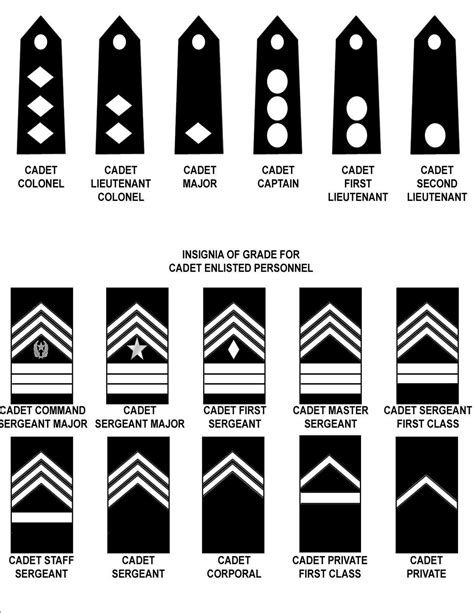
The JROTC ranking system is divided into several categories, including cadet enlisted ranks, cadet non-commissioned officer (NCO) ranks, and cadet officer ranks. Each rank has its own set of responsibilities and privileges. Here is a breakdown of the different cadet ranks in JROTC: - Cadet Private (PVT): The entry-level rank for new cadets. - Cadet Private First Class (PFC): Cadets who have completed basic training and have demonstrated leadership potential. - Cadet Corporal (CPL): Cadets who have shown exceptional leadership skills and are responsible for leading small teams. - Cadet Sergeant (SGT): Cadets who have demonstrated strong leadership abilities and are responsible for leading larger teams. - Cadet Staff Sergeant (SSG): Cadets who have shown excellent leadership skills and are responsible for leading squads or sections. - Cadet Sergeant First Class (SFC): Cadets who have demonstrated outstanding leadership abilities and are responsible for leading platoons or companies. - Cadet Master Sergeant (MSG): The highest enlisted rank in JROTC, responsible for leading battalions or brigades. - Cadet Second Lieutenant (2LT): The entry-level officer rank, responsible for leading platoons or companies. - Cadet First Lieutenant (1LT): Cadets who have demonstrated strong leadership skills and are responsible for leading companies or battalions. - Cadet Captain (CPT): Cadets who have shown exceptional leadership abilities and are responsible for leading battalions or brigades.
Rank Structure and Promotions
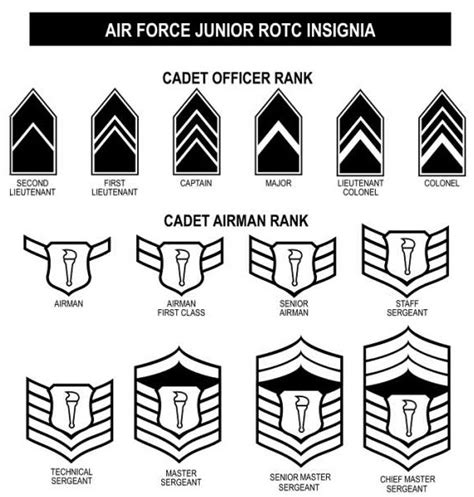
The rank structure in JROTC is designed to mirror the United States military ranking system. Cadets can be promoted to higher ranks based on their performance, leadership skills, and time in service. Promotions are typically awarded at the discretion of the JROTC instructors and are based on a cadet’s ability to demonstrate leadership potential, academic achievement, and community service. The promotion process typically involves a board review, where a panel of JROTC instructors evaluates a cadet’s qualifications and determines whether they are eligible for promotion.
| Rank | Responsibilities | Privileges |
|---|---|---|
| Cadet Private (PVT) | Follow instructions, complete tasks | Participate in JROTC activities |
| Cadet Private First Class (PFC) | Lead small teams, assist NCOs | Wear rank insignia, participate in leadership roles |
| Cadet Corporal (CPL) | Lead squads, assist officers | Wear rank insignia, participate in leadership roles |
👮 Note: The rank structure and promotion process may vary depending on the specific JROTC program and school.
Benefits of JROTC Ranks
The JROTC ranking system provides numerous benefits to cadets, including: * Leadership development: Cadets learn valuable leadership skills and have the opportunity to apply them in a real-world setting. * Community service: Cadets participate in community service projects and develop a sense of civic responsibility. * Academic achievement: Cadets are encouraged to excel academically and are eligible for scholarships and awards. * College and career opportunities: Cadets who complete the JROTC program are eligible for college scholarships and military service.
In summary, the JROTC ranking system is an essential aspect of the program, providing cadets with leadership opportunities, community service experience, and academic achievement. By understanding the different JROTC ranks and their responsibilities, cadets and parents can navigate the program effectively and make the most of the benefits and opportunities it provides.
What is the highest rank in JROTC?
+
The highest rank in JROTC is Cadet Colonel (COL), but this rank is not always available in every JROTC program. Typically, the highest rank available is Cadet Captain (CPT) or Cadet Lieutenant Colonel (LTC).
How do cadets get promoted in JROTC?

+
Cadets can be promoted to higher ranks based on their performance, leadership skills, and time in service. Promotions are typically awarded at the discretion of the JROTC instructors and are based on a cadet’s ability to demonstrate leadership potential, academic achievement, and community service.
What are the benefits of participating in JROTC?

+
The JROTC program provides numerous benefits to cadets, including leadership development, community service experience, academic achievement, and college and career opportunities. Cadets who complete the JROTC program are eligible for college scholarships and military service.