5 Tips for Identifying Polygons Worksheet Answers

Whether you are a student grappling with the basics of geometry or an educator seeking to enhance teaching methods, understanding how to effectively identify polygons on worksheets can significantly enhance your grasp on the subject. Polygons, as fundamental shapes in mathematics, not only intrigue students but also form the bedrock for more complex geometrical concepts. Here are five insightful tips to help you master the art of identifying polygons through worksheet answers:
Understand the Definition

The first step to successfully answering a polygons worksheet is to have a solid understanding of what a polygon actually is. A polygon is a plane figure that is bounded by a closed path or circuit, composed of straight line segments. Here are key points:
- Each line segment meets another at an endpoint (vertex).
- No two edges (sides) overlap or cross each other.
- A polygon can be convex (no internal angles greater than 180 degrees) or concave (with one or more internal angles greater than 180 degrees).
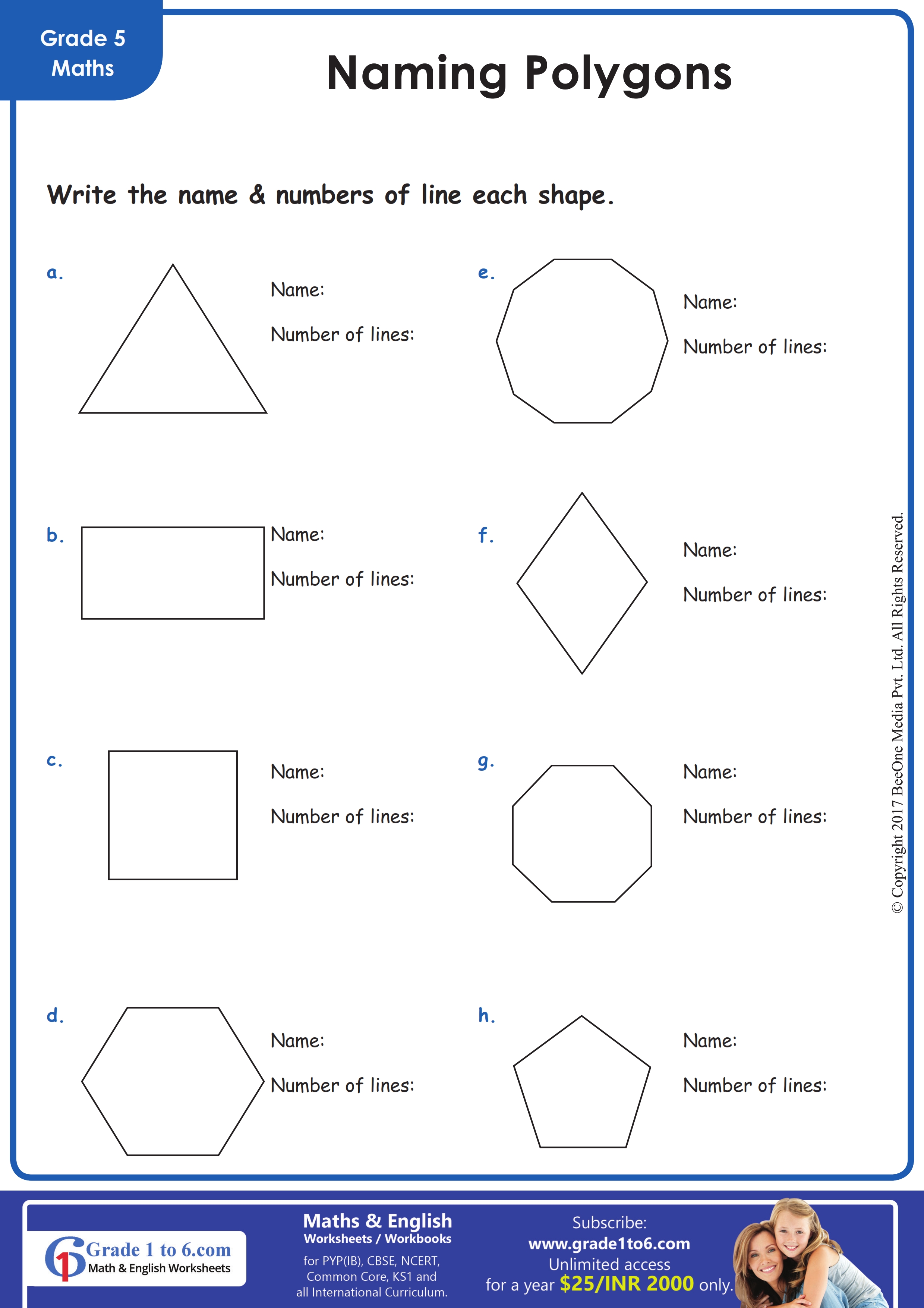
Recognize the Basic Shapes

Polygons come in various forms, but recognizing the most common types is essential for quickly identifying them:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
Understanding these shapes visually will help in swiftly discerning polygon types on a worksheet.
Check for Parallel and Equal Sides

Many polygons have characteristics related to their sides that can be used to identify them:
| Polygon | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Square | All sides are equal, all angles are 90° |
| Rectangle | Opposite sides are equal and parallel, all angles are 90° |
| Parallelogram | Opposite sides are equal and parallel |

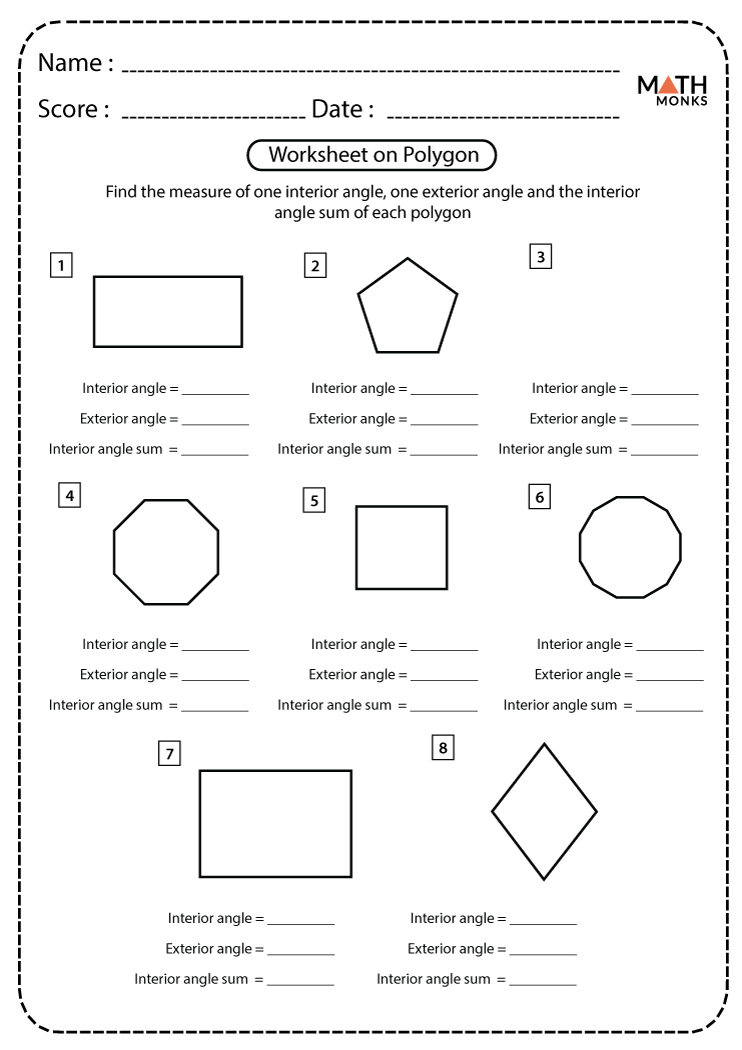
Identify Special Angles

Angles play a crucial role in identifying polygons, especially when looking at:
- Right angles (90°) which indicate rectangles or squares.
- Sum of internal angles, which is always (n - 2) × 180° where ‘n’ is the number of sides.
- Exterior angles, where the sum is always 360°.
Use Formulas and Properties

Geometry isn’t just about recognizing shapes by sight. Utilizing formulas and properties can confirm your identification:
- Area formulas: For example, the area of a triangle can be calculated as ½ × base × height.
- Perimeter: Simply add up all the sides.
- Interior angles: Knowing how to calculate these can help identify complex polygons.
⚠️ Note: Make sure to use accurate measurements or visual cues if you are solving these problems without a ruler or protractor.
In closing, identifying polygons on worksheets becomes straightforward when you combine a thorough understanding of basic definitions, recognize common shapes, check for characteristic sides and angles, and utilize geometric formulas. With practice, you'll not only identify polygons accurately but also appreciate the underlying symmetry and beauty in geometry.
Can a polygon have more than 10 sides?
+
Yes, polygons can have any number of sides beyond 10. They are often referred to as n-gons where n is the number of sides.
What’s the difference between regular and irregular polygons?

+
Regular polygons have all sides and angles equal, while irregular polygons have sides and/or angles of different lengths or sizes.
How do you determine if a shape is not a polygon?
+
A shape is not a polygon if it has curved edges, is not closed, or if any of its sides cross each other.
What are the practical applications of studying polygons?

+
Polygons are used in architecture, design, mapping, and even in computer graphics for modeling and rendering shapes.



