5 Quick Tips for Mastering Isotope Notation Worksheet 4-2

Isotopes Overview


Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. This basic definition opens up a world of complexity in chemistry, as isotopes significantly influence an element’s mass, its reactivity, and its applications in various scientific fields. An Isotope Notation Worksheet is a valuable tool to understand how isotopes are represented and how one can calculate an element’s atomic mass based on its isotopic composition. Here, we’ll explore five quick tips for mastering your isotope notation worksheet 4-2.
1. Understand the Structure of Isotope Notation

Before delving into worksheet specifics, grasp the conventional way to denote isotopes:
- Element Symbol: This remains constant regardless of the isotope (e.g., “C” for Carbon).
- Mass Number: Placed in the upper left of the element symbol, it equals the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
- Atomic Number: Found in the lower left, this indicates the number of protons in an atom, which is always the same for all isotopes of an element.
2. Practice with Multiple Examples

The key to mastering isotope notation is repetition. Here are examples to practice with:
- Nitrogen-14: 14N7
- Carbon-12: 12C6
- Uranium-238: 238U92
Once you’ve identified the isotope notation of these examples, calculate the number of neutrons in each. Remember, the neutron count equals the mass number minus the atomic number.
3. Use Mnemonics and Visual Aids
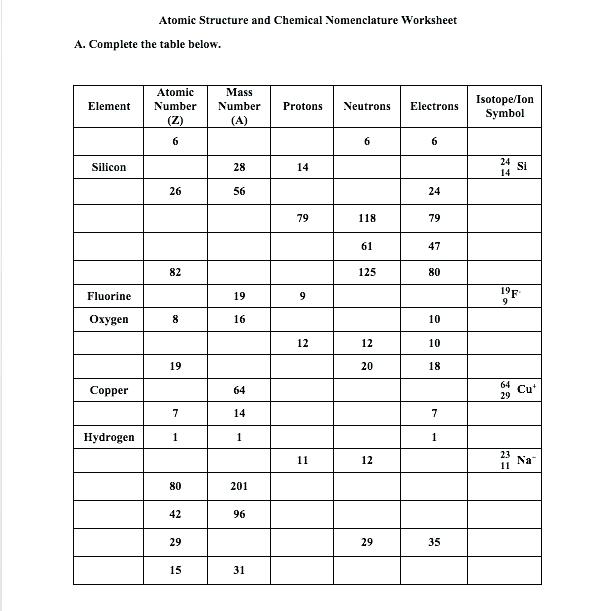
Memory tricks and visual aids can significantly improve your retention. Try these:
- Mnemonic: Think “Protons are prime, Neutrons add to the mass” to remember the atomic number versus mass number placement.
- Visual Aid: Sketch a nucleus with protons and neutrons, labeling each with the element symbol and its mass number to internalize the relationship.
4. Check and Balance your Isotopic Calculations

Calculating the atomic mass from isotopic abundances is a critical part of the worksheet. Here’s how:
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Mass (u) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon-12 | 98.89 | 12.0000 |
| Carbon-13 | 1.11 | 13.0034 |
| Weighted Average Mass | 12.0107 u | |

The weighted average mass calculation is essential for verifying your understanding of isotope notation. Make sure you balance your equations correctly:
🔍 Note: Always round your final answer to the correct significant figures.
5. Understand the Implications of Isotopes

Isotopes have far-reaching implications beyond just chemical properties. Here’s what to know:
- Medical Use: Isotopes like Technetium-99m are used in medical imaging.
- Nuclear Power: Uranium isotopes are the backbone of nuclear reactors.
- Archaeology: Carbon-14 dating helps determine the age of historical artifacts.
- Environmental Monitoring: Isotopes aid in studying geological and climate changes.
By understanding these implications, you'll appreciate why mastering isotope notation is more than just a worksheet task; it's about grasping the real-world significance of isotopes.
Recap the tips for mastering your isotope notation worksheet 4-2:
- Understand the structure of isotope notation and how to interpret it.
- Regularly practice with examples, including calculating neutron numbers and atomic masses.
- Employ mnemonics and visual aids to reinforce your learning.
- Balance isotopic calculations and check your work for accuracy.
- Appreciate the broader implications of isotopes in science and technology.
Having these tips in your toolkit, you're now ready to tackle your isotope notation worksheet with confidence. Remember, isotopes are more than just numbers; they're key to unlocking numerous scientific mysteries. Whether you're studying for an exam or exploring the fascinating world of chemistry, isotopes are at the heart of many scientific breakthroughs, from archaeology to medicine. Isotope notation provides a structured way to explore these phenomena, and mastering this skill will enhance your scientific understanding and appreciation.
What is the difference between an isotope and an ion?

+
An isotope refers to atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. An ion, however, is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in a charged particle. Isotopes affect the mass of an element but not its chemical behavior, whereas ions change the charge and thus the chemical properties.
Why does the atomic mass of an element differ from the mass of its most common isotope?

+
Atomic mass is a weighted average of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element, taking into account their relative abundances. It’s not the mass of any single isotope but a blend reflecting the natural distribution of isotopes in nature.
Can isotopes of an element be separated?

+
Yes, isotopes can be separated through methods like mass spectrometry or, on a larger scale, through processes like isotope separation techniques used in the nuclear industry, such as gaseous diffusion or centrifuge separation. However, these methods are energy-intensive and only viable when necessary.
What does the stability of an isotope depend on?

+
Isotopic stability depends on the ratio of neutrons to protons in the nucleus. As elements get heavier, stable isotopes require more neutrons to balance the nuclear forces. Magic numbers of protons or neutrons (2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, and 126) also play a role in determining stability due to filled nuclear shells.
How do isotopes affect the behavior of a substance?

+
While isotopes of an element have identical chemical properties, their differences in mass can impact physical properties like density or boiling point. Also, radioactive isotopes can change the chemical behavior due to radioactive decay, emitting particles that can alter the electron shell configuration.