5 Ways Army Infantry Pay Works
Understanding Army Infantry Pay: A Comprehensive Guide

Serving in the Army Infantry can be a rewarding and challenging career path, but it’s essential to understand how pay works to make informed decisions about your future. The Army offers a competitive compensation package, but it’s not just about the base pay. In this article, we’ll delve into the five ways Army Infantry pay works, exploring the various components that make up your overall compensation.
1. Base Pay: The Foundation of Your Compensation
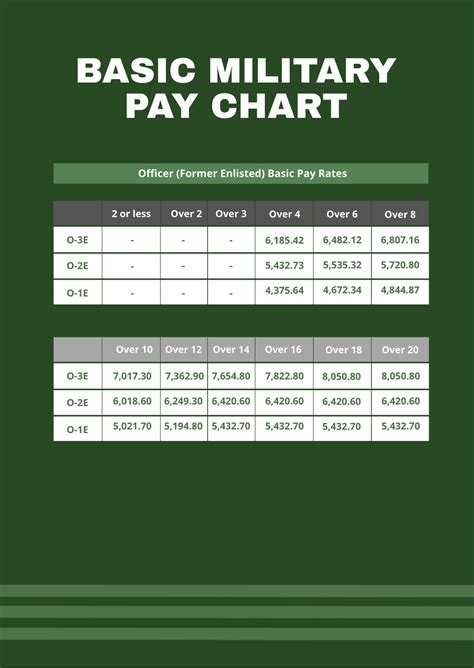
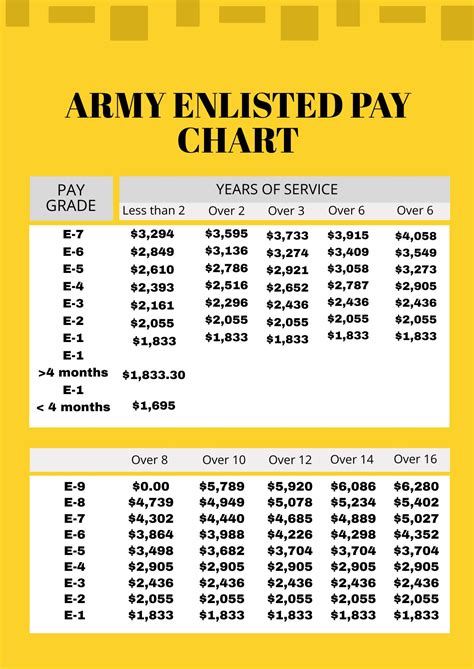
Base pay is the primary component of your Army Infantry compensation. It’s the amount you receive based on your rank and time in service. The Army uses a pay scale to determine base pay, with higher ranks and more time in service resulting in higher pay. For example, a Private (E-1) with less than two years of service would receive a base pay of around 1,733 per month, while a Sergeant (E-5) with over six years of service would receive around 3,287 per month.
| Rank | Time in Service | Base Pay (Monthly) |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | Less than 2 years | $1,733 |
| Private First Class (E-2) | 2-3 years | $1,942 |
| Sergeant (E-5) | Over 6 years | $3,287 |

📝 Note: Base pay rates are subject to change, and the above figures are for illustration purposes only.
2. Allowances: Additional Forms of Compensation

In addition to base pay, the Army provides various allowances to help cover the costs of living and serving. These allowances can include:
- Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS): a monthly stipend for food, currently set at $369.39 for enlisted personnel.
- Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH): a monthly stipend for housing, which varies depending on location and rank.
- Cost of Living Allowance (COLA): a monthly stipend to help offset the costs of living in high-cost areas.
- Special Duty Pay: additional pay for serving in specific roles, such as airborne or hazardous duty.
These allowances can significantly impact your overall compensation, so it’s essential to factor them into your financial planning.
3. Bonuses and Incentives: Extra Pay for Special Skills

The Army offers various bonuses and incentives to attract and retain personnel with specialized skills. These can include:
- Enlistment Bonuses: one-time payments for enlisting in specific Military Occupational Specialties (MOS).
- Reenlistment Bonuses: one-time payments for reenlisting in specific MOS.
- Special Duty Pay: additional pay for serving in specific roles, such as airborne or hazardous duty.
- Language Proficiency Pay: additional pay for speaking a foreign language.
These bonuses and incentives can provide a significant boost to your compensation, but be sure to review the eligibility requirements and service commitments carefully.
4. Education Benefits: Investing in Your Future

The Army offers various education benefits to help you invest in your future. These can include:
- GI Bill: a program that provides education benefits for college, vocational, or technical school.
- Tuition Assistance: a program that provides financial assistance for college courses.
- Student Loan Repayment: a program that helps repay student loans.
These education benefits can help you pursue higher education or technical training, setting you up for success in your military and civilian careers.
5. Benefits and Perks: Additional Forms of Compensation

In addition to monetary compensation, the Army offers various benefits and perks, including:
- Healthcare: comprehensive medical, dental, and pharmacy benefits.
- Housing: on-base housing or a housing allowance.
- Food: access to on-base dining facilities or a food allowance.
- Recreation: access to on-base recreational facilities.
- Shopping: access to on-base shopping facilities.
These benefits and perks can significantly enhance your quality of life and overall compensation package.
As you can see, Army Infantry pay is more than just base pay. By understanding the various components of your compensation package, you can make informed decisions about your future and take advantage of the benefits and incentives available to you.
In the next section, we’ll explore some important notes to keep in mind when considering your Army Infantry pay.
📝 Note: This article is for general information purposes only and should not be considered as professional advice. For specific information about your compensation package, consult with your unit's personnel office or a financial advisor.
To wrap up, serving in the Army Infantry can be a rewarding and challenging career path, with a comprehensive compensation package that includes base pay, allowances, bonuses, education benefits, and benefits and perks. By understanding the various components of your pay, you can make informed decisions about your future and take advantage of the opportunities available to you.
What is the average base pay for an Army Infantry soldier?

+
The average base pay for an Army Infantry soldier varies depending on rank and time in service. However, according to the Army’s pay scale, a Private (E-1) with less than two years of service would receive around 1,733 per month, while a Sergeant (E-5) with over six years of service would receive around 3,287 per month.
What are some common allowances for Army Infantry soldiers?

+
Common allowances for Army Infantry soldiers include Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS), Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH), Cost of Living Allowance (COLA), and Special Duty Pay.
What education benefits are available to Army Infantry soldiers?
+
The Army offers various education benefits, including the GI Bill, Tuition Assistance, and Student Loan Repayment. These benefits can help you pursue higher education or technical training.